Playlist
Show Playlist
Hide Playlist
Pediatric Intussusception
-
Slides GD Pediatric GI.pdf
-
Download Lecture Overview
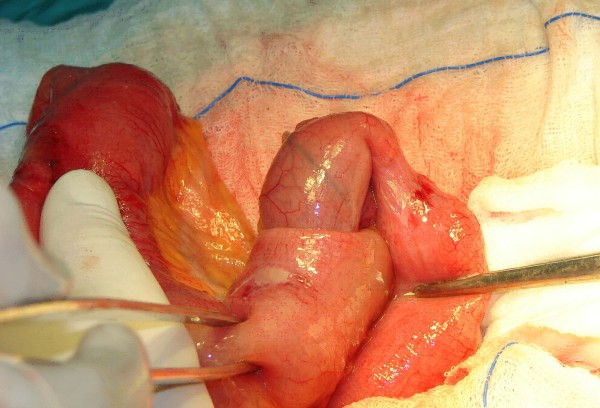
00:01 Our topic now goes into pediatric intussusception. 00:05 How did this take place? Well, intussusception here, maybe perhaps there is a vasculitis taking place of the intestines such as Henoch-Schönlein purpura. 00:16 Maybe there is that Meckel's diverticulum or maybe in general, you just had folding of one intestine to the other. 00:24 Folding. 00:25 There’s something called intussuscipien, intussusceptum. 00:27 That’s a little bit too much detail. 00:29 The point is that the – there’s telescoping. 00:32 Think about telescope. What do you do with a telescope? You pull it out. 00:35 When you want to see something and you put it back in. 00:39 Well, that’s what’s happening with intussusception. 00:41 One area of the intestine is folding into another. 00:45 Literally, telescoping. 00:47 This is not good. 00:49 The child is going to then have bilious vomiting. 00:52 The child may then be passing blood through the stool. 00:56 You might have heard of something called currant jelly stool. 00:59 It looks so incredibly appetizing. 01:02 I’m sorry that I’m being a little sick here, but whatever. 01:04 It does, it looks like currant jelly. 01:06 Amazing! There’s blood in the stool. 01:09 In addition, When you feel the abdomen, but this time, you have a folding. 01:15 This is not an olive. 01:17 An olive means what? Pyloric stenosis. 01:20 So what is this? You’re feeling a sausage and I’ll show you a picture upcoming. 01:25 Let’s talk about intussusception. 01:27 A portion of the GI tract telescoping into the portion distal to it. 01:32 Early: six to two years of age. 01:35 In fact, as rule of thumb in practice, you have an infant or a child between two months to two years with obstruction and colic. 01:49 At this point, with that type of history, you are being very aggressive in terms of investigating intussusception. 01:56 It is associated with lymphoid hyperplasia, Peyer’s patches, Meckel’s diverticulum or perhaps even rotavirus vaccine. 02:07 Signs and symptoms would be the following. 02:09 Acute onset, cramping, intermittent pain to the point where the child and the infant is crying, lethargy. 02:17 What does currant jelly stool mean to you? It’s dark. 02:20 Why? There’s passage of blood with the stool. 02:24 And upon examination, sausage-shaped mass. 02:30 I’ll show a picture where you’ll never forget it. 02:32 Diagnosis: Clinical history is sufficient for intervention. 02:36 By clinical history, we mean there’s quite a bit of colic and pain between the ages of two months and two years. 02:42 Ultrasound, plain films are supportive. 02:46 And air enema is diagnostic and therapeutic. 02:50 That’s what you’re paying attention to. 02:52 Literally, remember, this is causing what kind of obstruction? Mechanical obstruction. 02:57 So therefore, barium enema is actually going to then cause, well, increasing diameter of the intestine. 03:04 And very much, it’s going to relieve the child’s discomfort, diagnostic and therapeutic. 03:11 You definitely want to know those tests, which then provide both those types of experiences or those type of luxuries. 03:24 Enema reduction successful in 50% of your cases, in fact apart from it being diagnostic. 03:30 And take a look at this please. 03:32 Let me walk you through this. 03:33 On the left end, you find that there’s a little bit of -- it’s a smaller end, meaning to say that that was a normal intestine. 03:43 It folded into the distal portion. 03:46 And that red, beefy type of intestine that you’re seeing there, If you were feel that in the abdomen, it would feel like what? A sausage. 03:57 With such pictures, I believe that there’s absolutely no way that you are going to miss such questions. 04:03 Sausage shape. 04:05 Currant jelly. 04:06 The child being quite discomfort. 04:08 Welcome to intussusception.
About the Lecture
The lecture Pediatric Intussusception by Carlo Raj, MD is from the course Pediatric GI Pathology.
Included Quiz Questions
Which of the following is NOT a risk factor for intussusception?
- Paralytic ileus
- Henoch-Schonlein purpura
- Polyps
- Meckel's diverticulum
- Rotavirus vaccine
What is the characteristic description of the type of stools in a patient with intussusception?
- Currant-jelly stools
- Rice-water stools
- Hematochezia with mucus
- Foul-smelling, mucoid stools
- Melena
Which of the following tests is diagnostic and therapeutic for intussusception?
- Air enema
- Ultrasound scan
- Colonoscopy
- Gastroscopy
- Plain X-ray
A patient presents with a sausage-like mass in the right lower quadrant with currant-jelly stools. Which of the following investigations is NOT helpful for the diagnosis of intussusception?
- Sigmoidoscopy
- USG abdomen
- Air enema
- Barium enema
- X-ray plain films
A 2-year-old boy presents with a history of passage of bright red stools. He complains of pain and has a banana-shaped mass felt on examination. His vomitus is green. What is the pathophysiology of this condition?
- A part of the intestine curled up into the other part of the intestine
- Hypertrophy of the pyloric part of the stomach
- Twisting of the bowel wall
- Necrosis and inflammation of the bowel wall
- Inflammation of a diverticulum arising about 2 feet from the ileocecal junction
Customer reviews
5,0 of 5 stars
| 5 Stars |
|
5 |
| 4 Stars |
|
0 |
| 3 Stars |
|
0 |
| 2 Stars |
|
0 |
| 1 Star |
|
0 |