Playlist
Show Playlist
Hide Playlist
Neuromuscular Junction Disorders: Clinical Features and Pathophysiology
-
Slides Strowd Neuromuscular Junction Disorders.pdf
-
Download Lecture Overview
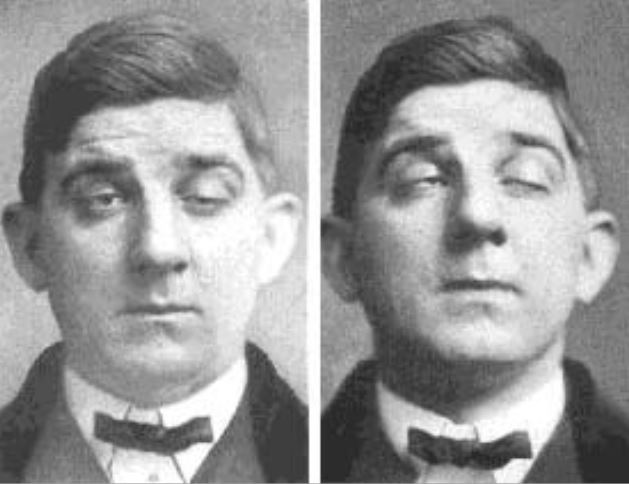
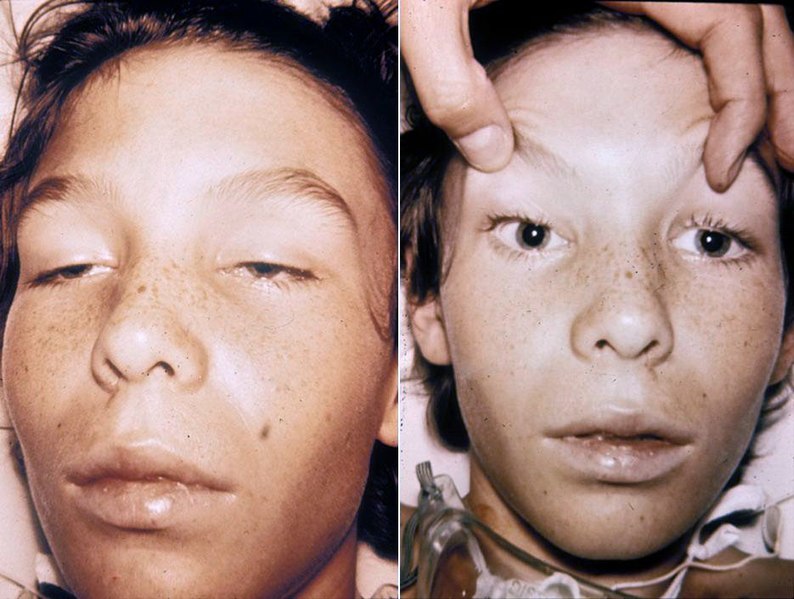
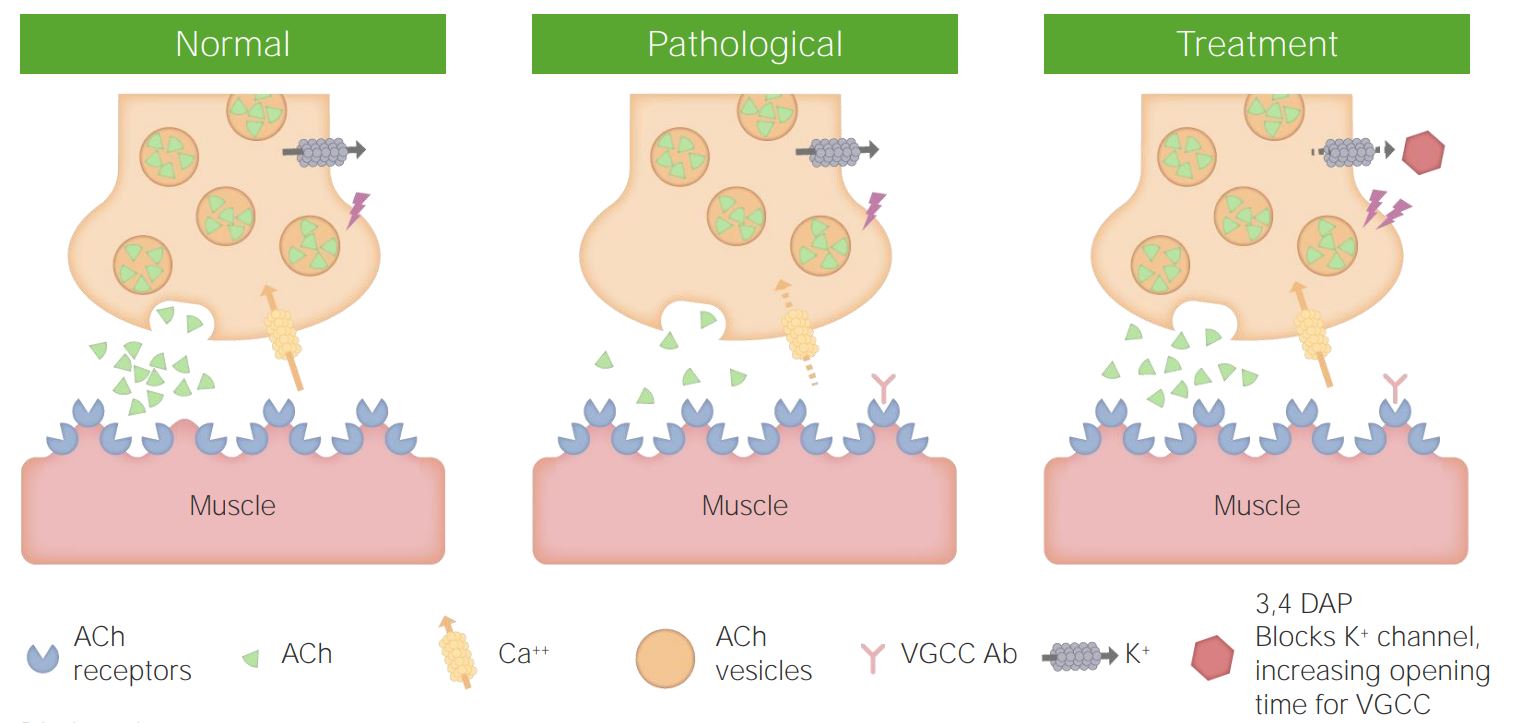
00:00 And again, when we evaluate patients, we're thinking of the distribution. 00:05 Where are the problems? Where does this weakness occur? We should see presence of bulbar findings. 00:11 And the presence of ptosis, diplopia, dysarthria, and dysphasia point towards a neuromuscular junction etiology. 00:19 Sensory findings are normal. 00:21 Reflex examination often shows normal reflexes. 00:24 And we're looking for that wildcard symptom the presence of fatigability. 00:28 Symptoms that worsen when muscles are contracted. 00:32 After our first step is, to localize to the neuromuscular junction, we move to step two. 00:37 What is this junctional disorder? And we can walk through the types of problems that pathophysiologic processes that occur in the body. 00:45 We can look for immune disorders. 00:47 And the immune disorder at the neuromuscular junction is called Myasthenia gravis. 00:51 We can look for infections. 00:53 And the primary infection to effect the neuromuscular junction is botulism. 00:57 It has a tropism and affinity for the neuromuscular junction. 01:02 The neoplastic or paraneoplastic disorder that affects the neuromuscular junction is called Lambert-Eaton myasthenic syndrome. 01:09 Toxins and metabolic problems can also affect the neuromuscular junction. 01:14 And there are specific drugs that we need to think about that can cause problems in the neuromuscular junction. 01:20 And then there are some inherited and congenital problems. 01:23 Congenital Myasthenia, and Neonatal myasthenia that can also affect the neuromuscular junction. 01:29 We're going to walk through each of these disorders in subsequent lectures. 01:33 But right now, I want you to know that those are the conditions that we should focus on when we're dealing with a problem or a patient who presents with neuromuscular junction signs and symptoms. 