Playlist
Show Playlist
Hide Playlist
Other Spirometry Patterns – Laboratory Diagnostics
-
Slides Diagnostics PulmonaryFunctionTest RespiratoryPathology.pdf
-
Reference List Pathology.pdf
-
Download Lecture Overview
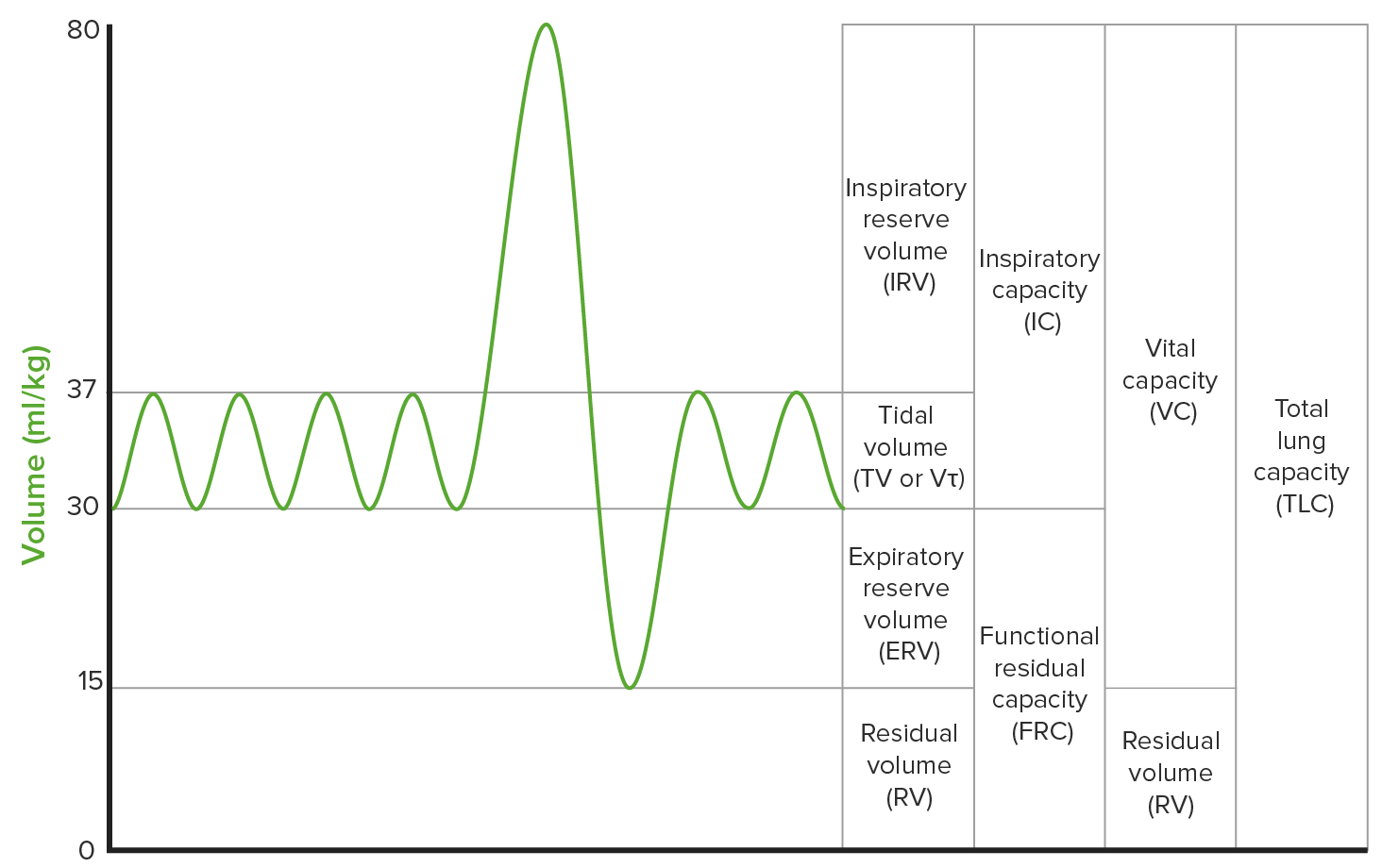
00:01 Other important patterns that you want to keep in mind. 00:04 You will like this. Watch. The first one is called fixed obstruction. 00:09 What does this mean? Well, this could mean that first and foremost, let's begin the same way, organization. 00:18 The loop spirometry, different pathologic patterns that you are responsible for understanding. 00:23 We will begin with residual volume. 00:25 Okay. Does this even look normal? No, it doesn't. 00:29 Actually, the both, the bottom half and the top half look like they are kind of sandwiched, isn't it? It looks like a burger, doesn't it? Looks like buns. That's what it looks like. 00:40 And that black line in the middle that's your piece of bacon. I don't know, whatever. 00:43 So, the point is they are compressed. 00:45 What happened here? There is difficulty with inspiration, hence flattened and there is also difficulty with expiration. 00:52 What the heck kind of disease is going to give you a fixed obstruction? A ENT tumor. In other words, you have perhaps dangerous, a head and neck type of cancer. 01:05 When there is a head and neck type of tumor or cancer, this is then causing a fixed large obstruction of both inspiration which is the bottom half of the curve and the top half. 01:16 That is fixed. Let's move on to another one. 01:19 Now, first and foremost, dissect the curve, interpret this. 01:24 Where is my problem, please? Inspiration? Exhalation? Good. Inspiration only. You see that there is only a problem with inspiration. 01:33 Wow. What the heck kind of problem or disease or pathology has given me a problem with inspiration only? The problem is extra thoracic pathology. 01:45 Meaning, maybe with the vocal cords. 01:49 So, with the vocal cord type of dysfunction or maybe perhaps fibrosis or an upper airway mass, this is the most tested, well, please understand, that you are going to have a hard time inspiring. 02:02 Is that clear? So, therefore, the bottom half of the curve has not been affected. 02:06 But, you do not have problems at getting the air out. 02:09 This is not, not I repeat, anything to do with obstructive in terms of the pulmonary issue. 02:15 Obstructive here, I wouldn't even use this word. 02:18 I would just think of this as being inspiratory issues. 