Playlist
Show Playlist
Hide Playlist
Types of Non Germ Cell Tumors
-
Slides Testicular Neoplasms and Prostate-Male Reproductive Pathology.pdf
-
Reference List Pathology.pdf
-
Download Lecture Overview
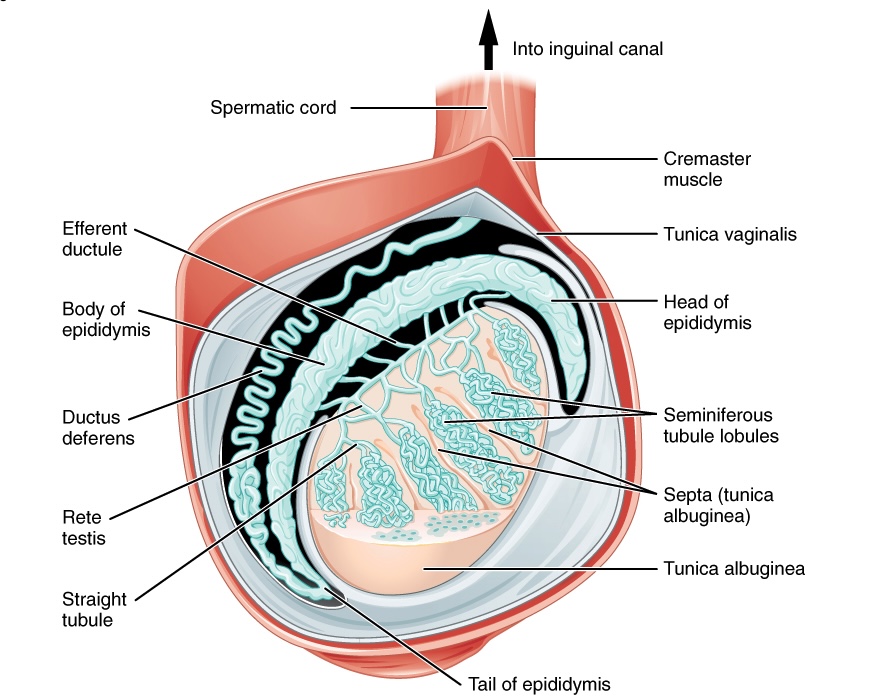
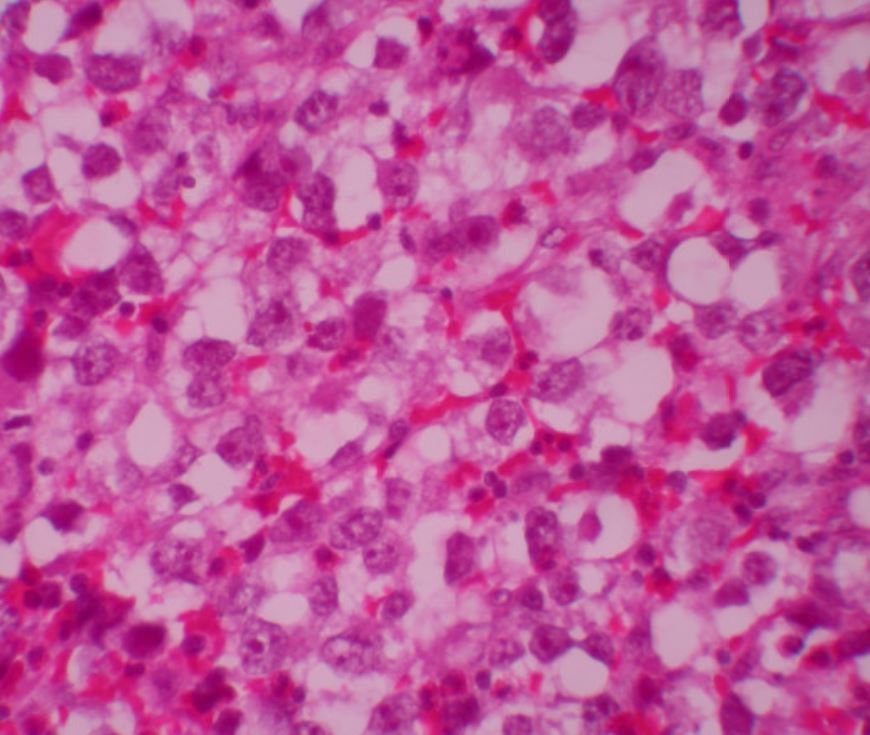
00:02 Our topic here is testicular neoplasia and now we’re moving away from germ cell tumors. 00:07 These are non-germ cell tumors. 00:10 Some types of non-germ cell tumors are called sex cord-stromal tumors and they present as an asymmetric testicular mass. The majority are painless, however if a patient develops pain, it may indicate there is bleeding into the tumor. Non-germ cell testicular tumors represent about 5% of all testicular cancers, recall that the other 95% are germ cell tumors as we already discussed. The non-germ cell tumors may produce androgens - also known as testosterone - and this may cause precocious puberty in boys. If the testosterone that is produced undergoes aromatization into estrogen, it can present with gynecomastia in 20 to 50% of patients. The most common sex cord-stromal tumor is called a Leydig cell tumor but overall, this accounts for only 1 to 2% of all testicular tumors. Gynecomastia is seen in 20 to 30% of patients with Leydig cell tumors. The histology shows Reinke crystals which are pathognomonic and should be memorized for testing purposes. 01:05 These appear as cytoplasmic dense needle-like or rhomboid structures. They are rarely seen in a normal testes but are seen in about one-third of Leydig cell tumors. Leydig cell tumors are seen in both children and adults, with the peak ages of presentation between ages 5-10 then later between ages 30 to 35. Overall, Leydig cell tumors are seen more often in adults than children. 01:28 Two other types of testicular cancer that are non-germ cell tumors, are classified as sex cord-stromal tumors. These are Sertoli cell tumors and Granulosa cell tumors. Sertoli cell tumors present with a painless testicular mass and a minority of patients have gynecomastia. They occur in all age groups, more often in adults. Granulosa cell tumors have both a juvenile and an adult type. The juvenile type presents in babies under age 6 months, and for the adult type, the average age of presentation is 44 years old. It is important to know the age group of presentation for the different types of testicular cancers for testing reasons. 02:04 Testicular lymphoma is not always considered testicular cancer but rather a form of Hodgkin lymphoma. It can be primary or metastatic and is seen in both young adults and men over age 55. To summarize: Testicular cancer in the most common malignancy in young men ages 15 to 35, but 7% of testicular cancer occurs in men over age 55. 02:27 Germ-cell tumors make up 95% of all testicular cancer, and non-germ cell tumors make up the remaining 5%. 02:35 One classification of non-germ cell tumors are called sex cord-stromal tumors, which are Leydig cell, Sertoli cell, and the rare granulosa cell tumor.
About the Lecture
The lecture Types of Non Germ Cell Tumors by Carlo Raj, MD is from the course Male Reproductive System Diseases.
Included Quiz Questions
What clinical presentation is seen in 20% to 50% of boys and men with sex-cord stromal tumors (Leydig cell, Sertoli cell, and granulosa cell tumors)?
- Gynecomastia
- Testicular pain
- Testicular torsion
- Bilateral symmetric scrotal enlargement
- Hyperthyroidism
Customer reviews
5,0 of 5 stars
| 5 Stars |
|
1 |
| 4 Stars |
|
0 |
| 3 Stars |
|
0 |
| 2 Stars |
|
0 |
| 1 Star |
|
0 |
Very clearly articulated and organized. I like the quick break down of the NGCTs.