Playlist
Show Playlist
Hide Playlist
3 Major Types of CNS Tumors: Medulloblastoma & Primitive Neuroectodermal Tumor (PNET), Ependymoma and Glioma
-
Slides CNS Pediatrics.pdf
-
Download Lecture Overview
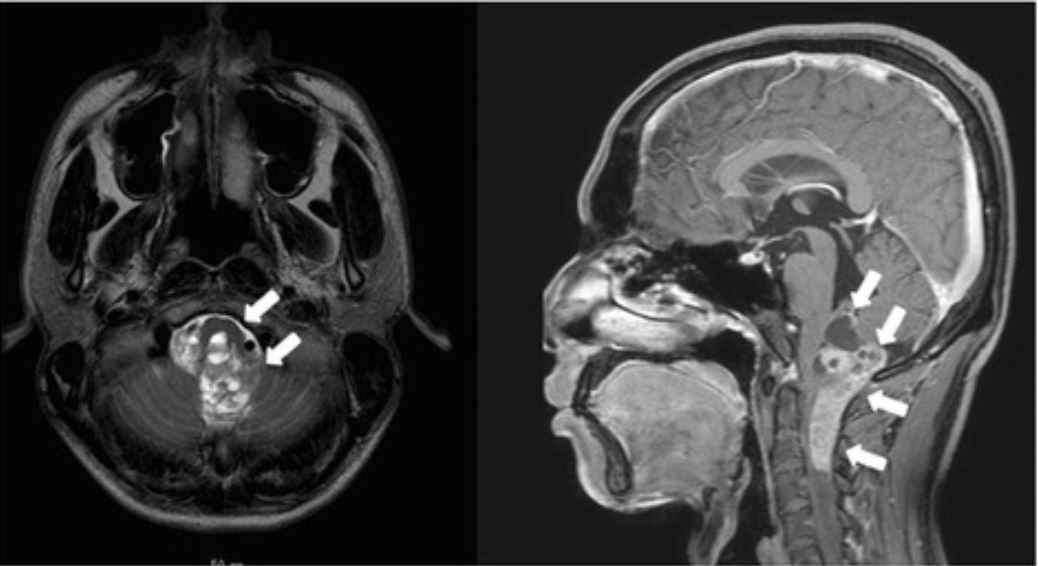
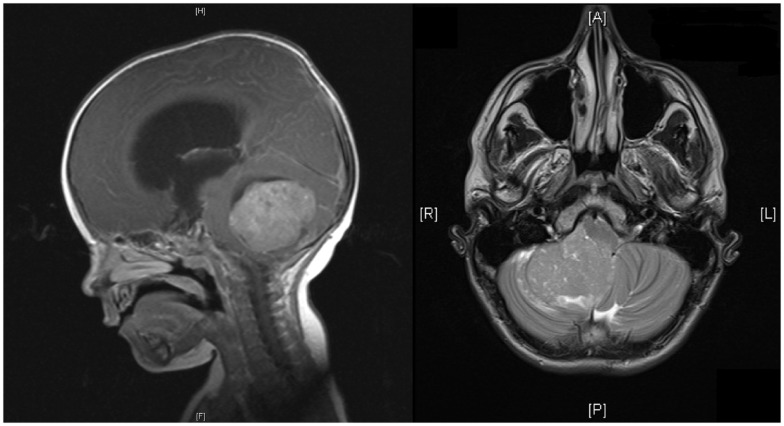
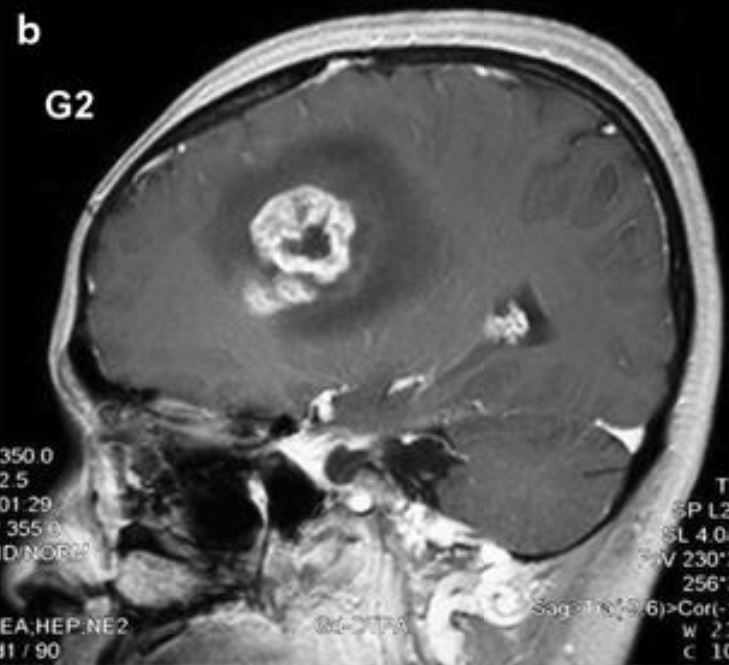
00:01 So let's review the 3 major types of CNS tumors in children. 00:07 Let's first talk about medulloblastomas and the PNET or primitive neuroectodermal tumor. 00:13 The PNET and medulloblastoma are about 20% of all pediatric brain tumors. 00:23 There are 40% of these are cerebellar tumors or tumors arriving in the cerebellum. 00:29 These typically happen in children between 5 and 7 years of age. 00:33 These are a variety of small round blue cell tumors. 00:38 For these patients, we typically treat with resection if we can as well as radiation or a combination of therapies. 00:46 These are the most likely brain tumor to metastasize. 00:51 There is generally a decent survival for standard risk PNETs and medulloblastomas of around 75 to 85%. 01:01 However, in high-risk patients, that survival rate can drop fairly dramatically, even as low as 25%. 01:09 It really depends on the type of tumor. 01:12 Also, just because a patient has survived, it doesn't mean they've survived normally. 01:17 In general for brain tumors, if surgery is going to be done, younger babies are able to accommodate over life because the brain is so plastic but older children are less likely to accommodate for brain injury. 01:31 Next, the ependymoma. 01:35 So this constitutes about 10% of pediatric brain tumors and is more common in the first decade of life. 01:42 It occurs in the ventricular system, usually the posterior fossa at the floor of the fourth ventricle and this can cause extreme emesis. 01:52 So these are commonly in patients who are vomiting very profoundly. 01:56 They can be locally invasive and spread through the spinal canal downward. 02:01 Also, CSF and spine MRI are important for metastatic workup. 02:06 Surgical resection is indicated followed by radiation and there's a relatively poor survival, a 5-year survival rate of 10 to 70% depending on the type of tumor. 02:18 Last, let's review the gliomas. 02:22 This is the most common CNS tumor, it's the low-grade glioma. 02:28 It is a non-aggressive tumor. 02:31 It has a good overall prognosis assuming it can be handled. 02:36 These do not spread but spinal cord metastasis is possible in about 5%. 02:43 Treatment is resection. 02:45 As long as you can resect these, the prognosis is a little better and 90% will have a full cure after resection. 02:53 For unresectable tumors, the prognosis is worse and these patients may require radiation and chemotherapy for recurrent tumors. 03:02 Lastly, the high-grade anaplastic astrocytoma and glioblastoma multiforme. 03:11 This is about 10% of all CNS tumors but it's rare in children. 03:15 It generally affects cerebral hemispheres and it's regionally invasive, like you can see this one growing over into the other hemisphere. 03:25 It's difficult to surgically resect. This can be quite challenging to treat. 