Playlist
Show Playlist
Hide Playlist
SNRIs, Serotonin Antagonists and SSRIs – Antidepressants
-
Slides SNRIs Serotonin Antagonists SSRIs Antidepressants.pdf
-
Reference List Pharmacology.pdf
-
Download Lecture Overview
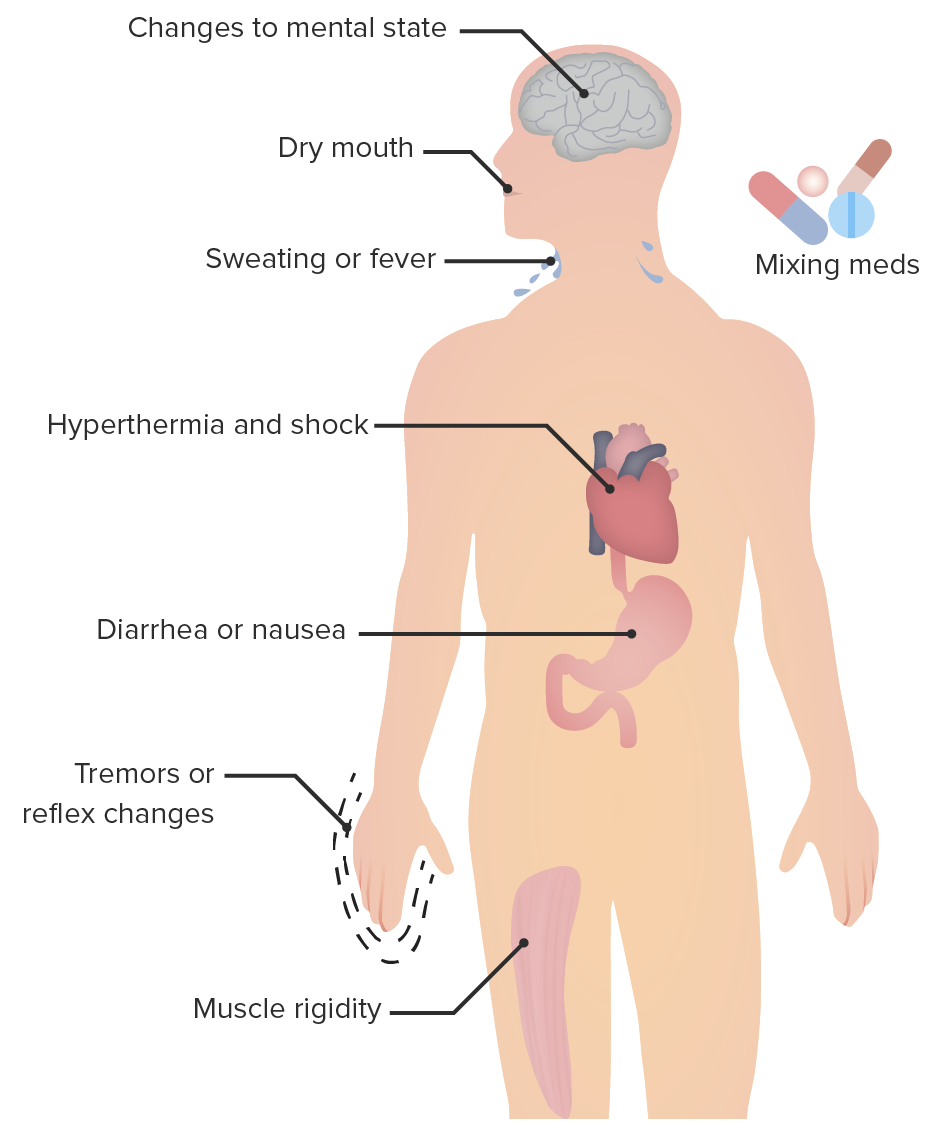
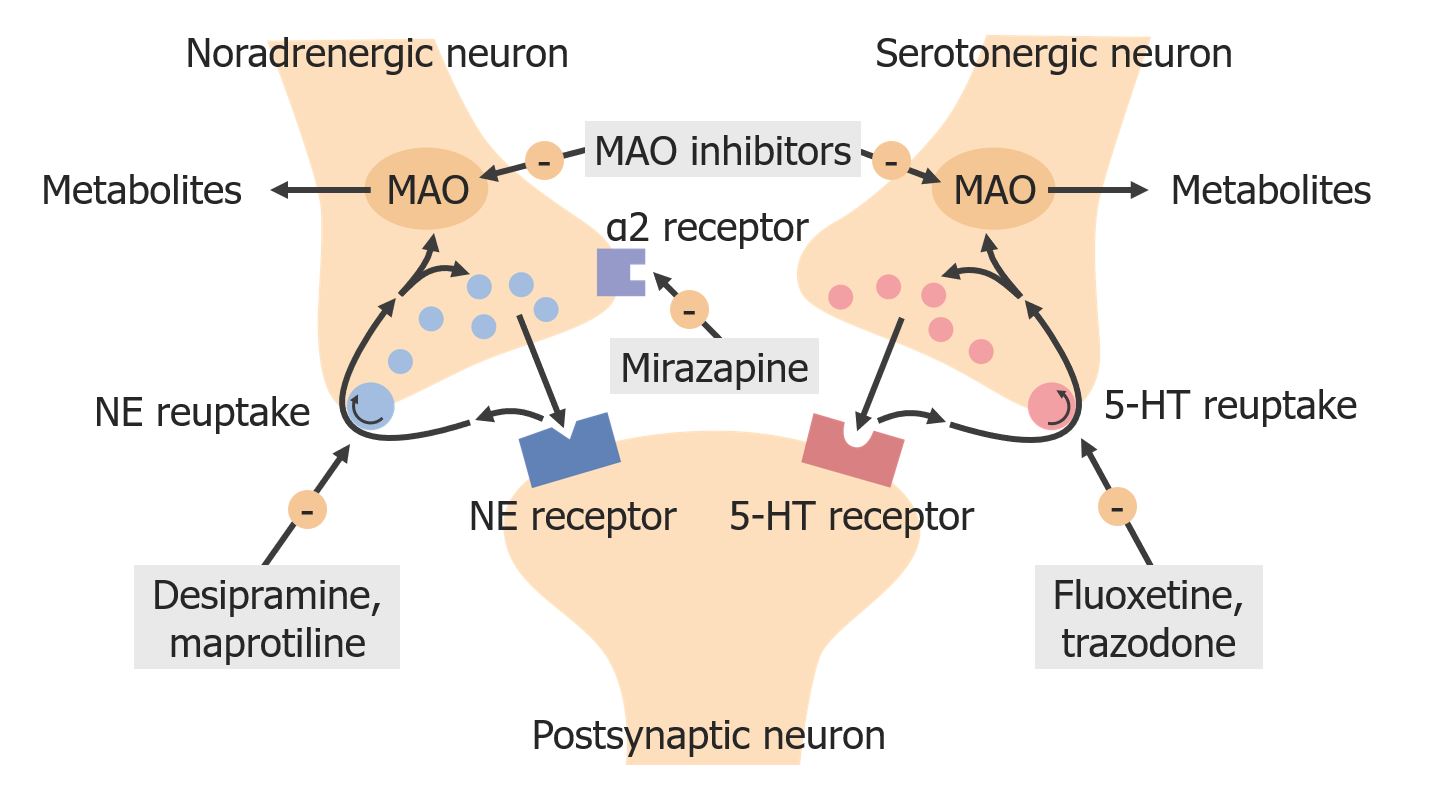
00:01 Let's move on to a different class. 00:03 These are called SNRIs, the Serotonin and Norepinephrine Reuptake Inhibitor. 00:09 Now, in classical pharmacology, we would classify this under the heterocyclic antidepressants. 00:15 But we've separated these agents out from a clinical point of view. 00:18 And so now in pharmacology, we separate them out too. 00:21 The SNRIs are very similar to the TCAs, but they have more specific reuptake actions. 00:29 So you can see here our diagram shows you what we're talking about. 00:32 The SNRIs do not have a blocking effect on the peripheral tissues, so we believe that they're going to have fewer side effects. 00:40 Cymbalta is the most commonly used in this particular class. 00:45 It is used in depressive disorders, sometimes used in neuropathic pain disorders. 00:49 And it's also used more recently in diabetic neuropathy. 00:52 So we are seeing it in my diabetes clinic for example. 00:56 Venlafaxine or Effexor XR is a heavily prescribed drug, because it has relatively few side effects, and it has less affinity for norepinephrine transporters than duloxetine. 01:08 In terms of the side effect profile, you can get an increased blood pressure with this agent and the side effects are very similar to the SSRIs. 01:18 The withdrawal symptoms are a particular concern with venlafaxine. 01:22 And incidentally, this is a good exam question. 01:24 Even if you miss one dose of this drug, you can have withdrawal symptoms. 01:28 So it's very important number one to learn this for your exams. 01:32 And number two, when you're out in practice, make sure you prescribe enough Effexor, enough venlafaxine to ensure that these patients don't run out. 01:42 And I think that some of the new laws coming out allowing pharmacists to prescribe are good. 01:48 In the event that they can't get to their doctor, the pharmacist can prescribe an emergency supply of Effexor so that you don't get those withdrawal symptoms. 01:57 These SNRIs have relatively targeted activity against the serotonin receptor. 02:05 Now, remember that the serotonin receptor is a G-protein-mediated receptor. It's located in the neocortex. 