Playlist
Show Playlist
Hide Playlist
Other Structures – Female Reproductive System
-
Slides 09 Human Organ Systems Meyer.pdf
-
Reference List Histology.pdf
-
Download Lecture Overview
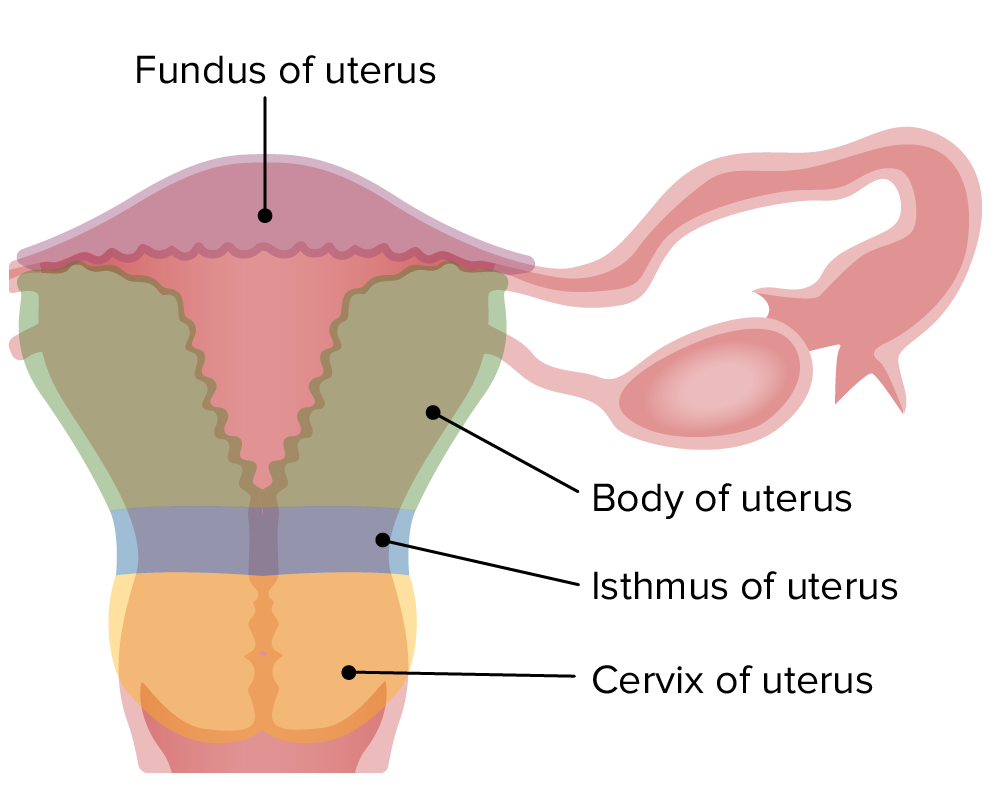
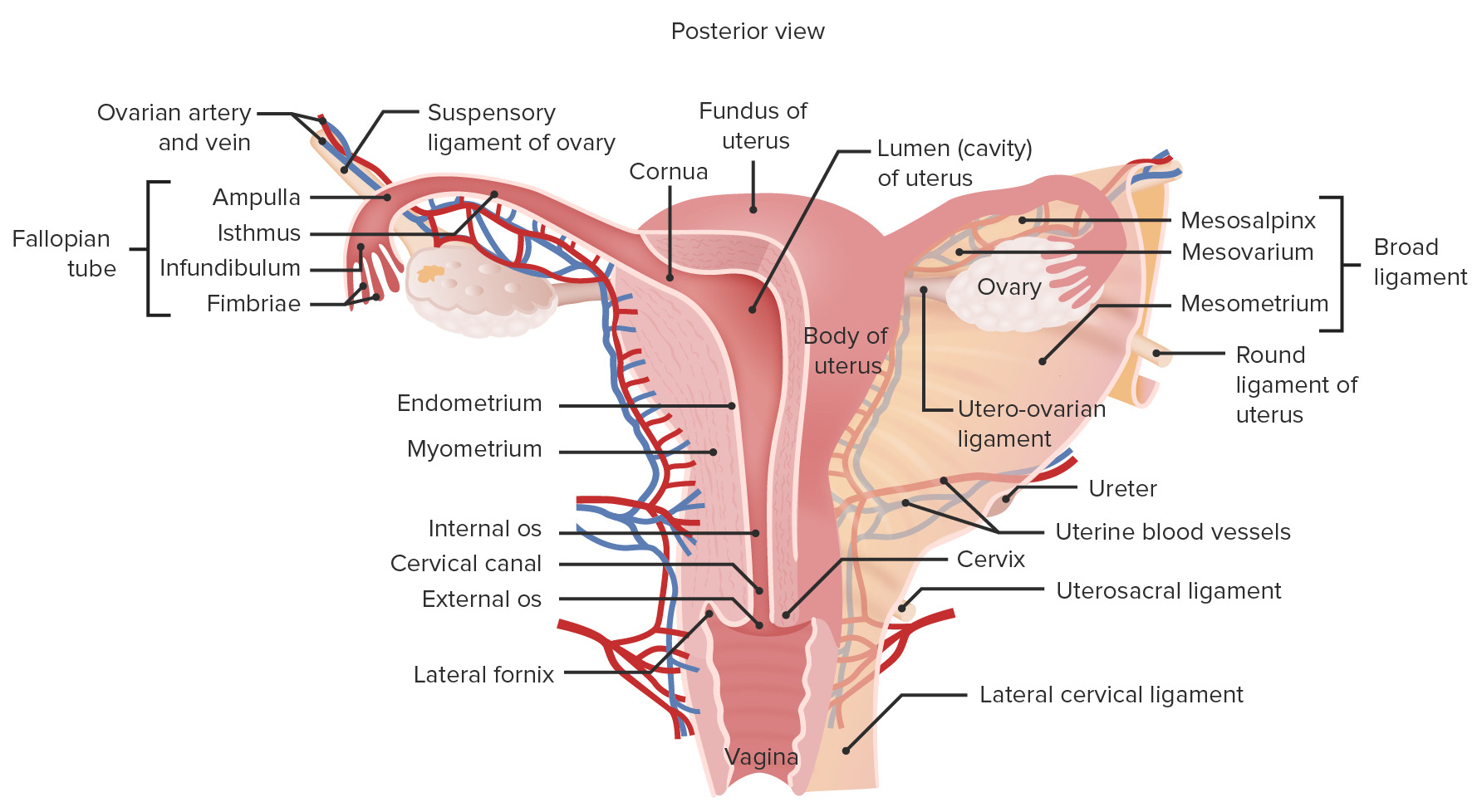
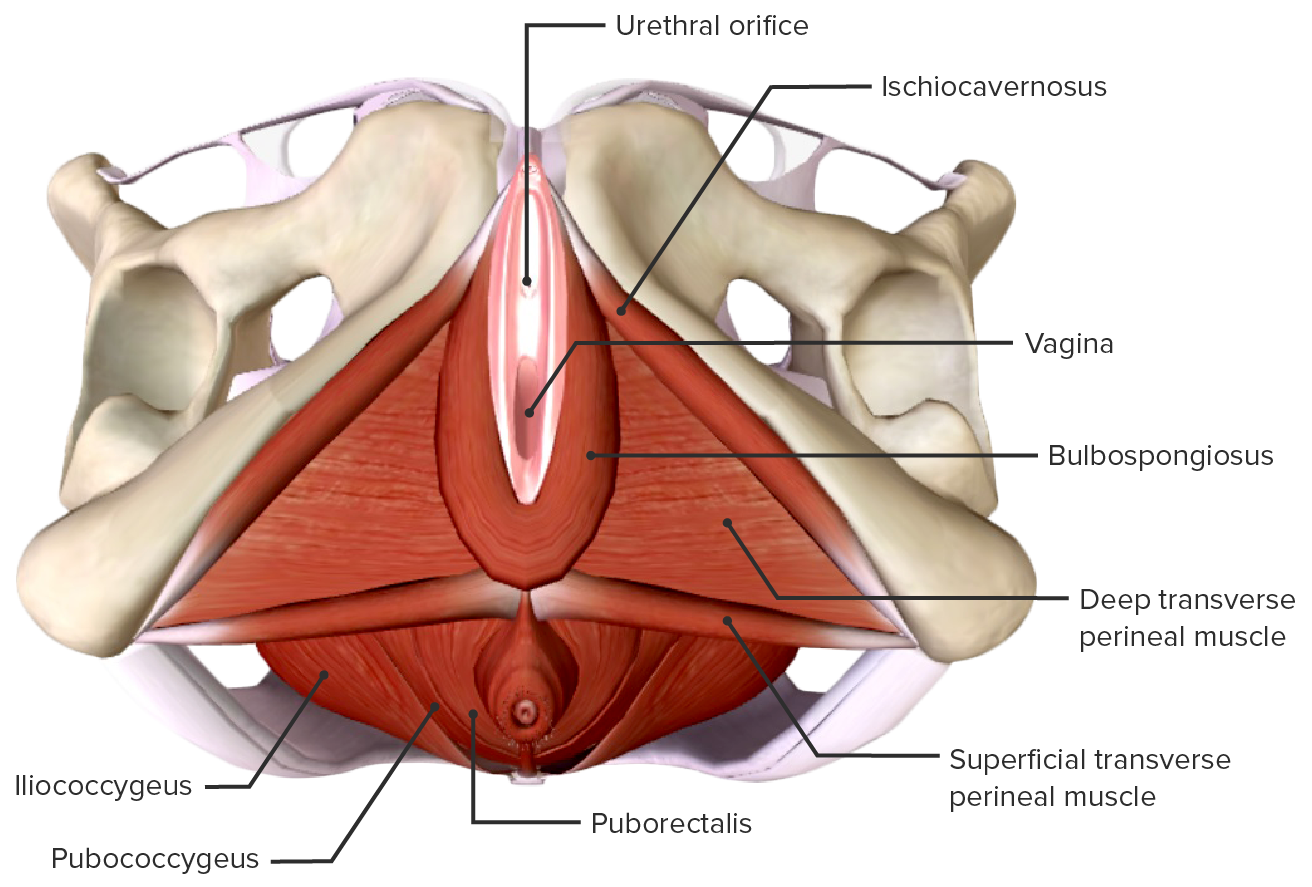
00:01 In this lecture, I’m going to describe the organs of the female reproductive system, except the ovary which I’ll cover in another lecture. You are going to learn the histological structures associated with the uterine tube, the uterus, cervix, vagina, and the mammary gland. And also, I’m going to stress the functions of each of these organs. When I describe all these features, I’d like you to understand firstly, the structure and function of the uterine tube. I’d like you to understand all the phases of the menstrual cycle and the changes that occur in the uterus during the menstrual cycle. And I want you to recall that both the ovarian cycle and the menstrual cycle are regulated by hormones secreted by various tissues both within the female reproductive system, the ovary, the uterus, and also from the pituitary gland. And then I want you to have a very clear understanding of the structure of the cervix and vagina, and also the lactating and non-lactating breast. 