01:43 So let's look at where those occur. 01:45 We said junctional disorders should be broken down into presynaptic and postsynaptic disorders, where to each one of those fall. 01:52 Well, Myasthenia gravis the most common junctional disorder and one that we really need to know is a postsynaptic problem. 01:58 This disorder results from problems abnormality with the postsynaptic acetylcholine receptor. 02:06 Anesthetics affect the postsynaptic action of acetylcholine binding to that postsynaptic acetylcholine receptor and muscle depolarization. 02:15 Lambert-Eaton Myas Syndrome. 02:17 Myasthenic syndrome is an important cause of a presynaptic junctional disorder. 02:21 Antibodies to the presynaptic voltage-gated calcium channels prevent that influx of calcium and the communication can't proceed down the presynaptic terminus into the junction. 02:34 Botulism is a disorder and infection that affects the binding of the vesicles to the presynaptic membrane. 02:40 And so this is also another important presynaptic junctional disorder. 02:44 And then lastly, cholinestarase inhibitors affect that cholinestarase enzyme in the synaptic cleft. 02:51 So again, I want you to know about the important presynaptic and postsynaptic disorders that affect the neuromuscular junction.
About the Lecture
The lecture Neuromuscular Junction Disorders: Clinical Features and Pathophysiology by Roy Strowd, MD is from the course Disorders of the Neuromuscular Junctions.
Included Quiz Questions
Which of the following statements is false?
- Anesthetics typically work at the presynaptic terminal.
- Lambert-Eaton syndrome is due to antibodies against presynaptic calcium receptors.
- Myasthenia gravis is due to antibodies at the postsynaptic receptor.
- Botulism is due to disruption of presynaptic vesicle binding.
- Cholinesterase inhibitors work within the synaptic cleft.
Which of the following is not a typical cause of a neuromuscular junction disorder?
- Trauma/injury
- Autoimmune/inflammatory conditions
- Infections
- Neoplastic/paraneoplastic syndromes
- Toxic/metabolic conditions
Customer reviews
5,0 of 5 stars
| 5 Stars |
|
5 |
| 4 Stars |
|
0 |
| 3 Stars |
|
0 |
| 2 Stars |
|
0 |
| 1 Star |
|
0 |