02:15 It's important to know that for the future because we're going to have new drugs that are coming out that will target this mechanism. 02:22 Bottom line, it's a more specific type of activity than the previous class of drugs that I discussed. 02:27 The activity of these classes of drugs on the receptor and on reuptake results in antianxiety and antidepressant activity. 02:40 Let's move on to another class of drugs called the serotonin antagonists. So, this is a little bit different. 02:47 It's not acting on reuptake its actually acting right on the receptor. 02:50 Now, more specifically, it's acting on the serotonin type 2A receptor. 02:55 It is again a G-protein-coupled receptors located in the neocortex. 03:02 It is a short acting agent and maybe prescribed between two or four times a day. It's a multidose regimen drug, and you have several agents out there. 03:14 In addition, these medications weekly inhibit serotonin reuptake by presynaptic neurons. 03:18 Now, we don't use some of them because of intense cytochrome interaction and we have others that are better used. 03:26 Now, the most common in this drug class is something called Trazodone. 03:31 Trazodone is commonly used as a sleep aid. 03:34 It is a relatively short acting drug. 03:36 And we like it for that reason, because if we give it at night to help people go to sleep, it wears off halfway through the evening. 03:44 so that when they wake up, they shouldn't feel tired. 03:47 Additionally, there are a couple other notable serotonin modulators used in the treatment of depression. 03:54 Both inhibit presynaptic reuptake and they also have additional serotonin receptor activity. 04:00 Vilazodone is a partial agonist of postsynaptic 5-HT1A receptors. 04:07 Vortioxetine acts on multiple 5-HT receptors, either as an antagonist or agonist. 04:15 An interesting aspect of Vortioxetine is that is may have a benefit for patients with cognitive dysfunction. 04:22 Let's move on to the SSRIs. 04:24 There are two ways to come up with this acronym. 04:28 The proper way are Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors, but some people say that the SSRI stands for Serotonin specific reuptake inhibitor regardless of which one you use, SSRI is the most common class of antidepressant drugs on the market. 04:46 I think personally that these are the best class because they have the fewest side effects. 04:50 Now, these act through inhibition of the serotonin reuptake transporter, there is minimal effects on norepinephrine uptake. 04:59 There are minimal side effects to these medications although they are present. 