Playlist
Show Playlist
Hide Playlist
Renal Case: 52-year-old Man with End-stage Renal Disease (ESRD)
-
Slides Potassium Disorders Hypo and Hyperkalemia.pdf
-
Reference List Nephrology.pdf
-
Download Lecture Overview
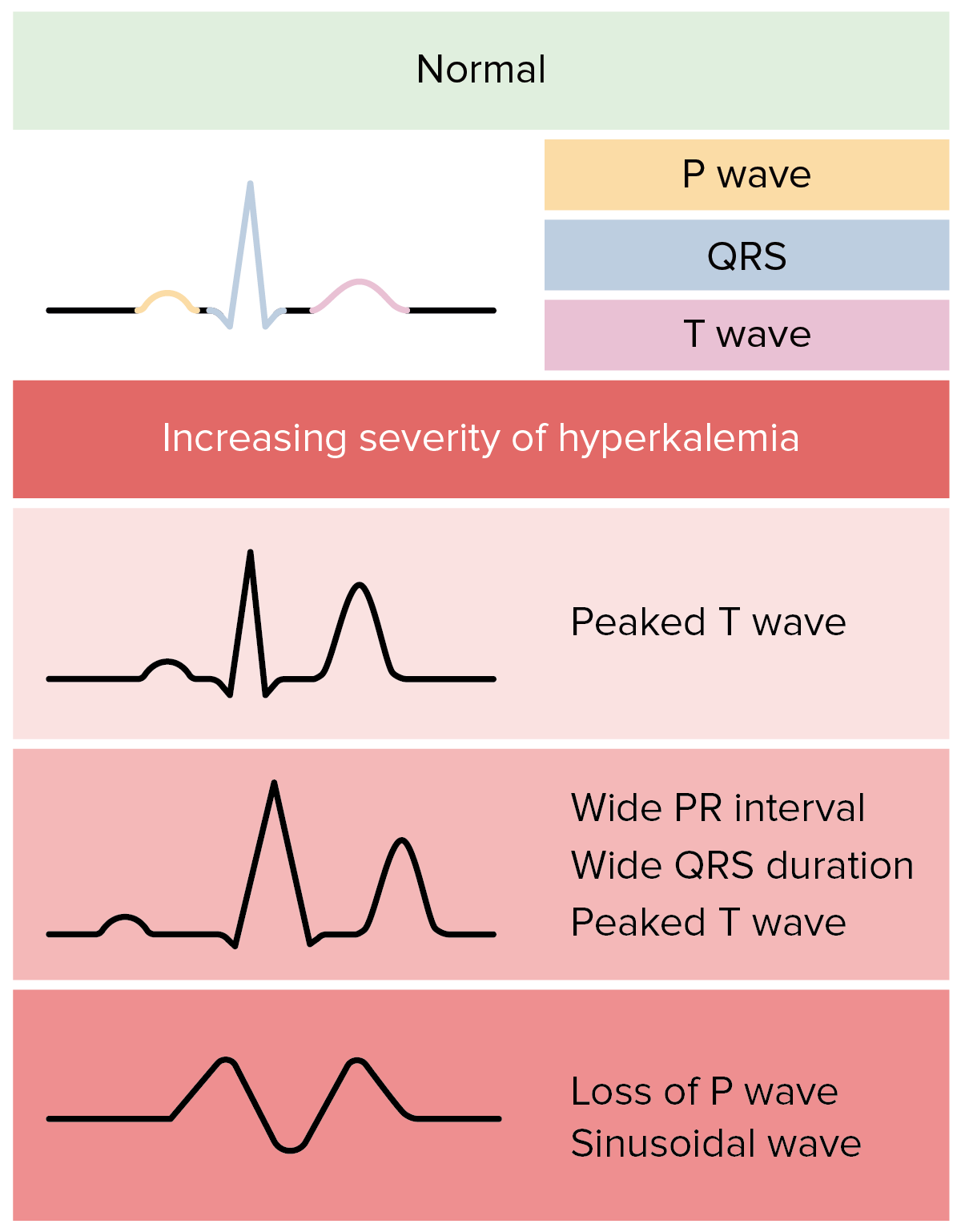
00:01 So let's end with a case. 00:04 You have a 52-year old man who has end-stage renal disease due to diabetic nephropathy and he presents to the emergency department complaining of weakness and heart palpitations. 00:13 He notes missing to dialysis sessions because he didn't have transportation to the dialysis center. 00:19 He makes only less than a hundred mils of urine daily. 00:22 His potassium is 8.0 and you can see that the normal is 3.5 to 5.1 milliequivalents per liter. 00:30 His EKG is shown below. 00:33 He was placed on the Telemetry Monitor and in the subsequent 15 minutes another 12-lead EKG was obtained and it showed the following. 00:41 So the question is what is the appropriate course of treatment for this particular gentleman? Before we answer that let's go through some of the history and see what's important here. 00:51 This is the gentleman who has end-stage renal disease and he's missed two hemodialysis sessions and he's feeling heart palpitations. 00:58 So this is concerning for cardiac effects from his hyperkalemia with a potassium of 8 that's extremely concerning. 01:05 Look at EKG in our first EKG, it shows peaked T-waves. 01:11 So that's very indicative of hyperkalemia. 01:13 But look what happens 15 minutes later that rhythm has degenerated into a sine wave appearance on EKG. 01:19 This gentleman needs urgent intervention. 01:23 So the question is which 3 therapy should be utilized and what is the correct order in which they should be administered in order to provide this patient with the best outcome for his hyperkalemia. 01:37 So we have insulin, beta agonists, dialysis, calcium chloride, Loop Diuretics sodium polystyrene sulfonate. 01:48 So I'm going to give you a moment and I'll let you pause in order to think about which three therapies you want to use in this gentleman and the order in which you want to use them. 02:01 The correct order is calcium chloride followed by insulin and beta-2 agonists. 02:06 And then finally dialysis. 02:08 Let's talk about why that's correct. 02:10 My very first choice in a gentleman who has a sine wave appearance on his EKG and a and a potassium of 8 is going to be to protect those cardiac myocytes and I'm going to do that with calcium chloride. 