Playlist
Show Playlist
Hide Playlist
Mitochondrion
-
Basic Histology 02.pdf
-
Reference List Histology.pdf
-
Download Lecture Overview
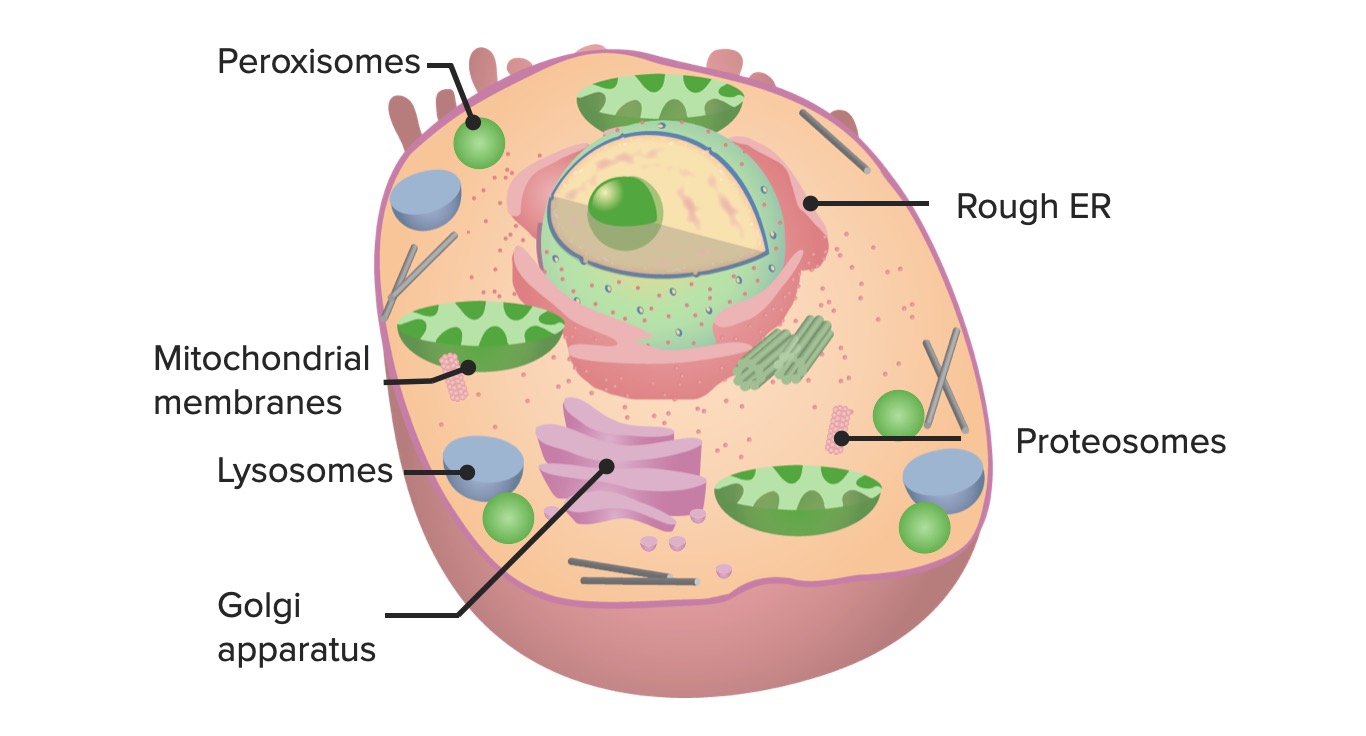
00:01 Let's first of all look at an organelle that's common in all cells, the mitochondrion, shown on the right hand-side in this diagram. 00:13 Mitochondria produce ATP. 00:18 They're involved with the breakdown of energy-rich organic substances that are taken in by the cell, for instance, pyruvates and fatty acids, and what they do is they break these components down and store them into energy in the form of ATP. 00:45 And when we talk about oxidative processes that break down components and produce ATP in mitochondria, we refer to that as being cellular respiration. 01:00 Have a look at the mitochondrion in this image. 01:03 It's a double membrane-bound organelle that's about the only one in all the cytoplasm. 01:11 The outer membrane is highly permeable to most things in the cell — water, ions, etc. 01:20 The inner membrane is not so permeable to all those elements. 01:26 And the inner membrane invaginates to form long parallel stacks of membranous components called cristae that run perpendicular to the long axis of the mitochondria. 01:45 The mitochondrial matrix contains mitochondrial DNA, RNA, and also mitochondrial ribosomes are housed within the matrix of the mitochondrion. 02:00 In this slide, you can see on the right-hand side an electron micrograph through a mitochondrion. 02:07 In fact, there's two there but in the top one, the large circular structure, you can see the outer membrane of the mitochondrion and you can see the inner cristae of the mitochondrion. 02:23 These inner cristae, you can see form parallel plates and that form is typical of mitochondria that produce proteins, whereas mitochondria that produce steroids, these cristae adopt a tubular form. 02:45 On the left-hand side, you can see circular structures. 02:51 Focus on the 1, 2, 3, 4 large pink circular structures with the clear space in the middle. 03:02 They're ducts or tubes in this salivary gland, and these particular ducts or tubes modify the salivary secretion before it's secreted into your mouth. 03:16 To do that, they require a lot of energy, a lot of transfer of materials across the cells that make up these ducts, and that energy has to be provided by mitochondria. 03:32 Mitochondria are collections of mitochondrion that sit at the very base of these epithelial cells making up the wall of the duct, and if you look very, very carefully at the basal part of some of these cells, you can just make out pink striations. 03:53 I know it's hard to see, but these pink striations indicate the columns of mitochondria that line up inside the cell to provide all the energy for these ducts to modify the salivary secretory product.
About the Lecture
The lecture Mitochondrion by Geoffrey Meyer, PhD is from the course The Mammalian Cell.
Included Quiz Questions
Which ONE of the following statements about mitochondria is INCORRECT?
- They stain shades of blue and purple within the cytoplasm.
- They store energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate.
- They are bounded by a double membrane.
- The inner membrane is extensively folded to produce cristae.
- Mitochondrial matrix contains DNA and ribosomes.
What is the major function of mitochondria?
- Synthesis of adenosine triphosphate
- Protein synthesis
- Cholesterol synthesis
- Enzyme degradation
- Production of phagolysosomes
Customer reviews
5,0 of 5 stars
| 5 Stars |
|
5 |
| 4 Stars |
|
0 |
| 3 Stars |
|
0 |
| 2 Stars |
|
0 |
| 1 Star |
|
0 |