05:03 And initiation of medications in the SSRI class results in very good anti-anxiety activity and very good antidepressant activity. 05:14 There are so many that I don't even know where to start in terms of listing the drugs. 05:20 There are over 120 SSRIs out on the market. 05:26 So the list is very long. 05:29 It has the same effectiveness in terms of antidepressant activity, as the tricyclic antidepressants. And I say that as a compliment. 05:36 And on top of that, they have fewer almost negligible side effects. 05:41 They do have side effects, but they're relatively rare. 05:44 SSRIs and SNRIs can both cause sexual dysfunction and decreased libido. 05:49 It is important to ask patients about this possible side effect. 05:52 This is very clinically relevant and testable. 05:55 In terms of toxicity and overdose, one must be aware that you can get headache nausea, an increase in anxiety paradoxically and an increase in agitation. 06:06 You can get the jitters. So patients are very jittery and tremulous. 06:10 And you can use a low dose benzodiazepine to treat the jitters when they have overdose. 06:15 Extrapyramidal side effects can occur as well. 06:18 These include akathisia and dyskinesias and some dystonic reactions. 06:26 In terms of drug interactions with this class of drugs, remember that one of them called fluoxetine or Prozac inhibits the CYP450 2D6 and 3A4 moieties So any drugs that go through that system can affect the drug levels. 06:42 You can also have increased plasma levels due to dextromethorphan, propranolol, tamoxifen and the tricyclic antidepressants. 06:51 Luvox can inhibit cytochrome P450 1A2 and other agents like Celexa can have effect other drugs with that go through the cytochrome P450 system. 07:06 However, in terms of those drug interactions, this particular drugs to citalopram affects fewer drugs than the others. 07:15 There is something that I want to talk about called serotonin syndrome. 07:19 It was first described as a reaction between Mono Amine Oxidase Inhibitors and the Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors. 07:27 Serotonin syndrome is not something to ignore. 07:31 It can be a life threatening problem or syndrome. 07:34 First of all, it has several components. 07:37 The CNS stimulation component can include severe muscle rigidity, myoclonus, and hyperreflexia. 07:44 You can also get hyperthermia suspected to be due to increased muscle activity, and you can also get seizures and mydriasis. 