02:22 The next thing I want to do is I want something that can cause transcellular shift that can move some of that potassium out of the ECF relatively quickly. 02:30 I want you to think about practically what's happening here. 02:32 You have a patient sitting in front of you in the emergency department. 02:35 That's going to take time to actually call the dialysis have a dialysis technician come cannulate the patient and hook them up to a dialysis machine. 02:43 We don't have that kind of time. 02:45 When you see a potassium of 8. 02:47 Therefore you've got to get it out of the ECF into the ICF for the intracellular compartment relatively quickly to give this patient a chance. 02:56 Finally. 02:56 We want to remove that excess potassium and we will do that through dialysis the other things, like for example, sodium polystyrene sulfonate, were a loop diuretic doesn't make sense to do in a patient who makes no urine and who is already on dialysis. 03:12 The most efficient way of moving that degree of potassium from this patient is going to be through dialysis. 03:19 I hope that giving these mechanisms that you've learned today and how potassium is regulated. 03:23 You'll be able to approach any patient who has hypokalemia or hyperkalemia be able to diagnose it and solve the problem as to what's causing it and implement the appropriate therapies. 03:35 And with that this concludes our lecture.
About the Lecture
The lecture Renal Case: 52-year-old Man with End-stage Renal Disease (ESRD) by Amy Sussman, MD is from the course Potassium Disorders: Hypo- and Hyperkalemia.
Included Quiz Questions
What is the initial step in the management of hyperkalemia with abnormal findings on ECG?
- Calcium chloride
- Dialysis
- Spironolactone
- Kayexalate
- Beta-adrenergic agonists
What is the correct order of steps in the emergency management of hyperkalemia?
- Cardioprotection, Moving potassium into the intracellular compartment, Removing excess potassium from the body
- Cardioprotection, Removing excess potassium from the body, Moving potassium into the intracellular compartment
- Removing excess potassium from the body, Moving potassium into the intracellular compartment, Cardioprotection
- Moving potassium into the intracellular compartment, Cardioprotection, Removing excess potassium from the body
Customer reviews
5,0 of 5 stars
| 5 Stars |
|
5 |
| 4 Stars |
|
0 |
| 3 Stars |
|
0 |
| 2 Stars |
|
0 |
| 1 Star |
|
0 |