Playlist
Show Playlist
Hide Playlist
Lymphoid Organs: Summary
-
Slides 11 Human Organ Systems Meyer.pdf
-
Reference List Histology.pdf
-
Download Lecture Overview
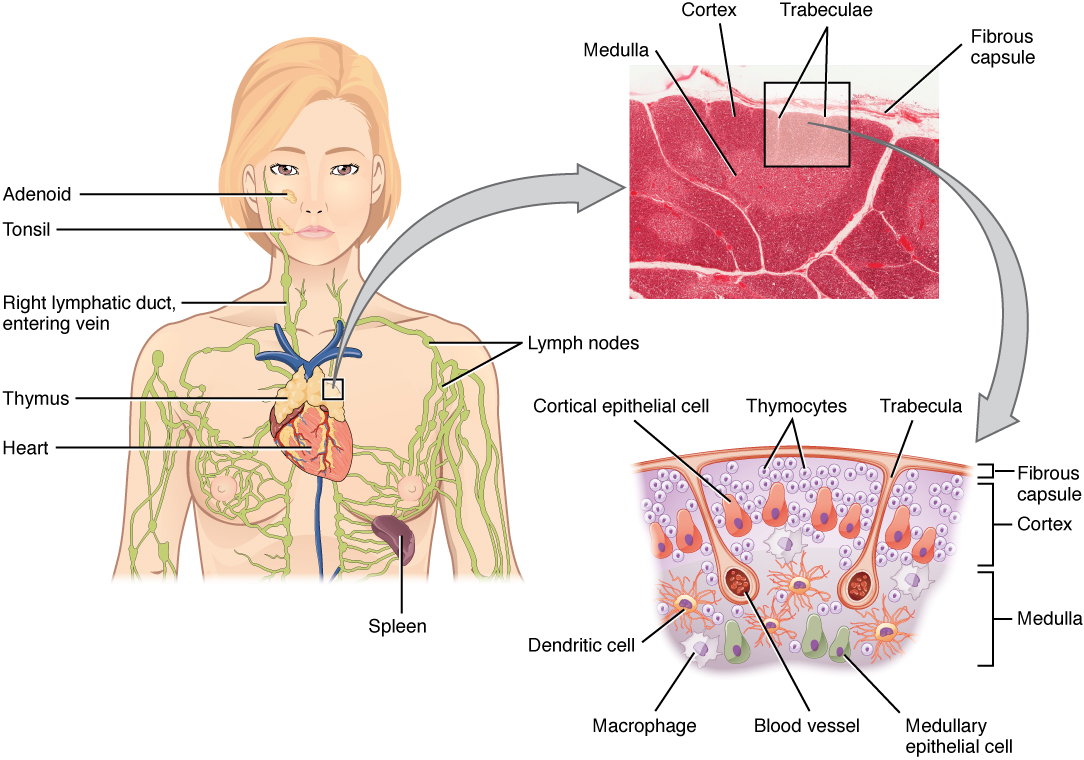
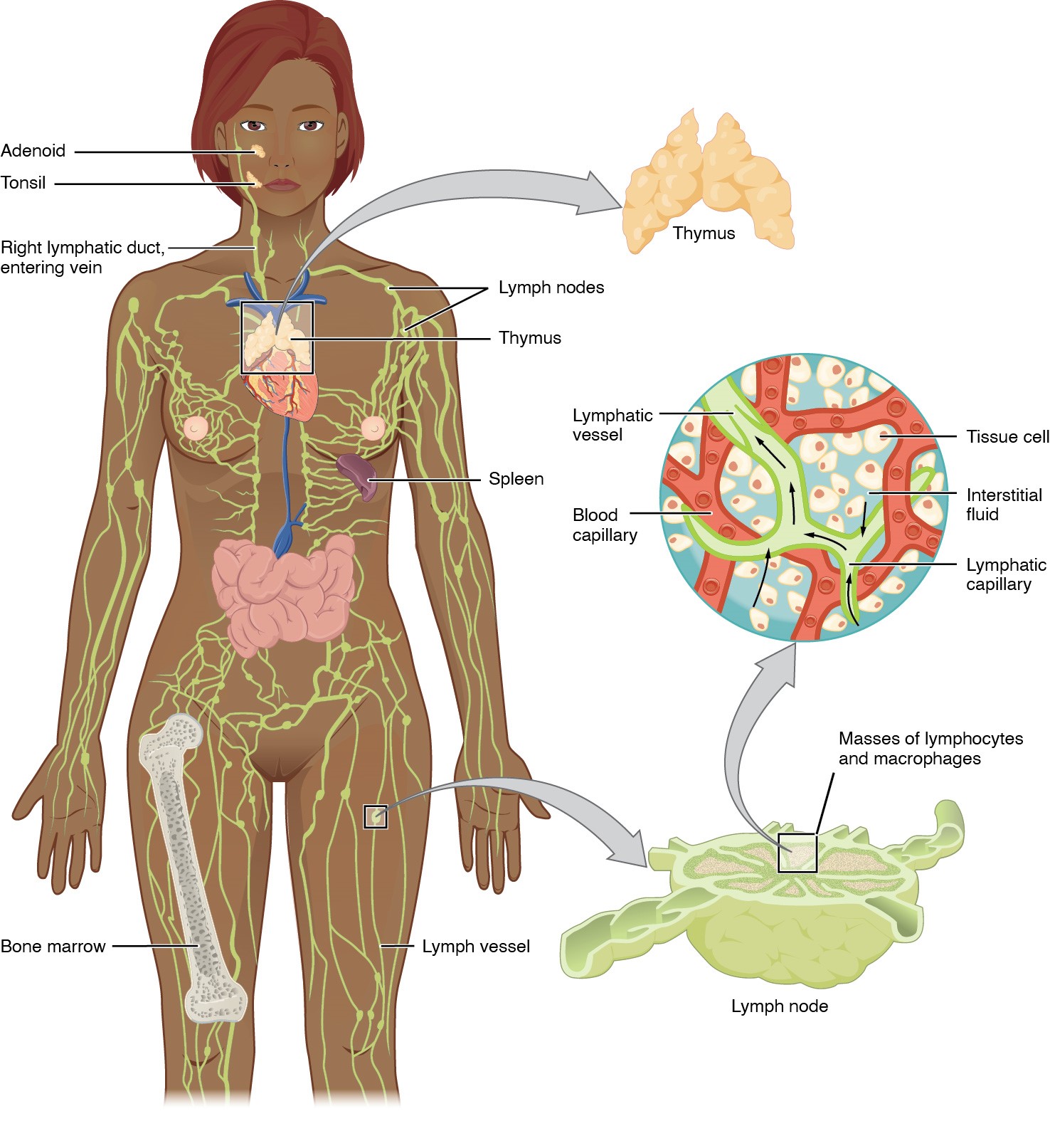
00:01 So in summary then, make sure that you understand diffuse lymphatic tissue in the mucosal areas. It’s representing spaces where cells can undergo surveillance and then mount a response against an invading antigen. Make sure you understand that lymph nodes filter lymph and they have the capacity to mount responses against antigens because the circulation of lymphocytes and the presence of certain lymphocytes. The thymus is where T cells are educated. It’s a complex structure, but histologically, it’s quite simple to identify. And the spleen filters lymph, and also, it can respond to antigens because of the presence of the central artery being housed or wrapped up by the periarterial lymphatic sheath, which actually replaces the tunica adventitia that you see in other vessels of the body.
About the Lecture
The lecture Lymphoid Organs: Summary by Geoffrey Meyer, PhD is from the course Lymphoid Histology.
Included Quiz Questions
What is another function of the spleen besides blood filtration?
- Immune response to antigens
- Bilirubin excretion
- Coagulation
- Erythrocyte production
- Plasma cell formation
Customer reviews
5,0 of 5 stars
| 5 Stars |
|
5 |
| 4 Stars |
|
0 |
| 3 Stars |
|
0 |
| 2 Stars |
|
0 |
| 1 Star |
|
0 |