Playlist
Show Playlist
Hide Playlist
Ovarian Abnormalities: Simple and Complex Cysts
-
Slides Ovarian Abnormalities.pdf
-
Download Lecture Overview
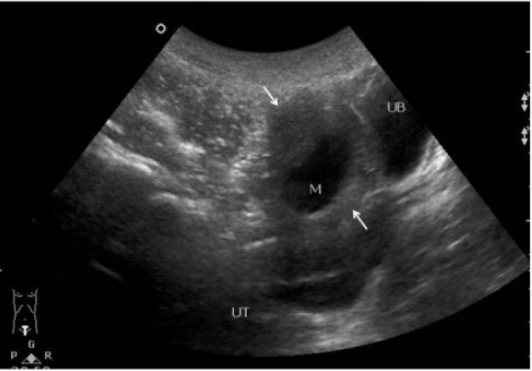
00:01 So in this lecture, we will be discussing ovarian abnormalities. 00:04 Let's start off with a case. 00:06 This patient presented with pelvic and abdominal pain. 00:10 She's 23 years old and her pain was on the right side. 00:13 Let's take a look at this. 00:15 Keep these images in mind as we go through the lecture. 00:17 So the two most common ovarian abnormalities are ovarian cysts and ovarian torsion. 00:23 Ovarian cysts can be both simple or complex. 00:27 So let's discuss what a simple cyst looks like on imaging. 00:33 This is an ultrasound image of the ovary and you can see an example of a simple cyst right here. 00:39 It's an anechoic thin-walled structure that's located within the ovary. 00:44 Surrounding it right here, is normal ovarian tissue. 00:47 So cysts can be managed in various different ways and it depends on whether the patient is pre-menopausal or post-menopausal. 00:54 If there are less than 3cm on a pre-menopausal female, then it's really considered a normal follicle and no further follow-up is indicated. 01:01 Anywhere between 3 to 5cm, it is now moved to the level of being a benign cyst rather than normal follicle but still, no further follow-up is indicated so these can be very commonly seen in pre-menopausal females and they come and go on their own. 01:16 If the cyst is greater than 5cm but less than 7cm, then we would follow it but really only a yearly follow-up is indicated so we still feel that this is probably within the benign category and we wanna make sure that it does go away in about a year or so. 01:31 However, if it's greater than 7cm, then we would move on to further evaluation and so this patient would need either an MRI for further evaluation or a surgical evaluation. 01:41 In a post-menopausal female, the follow-up is a little bit different. 01:44 These females are less likely to have normal simple cysts because there is no hormonal stimulation of the ovaries so malignancy is more of a thought within the post-menopausal female. 01:54 So in a cyst that's less than 1cm in size. 01:57 We still feel that that's probably normal and no follow-up is indicated. 02:00 However, if it grows to over 3cm but less than 7cm, then we would do a yearly follow-up just to make sure again that it goes away. If it's greater than 7cm, then this patient definitely needs either an MRI or surgical evaluation. 02:15 There are many different types of complex cysts within the ovaries. 02:19 The most common is a corpus luteal cyst and we'll go over these imaging findings. 02:23 Another very common complex cyst within the ovaries is a hemorrhagic cyst. 02:27 Endometriomas are occasionally seen and dermoid cysts are definitely seen as well. 02:34 So let's go over more details about the imaging findings of each of these complex cysts. 02:39 So let's talk about the corpus luteum. 02:41 A corpus luteum is a functional ovarian cyst that forms after an egg is expulsed from a follicle. 02:46 Normally, this can measure up to 3cm in size and it has a thick rim with a very prominent peripheral flow on color Doppler evaluation. 02:55 So as you can see here, this is the corpus luteal cyst with flow surrounding it within this very thick wall and this is the classic ring of fire appearance which is seen with corpus luteal cysts. 03:07 If you see this, you know that this is a benign finding and does not need any further follow-up. 03:12 Hemorrhagic cysts are also very commonly seen and this is what they look like on ultrasound. 03:16 It's a very thin-walled cyst that has multiple low level internal echoes. 03:22 So it doesn't look like a simple cyst which is completely anechoic but actually does have multiple low level echoes within it. 03:28 it resolves usually on follow-up imaging and the terms that it's associated with are reticular or lacy internal pattern. 