07:52 Cardiovascular symptoms associated with this syndrome include tachycardia and unstable meaning high blood pressures. 08:01 And GI issues can include increased bowel sounds, and you can actually have diarrhea as well. 08:09 Now, there's a mnemonic that you can use to remember the various symptoms in serotonin syndrome. 08:16 And the mnemonic is MADAM'S TIPS. 08:19 I apologize for the sexist nature of this mnemonic, but it works very well. Please accept my apologies. 08:28 There's M-A-D-A-M-S T-I-P-S. 08:31 So, each have the start with that letter. 08:35 Let's start with M, Mental status changes. 08:38 You can get Agitation, you can get Diarrhea. 08:41 A can be for Ataxia. 08:44 You can get Myoclonus and Shivering. 08:48 T stands for Tachycardia. You can get Increased reflexes. 08:52 You can get Pyrexia or what we call fever, And you can also get a lot of Sweating. 08:58 So there you have the mnemonic MADAM'S TIPS. 09:00 That will help you remember the serotonin syndrome.
About the Lecture
The lecture SNRIs, Serotonin Antagonists and SSRIs – Antidepressants by Pravin Shukle, MD is from the course CNS - Pharmacology. It contains the following chapters:
- Serotonin/Norepinephrine Reuptake Inhibitors
- Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors
Included Quiz Questions
Which statement is LEAST accurate?
- Duloxetine has less affinity for norepinephrine reuptake transporters than venlafaxine.
- Venlafaxine has a relatively high rate of discontinuation syndrome.
- Duloxetine may be used for neuropathic pain.
- Duloxetine may be used for diabetic neuropathy.
- Venlafaxine should be used cautiously in patients with hypertension.
Which condition is frequently treated with trazodone?
- Insomnia
- Hypertension
- Erectile dysfunction
- Smoking cessation
- Seizure
Which side effect is not expected from a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI)?
- Bradycardia
- Headache
- Myoclonus
- Akathisia
- Agitation
Which medication significantly increases the risk of serotonin syndrome if coadministered with a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI)?
- A monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI)
- A beta blocker
- Aspirin
- A nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug
- A glucocorticoid
Customer reviews
5,0 of 5 stars
| 5 Stars |
|
1 |
| 4 Stars |
|
0 |
| 3 Stars |
|
0 |
| 2 Stars |
|
0 |
| 1 Star |
|
0 |
This is the best teacher i have understood the most. I loved everything really. I would recommend my fellow classmates