Playlist
Show Playlist
Hide Playlist
Anion Gap & Osmolar Gap
-
Slides 09 ToolsCompensation AcidBaseBalance GeneralPhysiology.pdf
-
Download Lecture Overview
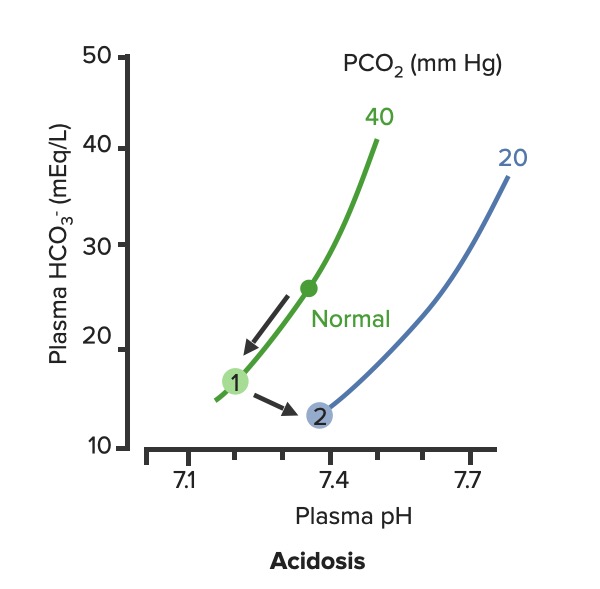
00:00 We have a number of different ways to get a metabolic acidosis. 00:07 So, what we have to do is have to diagnose this to understand which one they might have. 00:14 To do that, we use an Anion gap. And what is an Anion gap? And anion gap allows us to look at the total number of positive charges in the blood. 00:27 And compare that to the total number of negative charges in the blood. 00:31 So, it’s cations versus anions. 00:35 They have to equal each other. 00:39 The positive charges will always equal the negative charges. 00:43 And so, I know you’re wondering now, if they are equaling each other, why they have a gap? Well, there’s some amount of an anion that you’re not taking into a count. 00:54 So, let me explain this. 00:57 Metabolic acidosis with a normal anion gap, you have a certain amount of sodium. 01:05 Sodium is your only cation that you’re worried about. 01:10 Potassium you’re not worried about it, only sodium. 01:13 Then you compare it to your anions, chloride, bicarb and then something else. 01:21 That something else is your gap. 01:24 You don’t know what it is. It’s something out there that it’s taking a part of that total cation to anion comparison. 01:37 What should your anion gap be? Normally, somewhere between about 8 to 16. 01:43 So, in our example here having an anion gap of 10, perfectly normal. 01:48 Let’s compare it to a problem that has an abnormal anion gap. 01:53 You have a sodium value, you get this from your blood chemistry. 01:57 You put in your chloride, you put in your bicarb, and then something else is taking up a larger piece of those cations. 02:08 Cos again, they have to equal each other. 02:11 They call this a gap because it’s not something that you measure. 02:16 You’re only measuring the ions in the blood. 02:19 And so, you don’t know what was there that take up all the extra cations. 02:25 If it’s above 16, now that you know you have an elevated plasma anion gap. 02:32 So, you’re looking for a value between 8 and 16. 02:38 Once you have an increase plasma ion gap you know that you have a certain list of disorders. 02:46 You either have ketoacidosis, lactic acidosis. 02:50 You might have renal failure, aspirin overdose, methanol poisoning, propylene and glycol poisoning or maybe you’re not eating enough. 03:00 All those would have an increased plasma ion gap. 03:05 The ones you can eliminate if you have an elevated plasma ion gap are the ones that are associated with diarrhea, a renal tubule acidosis, you fear on certain drugs like carbonic anhydrase inhibitors or if you have a disease such as Addison’s Disease. 03:22 So, you can automatically, tease out which one of this list you were on if you have a metabolic acidosis. 03:30 After you’ve calculated the anion gap, there’s another differential diagnosis you can go through, and that is calculating on an Osmolar Gap. 03:40 So, if you were looking at a difference between two numbers, just like you were between cations and anions. 03:47 What you’re going to look at now is the difference between your measured osmolality to your estimated osmolality. 03:54 How do you do that? Estimate your osmolality you can take two times your sodium value. 04:01 You take glucose divided by 18 and then, you take your blood urea nitrogen divided by 2,8. 04:07 You sum those together and that should be within 10 of your measured osmolality. 04:15 If it is greater than that, something is taking up that osmolality. And it’s usually a poison. 04:23 Something like propylene glycol, there’s some other item that is causing an osmotic pull that normally would not be there. 04:33 And that is another way you can further differentiate if you have a metabolic acidosis with elevated plasma anion gap to tease out between those problems that were on that list. 04:49 You can use the osmolar gap to figure out if the person has ingest the poison.
About the Lecture
The lecture Anion Gap & Osmolar Gap by Thad Wilson, PhD is from the course Acid-Base Balance.
Included Quiz Questions
If you have identified a metabolic acidosis but not an elevated plasma anion gap, which of the following acid-base disorders is most likely?
- Renal tubular acidosis
- Ketoacidosis
- Lactic acidosis
- Ethylene glycol poisoning
Which of the following is the normal anion gap?
- 8 to 16 mM/L
- 4 to 8 mM/L
- 16 to 24 mM/L
- 24 to 30 mM/L
- 30 to 36 mM/L
What is considered a normal osmolar gap?
- <10
- <20
- <15
- <30
- <25
Which of the following statements is FALSE?
- The units of an osmolar gap is mM/L.
- Osmolar gap is the difference between the measured osmolar gap and estimated osmolar gap.
- In a healthy person, the cations must be equal to anions.
- Usually, the osmolar gap increases in the consumption of poisons.
- Ethylene glycol poisoning can have an increased anion gap.
Customer reviews
5,0 of 5 stars
| 5 Stars |
|
1 |
| 4 Stars |
|
0 |
| 3 Stars |
|
0 |
| 2 Stars |
|
0 |
| 1 Star |
|
0 |
This review, expose the useful tools Anion GAP and Osmolar GAP, it is easy and complete.