Playlist
Show Playlist
Hide Playlist
Pulmonary Embolism: Definition
-
Slides 11 VascularMedicine advanced.pdf
-
Reference List Vascular Medicine.pdf
-
Download Lecture Overview
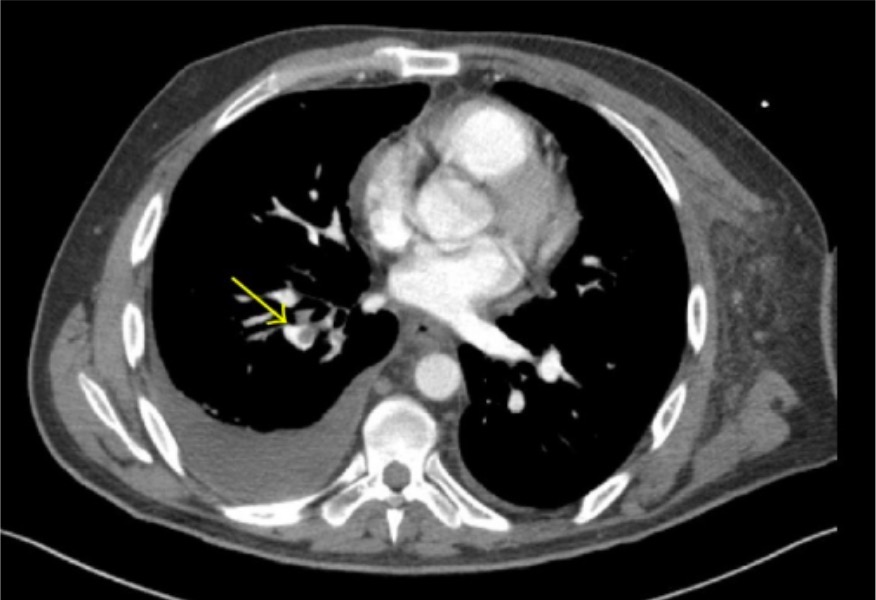
00:01 Continuing with Advanced Vascular Medicine, we’re going to talk for a while about pulmonary embolism, the most-dreaded complication of venous thromboembolism. 00:13 The definition of pulmonary embolism is blockage of a main artery of the lung or one of its branches by an embolus arising in the venous system. 00:25 Pulmonary embolism results from deep venous thrombosis, that is a blood clot in the deep veins, 90% of the time in the deep veins of the legs. And when the blood clot breaks off from the clot in the leg, it migrates in the circulation up into the lung. 00:43 The diagnosis again, as I said in previous lectures, can be difficult because the patient may have very non-specific symptoms and usually, in order to make the diagnosis, it requires one of our imaging techniques – a lung scan, with radionuclides, a pulmonary angiogram or MRI angiography or even CT angiography. And I’m going to talk about these in a little greater detail.
About the Lecture
The lecture Pulmonary Embolism: Definition by Joseph Alpert, MD is from the course Venous Diseases.
Included Quiz Questions
Which of the following techniques is NOT used for diagnosing pulmonary embolism?
- Endoscopic ultrasound.
- Lung scanning with radiolabeled albumin.
- CT scanning.
- Pulmonary angiography.
Customer reviews
5,0 of 5 stars
| 5 Stars |
|
5 |
| 4 Stars |
|
0 |
| 3 Stars |
|
0 |
| 2 Stars |
|
0 |
| 1 Star |
|
0 |