Playlist
Show Playlist
Hide Playlist
Vestibular Disorders: Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo, Vertigo and Ménière's Disease
-
Slides 11 VestibularSystem 2 BrainAndNervousSystem.pdf
-
Reference List Anatomy.pdf
-
Download Lecture Overview
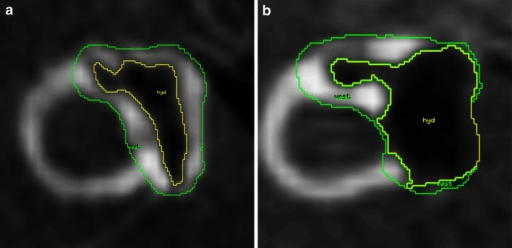
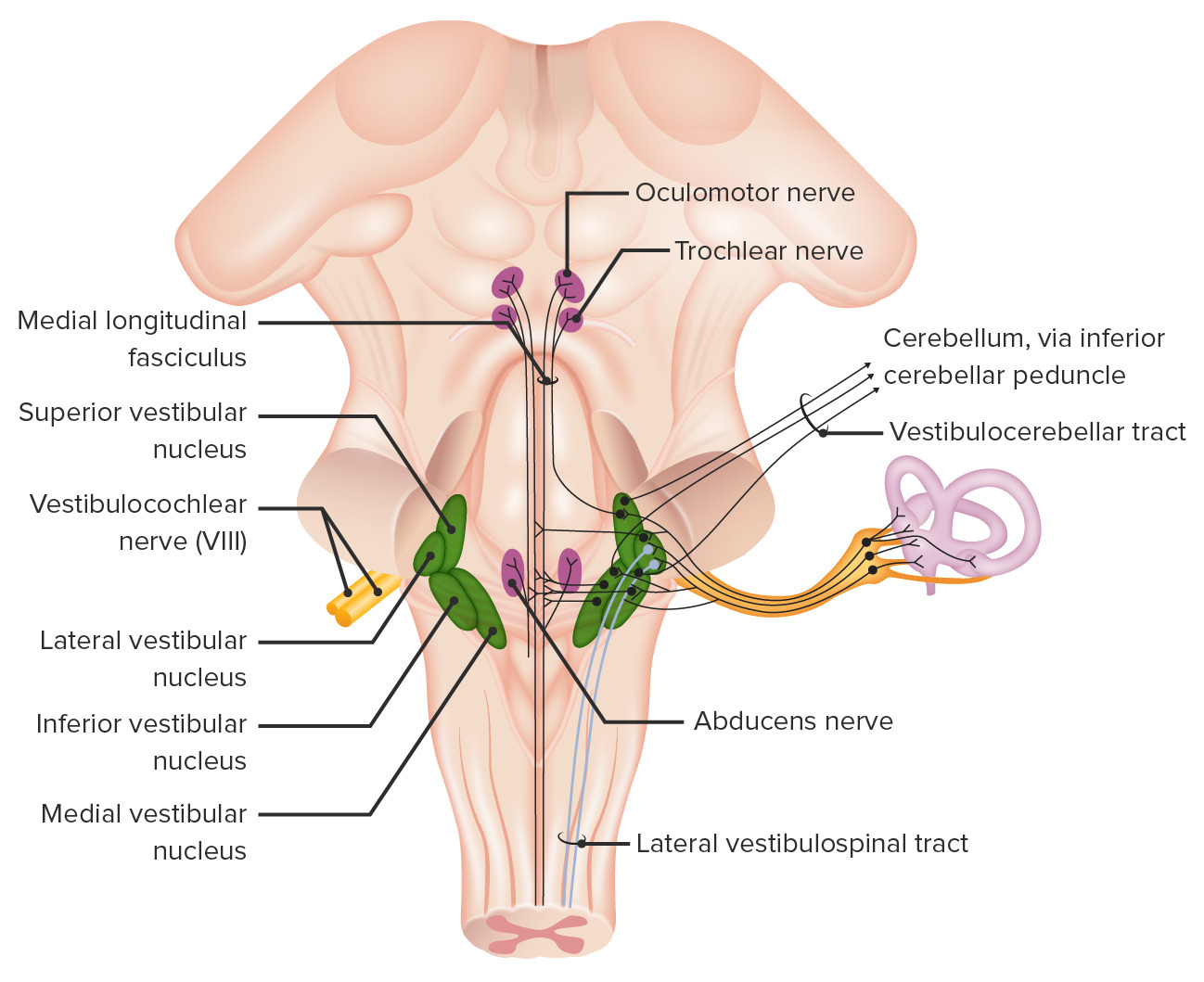
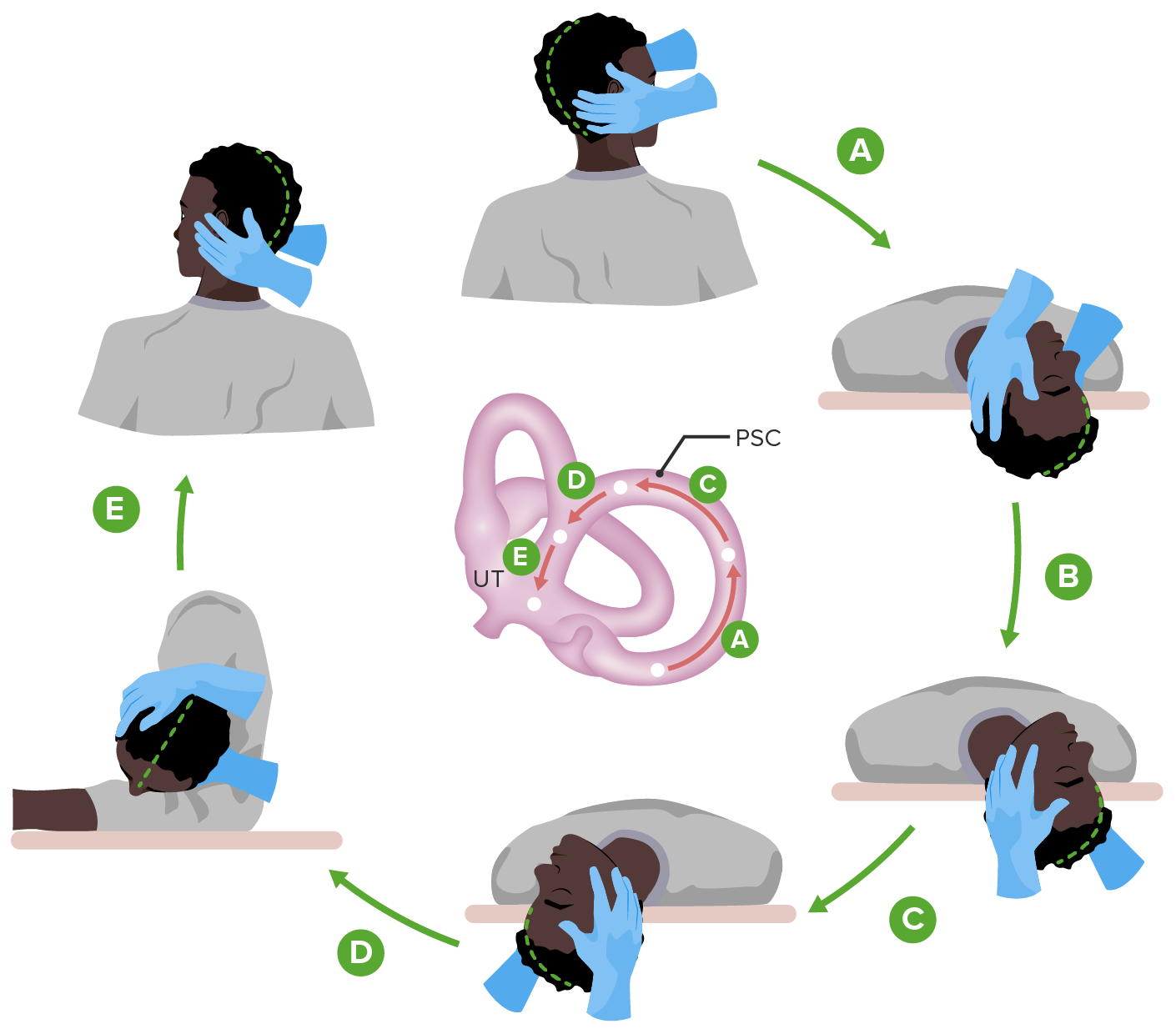
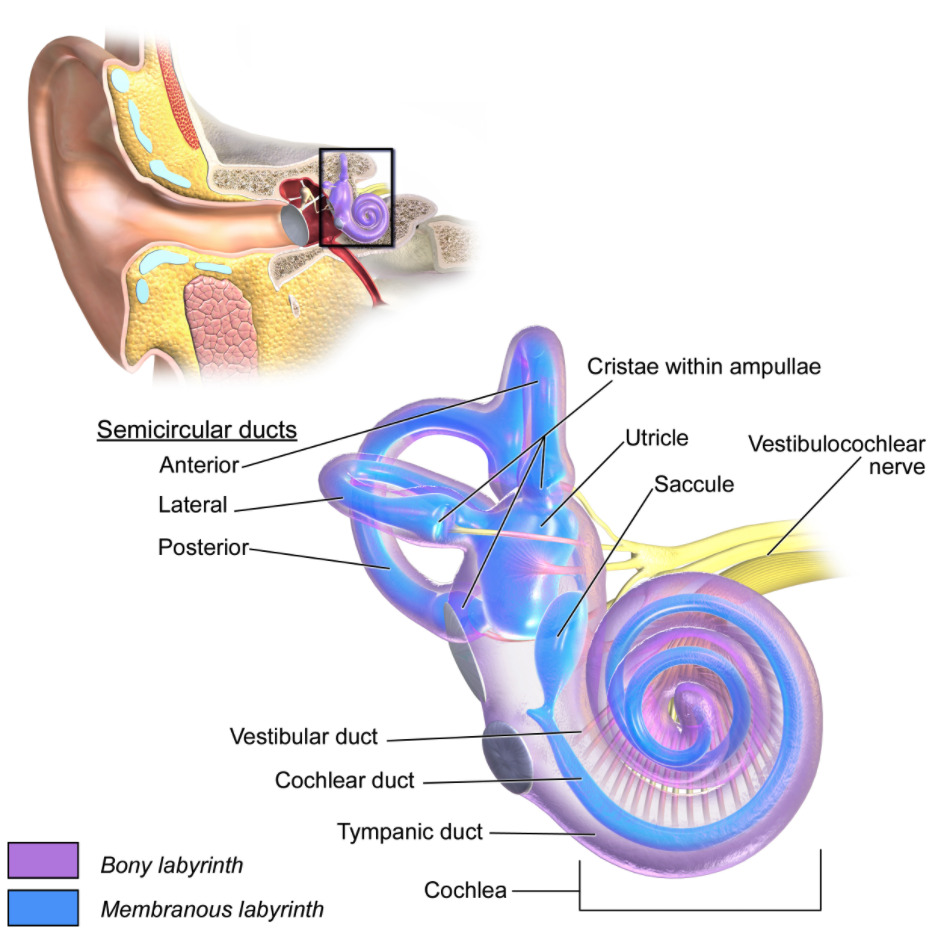
00:00 Now we’ll take a look at three different vestibular disorders. 00:06 We’ll take a look first at Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. 00:13 Then we'll look at vertigo. 00:15 And then we’ll finish up with a brief discussion about Meniere’s disease. 00:22 So, first, Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo, First thing for you to understand is that this is the most common form of vertigo. 00:37 Individuals with this form of vertigo have sudden onset of episodes. 00:44 However, this episodes of dizziness are of short duration. 00:52 Certain head positions or movements will trigger or prompt a given episode in individuals that have this disorder. 01:04 What causes this condition? We’ll it all relates to the macula. 01:12 Where we have the macula shown in through here of the utricle or saccule. 01:19 And the macula has embedded in it, this otoconia. 