01:15 I will also briefly describe the external genitalia in the female reproductive system. 01:21 There are a number of very important functions carried out by all the organs that I’m going to talk about. The uterine tube is really specialized for transport of the sperm and the oocyte to create a possible location for fertilization where the environment is very nutritious as well. It’s very important that the endometrium, the functional part of the uterus goes through cyclical changes under the influence of the hormones, estrogens, and progesterone, to prepare the endometrium for the possible implantation of a fertilized egg. The cervix acts as a very important transport, conduit, or passageway for sperm. And at the time of ovulation, that cervix changes the nature of secretion to try and optimize the transport of sperm. Normally, around the times other than ovulation, it’s a very important barrier to the invasion of pathogens. And the vagina, as well as being the organ of copulation in the female, provides a very protective environment, because entry into the vagina of any bacterial or pathogens can find their way all the way up through the cervix, to the uterus, through the uterine tube and beyond into the female body. And finally, the mammary gland is a very important gland. During lactation, it provides milk, nutrition's to the suckling child. I’m going to briefly describe that, and hopefully, you’ll understand the structure and function of this gland. We will
About the Lecture
The lecture Other Structures – Female Reproductive System by Geoffrey Meyer, PhD is from the course Reproductive Histology.
Included Quiz Questions
Which of the following is NOT a part of the female reproductive system?
- Pituitary gland
- Uterus
- Cervix
- Vagina
- Ovaries
Which of the following is a function of the cervix in pregnancy?
- Barrier against pathogens
- Provides nutrition to the fetus
- Provides a site for implantation
- Regulates hormones
- Acts as barrier against sperm
Customer reviews
5,0 of 5 stars
| 5 Stars |
|
5 |
| 4 Stars |
|
0 |
| 3 Stars |
|
0 |
| 2 Stars |
|
0 |
| 1 Star |
|
0 |