02:23 Now, when we do think about obstructive. 02:26 I want you to keep the theme of obstructive and inside the lung. 02:30 First and foremost, interpret the curve for me. 02:34 Where is my problem? Good. The top half. 02:38 What does that top half represent? Oh, exhalation. Interesting. 02:44 Earlier discussion, I just showed you obstructive lung disease with scalloped type of second half of exhalation with a left shift, meaning to say, an increase in TLC. That was obstructive. 03:00 Here, please understand, when you have such a obstructive pattern, that you will see at some point in time, that this is a problem inside my lung and this will be something like obstructive disease, or but also, intrathoracic tumor whereas the tumor in the first one, fixed. 03:17 Where was it? Oh, ENT. Ear, Nose, Throat. Clear? Blocking, fixed. What was the one with extrathoracic? That was vocal cord, problem with inspiration only. 03:27 Now, under the three main categories, take a look at lung volumes. 03:31 TLC, residual volume, and once again, the gold standard here for measuring lung volume will be your body box, plethysmography. 03:39 Lung volumes used in measuring residual volume, we talked about, that's spirometry cannot, report's out, your TLC and vital capacity will be two big ones. 03:48 Then reduced TLC seen in what kind of disease, please? Good. Restrictive. 03:55 Elevated TLC and residual volume will be seen in what kind of disease, please? Good. Obstructive. We will call this hyperinflation.
About the Lecture
The lecture Other Spirometry Patterns – Laboratory Diagnostics by Carlo Raj, MD is from the course Pulmonary Diagnostics.
Included Quiz Questions
Which of the following patterns would you expect in the loop spirometry of a patient with a nasopharyngeal tumor?
- Fixed obstruction
- Variable intrathoracic
- Variable extrathoracic
- Obstructive
- Restrictive
Which of the following curve patterns would you expect in a patient with inhalation dysfunction?
- Variable extrathoracic
- Variable intrathoracic
- Obstructive
- Fixed obstructive
- Restrictive
Why is a variable intrathoracic loop spirometry pattern seen in some form in all obstructive lung diseases?
- It represents an exhalation dysfunction.
- It represents an inhalation dysfunction.
- It shows a decrease in residual volume.
- It shows a decrease in TLC.
- It represents a mixed obstructive and restrictive pattern.
Customer reviews
5,0 of 5 stars
| 5 Stars |
|
5 |
| 4 Stars |
|
0 |
| 3 Stars |
|
0 |
| 2 Stars |
|
0 |
| 1 Star |
|
0 |