Playlist
Show Playlist
Hide Playlist
Acute Rheumatic Fever
-
Reference List Immune System.pdf
-
Download Lecture Overview
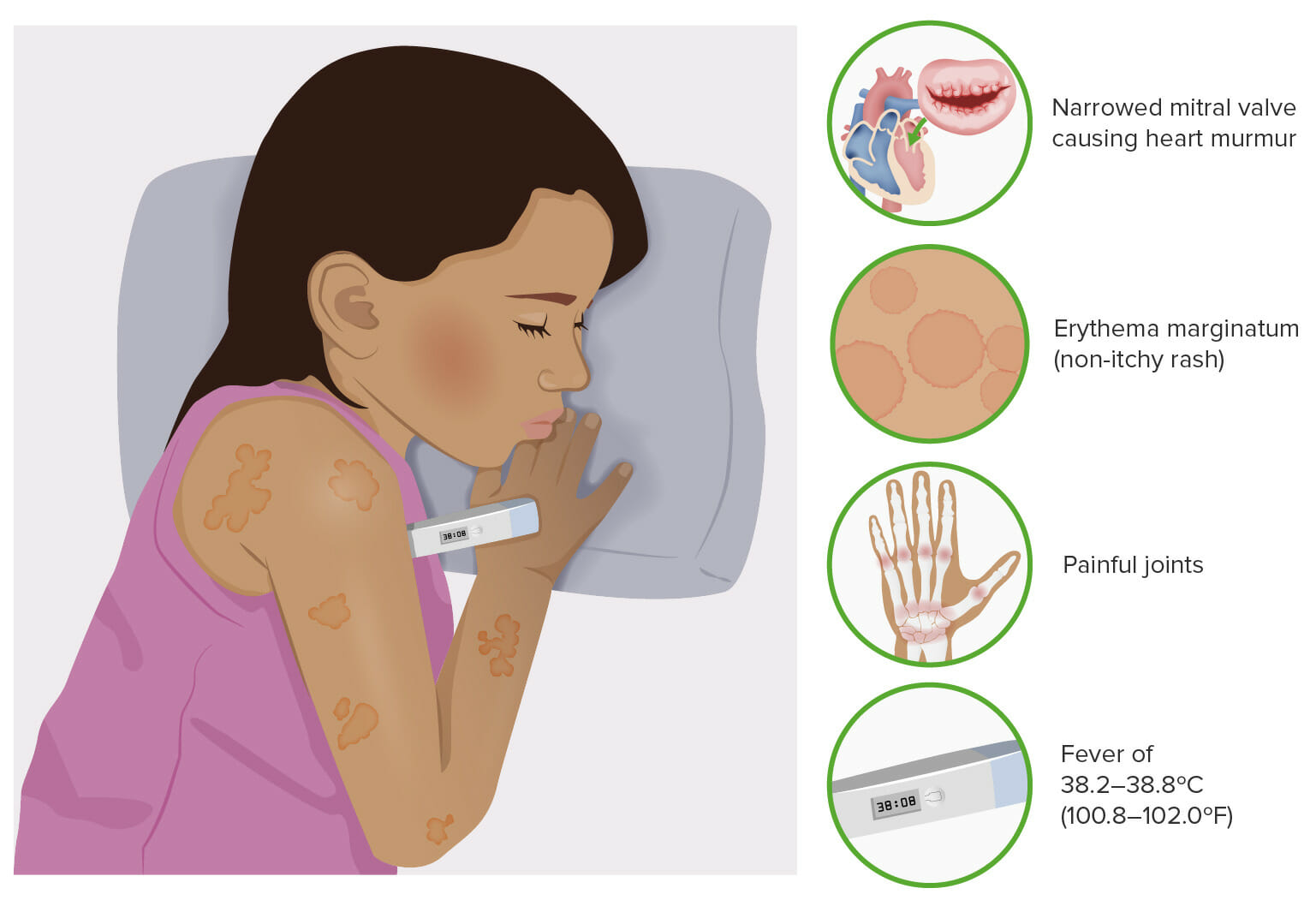
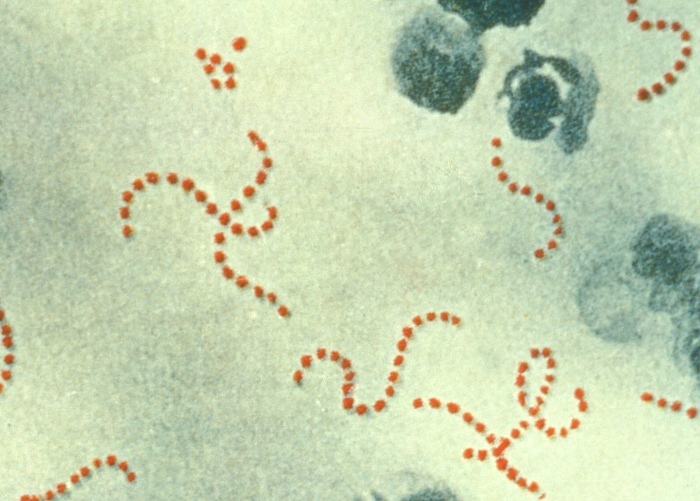
00:01 Acute rheumatic fever is quite an interesting type of autoimmune disease. 00:07 It occurs due to molecular mimicry between group A Streptococcus pyogenes and human antigens. 00:16 The Streptococcus pyogenes M protein and N-acetyl-glucosamine have structures that are very similar to cardiac myosin, laminin and other self antigens. 00:29 The result is a carditis caused by these cross-reactive antibodies that recognize valve endothelium and laminin. 00:40 There is also cross reaction of Th1 cells and Th17 cells. 00:48 And these release inflammatory cytokines. 00:52 The inflammatory lesions can also affect the joints, the subcutaneous tissue and the CNS.
About the Lecture
The lecture Acute Rheumatic Fever by Peter Delves, PhD is from the course Hypersensitivity and Autoimmune Disease.
Included Quiz Questions
Acute rheumatic fever most commonly occurs as a consequence of infection with of the following pathogens?
- Group A Streptococcus
- Staphylococcus aureus
- Listeria monocytogenes
- Streptococcus pneumoniae
- Neisseria meningitidis
Antibodies generated against the M protein in Streptococcus pyogenes attack which of the following host cells as a consequence of molecular mimicry?
- Cardiac myosin and laminin
- Glomerular basement membrane
- Helper T cell receptors
- Rhesus antigens
- Kupffer cells
Customer reviews
5,0 of 5 stars
| 5 Stars |
|
5 |
| 4 Stars |
|
0 |
| 3 Stars |
|
0 |
| 2 Stars |
|
0 |
| 1 Star |
|
0 |