03:36 So when you hear reticular or lacy internal pattern, the thing that you should think about is the hemorrhagic cyst. 03:42 And again, these are benign. 03:43 We usually do follow these to make sure that they resolve and usually on follow-up imaging, they do tend to go away. 03:49 So in a pre-menopausal female, they should be followed in about 6-12 weeks especially if they're greater than 5cm. If they're under 5cm and have a very classic appearance of a hemorrhagic cyst, they don't necessarily need to be followed. 04:03 However, in a post-menopausal female, regardless of size, we usually follow this by pelvic ultrasound in about 6 to 12 weeks to make sure that they resolve. 04:11 So dermoids are also occasionally seen within the ovaries. 04:14 A dermoid is a benign ovarian germ cell tumor. 04:17 It usually presents as a hyperechoic mass seen on ultrasound and it's usually an incidental finding. 04:22 It may be heterogeneous and on CT and MRI, the classic appearance is that it has fat within it. 04:29 on MRI, that means that it would be bright on T1 and it loses signal on T1 fat saturated images. 04:36 So let's take a look at this example of a dermoid cyst. 04:39 This is an ultrasound image and you can see here where the arrow points there's an echogenic mass within the ovary and this represents the dermoid. 04:49 If we take a look at the MRI images, let's look at each of these in a little bit of detail but we have T1, T2, T1 fat saturated images and then we also have a CT image to give you a good classic appearance of what a dermoid should look like on both CT and MRI. 05:04 So on ultrasound, it's an echogenic mass as we saw. 05:07 On MRI, you see two masses here and they both contain varying degrees of fat. 05:13 So if you look at the fat saturated images, they actually both lose a certain amount of signal on the fat saturated images which is what you would expect of a fat-containing structure. 05:22 So this tells you that this lesion does contain fat. 05:24 On T2 weighted images, both of these lesions are T2 hyperintense indicating that they are cystic. 05:31 So it's a cystic fat-containing mass and that's characteristic of a dermoid. 05:36 If you look at this last image here, this is an axial CT image, and you can see areas of low density within both of these lesions which represent lipid. So again, this is very characteristic of a dermoid cyst. 05:48 So these rarely undergo malignant transformation. 05:50 However, they can result in ovarian torsion and they may rupture. 05:54 So if they're less than 6cm in size, then they're just followed by ultrasound. 05:59 However, larger lesions are actually resected and we try to preserve ovarian tissue when we resect these.
About the Lecture
The lecture Ovarian Abnormalities: Simple and Complex Cysts by Hetal Verma, MD is from the course Abdominal Radiology. It contains the following chapters:
- Ovarian Abnormalities
- Corpus Luteum
Included Quiz Questions
A 60-year-old postmenopausal woman presents with right lower pelvic pain. Ultrasound demonstrates a 5 cm simple ovarian cyst. What is the correct management of this cyst?
- Annual follow-up ultrasound
- No follow-up is needed.
- MRI
- Surgical evaluation
- Follow-up ultrasound in 6 weeks
Which of the following combinations of simple ovarian cyst size and their management in a PREmenopausal woman is correct?
- 6 cm/annual follow-up
- 8 cm/annual follow-up
- 2.5 cm/normal follicle/annual follow-up
- 4 cm/annual follow-up
- 6 cm/no follow-up
A thick-rimmed ovarian cyst with a "ring of fire” appearance is seen with which of the following?
- Corpus luteum
- Hemorrhagic cyst
- Endometrioma
- Dermoid cyst
- Simple cyst
Customer reviews
5,0 of 5 stars
| 5 Stars |
|
5 |
| 4 Stars |
|
0 |
| 3 Stars |
|
0 |
| 2 Stars |
|
0 |
| 1 Star |
|
0 |