Playlist
Show Playlist
Hide Playlist
Lateral Compartment – Anatomy of the Leg
-
Slides 06 Lower Limb Anatomy.pdf
-
Download Lecture Overview
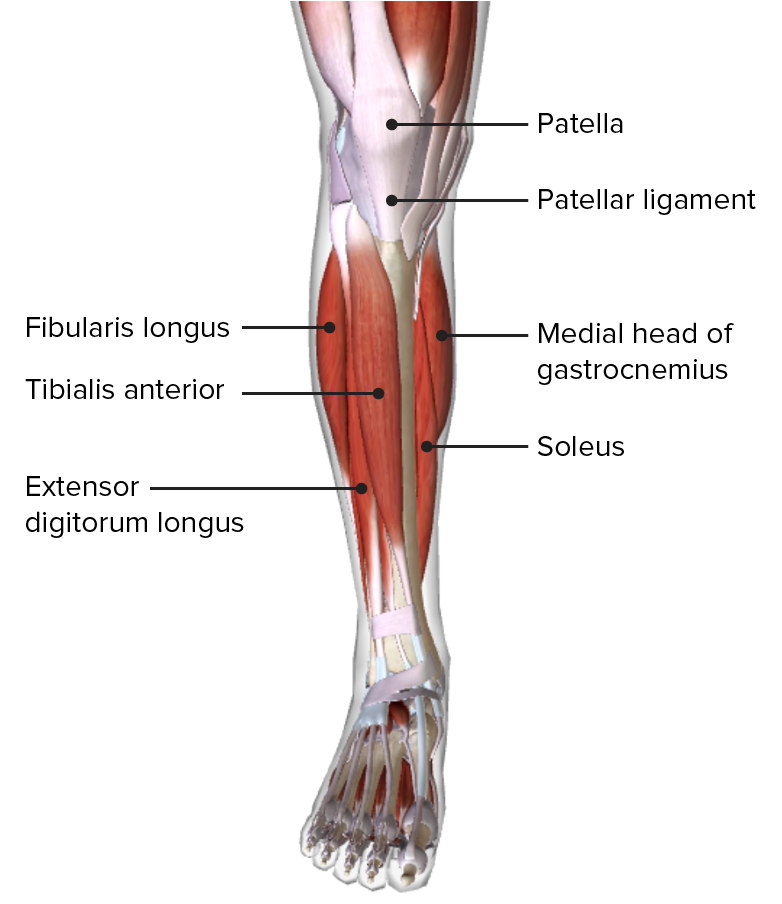
00:00 Let’s move on to the lateral compartment now, and the lateral compartment contains two muscles, and these are fibula muscles. 00:10 The lateral compartment, which we can see here, contains fibularis longus which has a long tendon and is more superficially located, and fibularis brevis which is deeper to fibularis longus and contains a shorter tendon. So we have fibularis longus. It originates from the head and proximal two-thirds of the lateral fibula, and it passes through the first metatarsal and medial cuneiform. Fibularis brevis is coming from the mid-portion of the lateral fibula, and it passes to the base of the fifth metatarsal. So what we can see is that the tendon of fibularis longus actually passes deep underneath the foot. And we’ll see this in a later lecture. We’ll see the pathway of this tendon. Here, we’ve got the fifth metatarsal here where fibularis brevis is attaching to. But actually, fibularis longus passes underneath the foot to attach to the base of the first metatarsal. 01:14 Contractions of these muscles support eversion. So they evert the foot. They can also assist in plantar flexion, but this is quite weak. The muscles in the lateral compartment are supplied by the superficial fibular nerve. We saw the muscles in the anterior compartment are supplied by the deep fibular nerve while these in the lateral compartment are supplied by the superficial fibular nerve. 01:43 And the superficial and the deep fibular nerves come away from the common fibula. If you remember, the common fibula is a branch that’s coming away from the sciatic. And this split superficial to deep occurs at the neck of the fibula. So it can be prone to damage because this is quite a superficial landmark. So here we can see we have the lateral compartments of the leg, and we’ve also got a close-up here of the foot. We can see the lateral aspect of the foot. We can see, again, we’ve got tibialis anterior, we’ve got extensor digitorum longus, and we’ve got extensor hallucis longus, these muscles from the anterior compartment. 02:26 We can also see running in the anterior compartment here, we’ve got that fibularis tertius tendon. 02:32 And these are running underneath the extensor retinaculum, the Y-shaped extensor retinaculum, the inferior and the superior parts of it. We can also see now on this lateral compartment, we have fibularis longus and we have fibularis brevis. We can see these some important evertors of the foot, and they’re attaching to the base of the fifth metatarsal of your fibularis brevis, and going under the foot to attach to the base of the first metatarsal of your fibularis longus. These are going to be supplied by those superficial fibular nerves, and also perforating branches of the anterior tibial artery. And we’ll look at this in a later lecture. We’ll look at a detailed review of the blood supply in a later lecture. 03:19 The fibular muscles also have a retinacula that helps to hold them in place, the fibular retinacula. 03:27 We have superior and inferior ones. We can see that the tendons of fibularis longus, we can see running down here, and fibularis brevis running down here, are running posterior to the lateral malleolus as they enter the foot deep to this fibular retinaculum. 03:47 We can see we have two parts to it. We have a superior one, we can see here, running from the lateral malleolus to the calcaneus. And we can see an inferior portion which is the continuation of the inferior extensor retinaculum. So we can see them here in greater detail on this lateral view of the foot. We can see the tendons, fibularis longus and fibularis brevis running down in this direction as they’re running posterior to the lateral malleolus. 04:17 We can see we have this superior one here and we have the inferior portion here. And these are holding the tendons tight against the lateral aspect of the foot.
About the Lecture
The lecture Lateral Compartment – Anatomy of the Leg by James Pickering, PhD is from the course Lower Limb Anatomy [Archive].
Included Quiz Questions
Where does the fibularis longus muscle originate?
- The head of the lateral fibula
- The base of the 1st metatarsal
- The base of the 5th metatarsal
- The medial cuneiform
- The middle of the lateral fibula
What movement does the contraction of the fibularis longus primarily result in?
- Eversion
- Extension
- Dorsiflexion
- Flexion
- Plantar flexion
What shape is the inferior extensor retinaculum?
- Y-shaped
- A thick, circular band
- W-shaped
- C-shaped
- V-shaped
What is the relationship of the peroneus brevis tendon to the lateral malleolus?
- Posterior
- Superior
- Deep
- Superficial
- Anterior
Customer reviews
5,0 of 5 stars
| 5 Stars |
|
5 |
| 4 Stars |
|
0 |
| 3 Stars |
|
0 |
| 2 Stars |
|
0 |
| 1 Star |
|
0 |