01:29 And in the case of this condition, it is the otoconia in the utricle that get dislodged and when they become dislodged they migrate into one of the semi- circular canals that we see over here in this smaller image. 01:48 So, here’s a semi-circular canal here for example. 01:51 And another one here and then in our third semi-circular canal are shown into there. 01:56 So, in otoconia they become dislodge and get into one of those semi- circular canals. 02:02 And when they get there they disrupt normal fluid movement within a semi-circular canal. 02:09 And this will send false signals in the vestibular system causing this episodes of dizziness. 02:21 The second vestibular disorder that I want you to understand is that vertigo. 02:26 And we’ll walk through several of this symptoms associated with vertigo in this table. 02:37 Individuals with vertigo may complain of spinning sensation. 02:42 They may complain that they are tilting because of the disruption of the vestibular apparatus, and the sensing of false signals. 02:54 They may feel that they are swaying. 02:58 As a result of this, they may feel very often that they’re off balanced or unbalanced. 03:05 And they tend to pull to one direction because of this impairment of the vestibular apparatus. 03:13 There are several different causes of vertigo. 03:16 You can have an inflammation of vestibular nerve or inflammation of the vestibular pathway of vestibular neuritis, a vascular lesions of the brain stem or the cerebellum may impair the vestibular apparatus resulting in vertigo. 03:35 Demyelination and once you lose your insulation you can have cross talk between nerve fibers leading to fault signals. 03:46 Certain drugs and ingestion of too much alcohol will certainly disrupt the vestibular system. 03:53 And acoustic tumors can also cause this types of symptoms. 04:05 The last vestibular disorder that I want you to understand is that of that Meniere’s disease. 04:12 This table will guide you through the symptoms that associated with Meniere’s disease as well as the causes. 04:22 Meniere’s disease is characterized by abrupt recurrent attacks of vertigo. 04:29 There’s also an associated hearing loss with this disorder. 04:34 Tinnitus or ringing of the ears is associated with Meniere’s disease. 04:40 Patients may complain of excess ear pressure or fullness with in their ear And nausea and vomiting are associated symptoms as well. 04:53 Several different causes to consider again, vestibular neuritis, vascular lesions of the brain stem or cerebellum, demyelination, certain drugs and alcohol and acoustic tumors. 05:14 Now this were the same causes that we walk through that you saw earlier with vertigo.
About the Lecture
The lecture Vestibular Disorders: Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo, Vertigo and Ménière's Disease by Craig Canby, PhD is from the course Auditory System and Vestibular System. It contains the following chapters:
- Clinical Correlations – Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo
- Clinical Correlations – Vertigo
- Clinical Correlations – Ménière's Disease
Included Quiz Questions
Which of the following could be a cause of benign paroxysmal positional vertigo?
- Migration of crystals within the semicircular canals
- Demyelination
- Acoustic tumors
- Vascular lesions of the brain stem
- Vestibular neuritis
Which of the following is NOT a symptom of Ménière's disease?
- Numbness
- Tinnitus
- Vertigo
- Hearing loss
- Ear fullness
Which of the following statements regarding benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV) is correct?
- It has an acute onset and a short duration of episodes.
- Demyelination is the most common cause of BPPV.
- A single episode can last several days.
- Change of position has no effect on BPPV.
- It is a very rare disorder.
Customer reviews
5,0 of 5 stars
| 5 Stars |
|
1 |
| 4 Stars |
|
0 |
| 3 Stars |
|
0 |
| 2 Stars |
|
0 |
| 1 Star |
|
0 |
Clear and concise, easy to understand and very clinically relevant.