Playlist
Show Playlist
Hide Playlist
Large Cell Carcinoma
-
Slides PulmonaryNeoplasia RespiratoryPathology.pdf
-
Download Lecture Overview
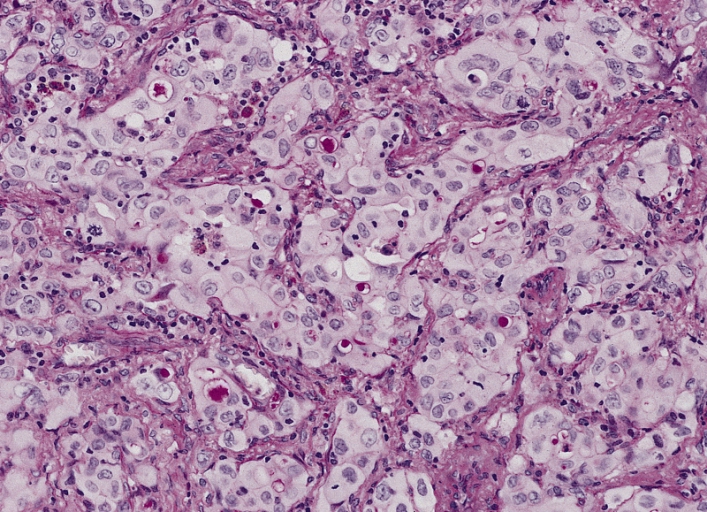
00:01 Now, we go to another one. This is large cell. This is a little scary. And the reason I say that, you will see. Peripherally located, so now we have two peripherally located. 00:10 The one that is most common. Say that you are running out of time and you have really a peripherally located nodule. One, away from the mediastinum. All you do real quick, is take a look. Well, is this a patient that is a female, is a non-smoker? Adenocarcinoma. I’m sorry, what? Non-smoker, female, peripherally located, adenocarcinoma. 00:31 Go with things that are most common, if you’re running out of time. 00:33 Okay, so with peripherally located nodule. 1: highly anaplastic, undifferentiated. So, that means that it has a really poor prognosis. Is less responsive to chemotherapy, removed surgically. Large anaplastic. Couple of other things here, histology – pleomorphic and may secrete βhCG. You hear a serum test with βhCG, hear about anaplastic. No doubt, peripherally located, large cell. Adenocarcinoma, female, non-smoker, peripherally located, then you know that one. Do not forget about the in-situ please, in adenocarcinoma.
About the Lecture
The lecture Large Cell Carcinoma by Carlo Raj, MD is from the course Lung Cancer .
Included Quiz Questions
Which of the following hormones/mediators may be inappropriately secreted in patients with large cell carcinoma?
- Beta-hCG
- ACTH
- ADH
- T4
- PTHrp
What is the first-line treatment for a patient with large cell carcinoma?
- Surgical removal
- Chemotherapy
- Surgical removal followed by chemotherapy
- Radiotherapy followed by chemotherapy
- Radiotherapy
Which of the following findings on histology best describes the appearance of large cell carcinoma?
- Pleomorphic giant cells, highly anaplastic and undifferentiated
- Keratin pearls and intercellular bridges
- Multinucleated giant cells
- Tall columnar cells with intact outer membrane
- Tall columnar cells and mucin+ staining
Customer reviews
5,0 of 5 stars
| 5 Stars |
|
5 |
| 4 Stars |
|
0 |
| 3 Stars |
|
0 |
| 2 Stars |
|
0 |
| 1 Star |
|
0 |