03:30 There is a grim prognosis for this. 03:34 The anaplastic astrocytoma has a survival rate of only 35% and the glioblastoma multiforme has a less than 10% 5-year survival. 03:44 These are dismal tumors to be diagnosed with. 03:47 So let's turn now to the diffuse pontine glioma in the pons in the brainstem. 03:54 These are unresectable. 03:56 They are about 10 to 20% of pediatric brain tumors and most patients die within 2 years of diagnosis. 04:04 These patients will respond to radiation which is often palliative and most recur within 1 year. 04:10 Chemotherapy does not improve prognosis so typically it isn't done. 04:14 So, complications and prevention. 04:19 Complications are usually related to radiation therapy and brain tumors. 04:23 This can result in growth failure, endocrinological abnormalities such as panhypopituitarism, secondary brain tumors which can happen later on as a result of the radiation, vasculopathy or an irregularity of the blood vessels as a result of the radiation therapy and long-term cognitive defects. 04:43 We want to avoid excessive radiation to the head such as head CT. 04:49 That's a way to prevent brain tumors in the first place. 04:52 Remember, young kids exposed to head CTs are at more risk for cancer likely than older people because they're having more active mitosis going on and that's more opportunity for errors in transcription of DNA resulting in a clonal population. 05:09 So, we were trying to do less and less of radiation of the head as much as we can. 05:15 Some patients such as patients with VP shunts are at increased risk and we are moving more and more towards MRI modalities for assessment of shunts so we can avoid cancer in the future for children. 05:28 So, that's my brief review of brain cancer in children. 05:32 Thanks for your time.
About the Lecture
The lecture 3 Major Types of CNS Tumors: Medulloblastoma & Primitive Neuroectodermal Tumor (PNET), Ependymoma and Glioma by Brian Alverson, MD is from the course Pediatric Oncology.
Included Quiz Questions
Which of the following statements is true about primitive neuroectodermal tumors of the central nervous system?
- They typically arise in the 1st decade of life.
- More than 90% are supratentorial.
- They are a rare type of brain tumor in children.
- They have a 5-year survival rate of < 10%.
- There is no role for surgery.
Where is the most common location of ependymoma in children?
- Fourth ventricle
- Hypothalamic region
- Spinal cord
- Lateral ventricle
- Frontal lobe
Which of the following is the most common type of central nervous system tumor in children?
- Low-grade glioma
- Meduloblastoma
- Neuroblastoma
- Primitive neuroendocrine tumor
- Ependymoma
Customer reviews
4,0 of 5 stars
| 5 Stars |
|
2 |
| 4 Stars |
|
0 |
| 3 Stars |
|
0 |
| 2 Stars |
|
1 |
| 1 Star |
|
0 |
Excellent overview for the practicing resident who wants to be able to diagnose CNS tumors.
Thank you so much, all your lectures are so great, full of good advice for my practice!
Way too much superficial on pathology. Slides are just lists: I can find this in books. I would have liked something like diagrams or drawings.