Playlist
Show Playlist
Hide Playlist
Ketone Body Metabolism
-
Slides CitricAcidCycle.pdf
-
Reference List Biochemistry.pdf
-
Download Lecture Overview
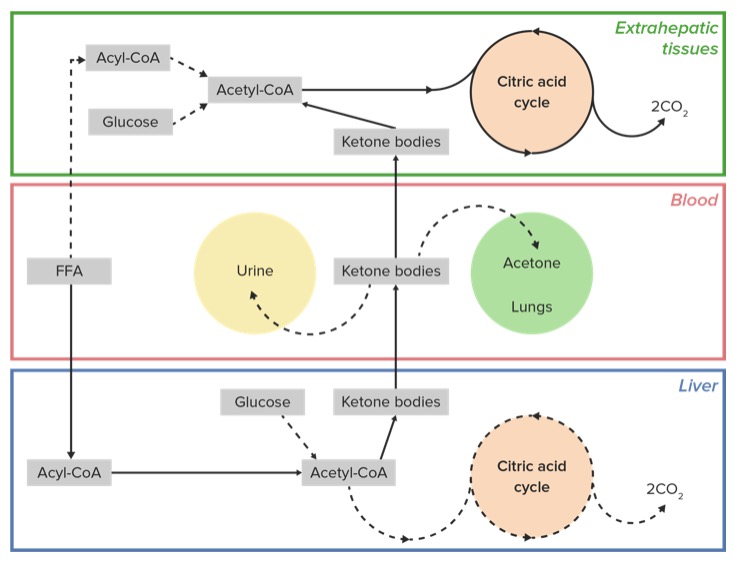
00:01 So as I noted earlier, animals have a bit of a dilemma. 00:04 They have a lot of energy stored in the form of fat but they can’t use that fat to directly make glucose. 00:11 And that’s because the breakdown of fat yields fatty acids and the breakdown of fatty acids yields only acetyl-CoA in addition to some glycerol. 00:20 Glycerol can be made into glucose but glycerol has a fairly minor component of fat. 00:26 Most of the energy of fat is in the fatty acids and cannot be made, the acetyl-CoA cannot be made in to glucose. 00:33 Well, glucose is the most important energy source in the cell and it’s used and maintained in a fairly constant level in the body. 00:41 When glucose concentrations fall low, the body needs, in animals, needs to have some sort of a back up source of energy for quick energy release. 00:51 There is a way that animals can use the energy of fatty acids to make quick energy. 00:58 Not to make glucose, but rather to make molecules or ketone bodies. 01:02 And that’s what I’m gonna talk about here. 01:04 Ketone bodies are made starting with acetyl-CoA molecules. 01:09 So we can see the process here with the joining of two acetyl-CoAs. 01:13 The joining of these is catalyzed by the enzyme thiolase, Which is also an enzyme that’s involved in fatty acid oxidation. 01:20 In this process, one molecule of coenzyme A is released in a four carbon molecule called acetoacetyl-CoA is produced as you can see here. 01:31 In the next step of the process, a third molecule of acetyl-CoA is added with release of one of the molecules of CoA, by the enzyme catalyzed by the enzyme HMG-CoA synthase to produce a molecule called Beta-hydroxy-Beta-menthylglutaryl CoA, long mouthful of the name, more commonly called HMG-CoA. 01:55 As we’ll see that molecule has some other importance in just the moment. 01:59 HMG-CoA is cut by the enzyme HMG-CoA lyase splitting out acetyl-CoA to form the first ketone body known as acetoacetate. 02:11 It’s a four carbon molecule as you can see here. 02:14 Now acetoacetate is relatively unstable and so the body will often convert to acetoacetate into a molecule known as Beta-hydroxybutyrate catalyzed by the enzyme Beta-hydroxybutyrate dehydrogenase as you can see here. 02:29 The Beta-hydroxybutyrate is more stable and travels in the blood more readily. 02:34 Acetoacetate on the other hand can readily non-enzymatically be decarboxylated to form the molecule acetone. 02:44 Now HMG-CoA, as I noted, is a very important molecule and this molecule reaction is shown here to make this molecule is important, because not only can HMG-CoA be used to make ketone bodies, it can also be used to make molecule known as cholesterol. 03:02 And so HMG-CoA is therefore a branch point in the synthesis of ketone bodies and ultimately in the synthesis of cholesterol. 03:11 In this side of lectures, I’ve talked about metabolism of pyruvate, we have metabolism of citric acid cycle, the glyoxylate cycle and ultimately talking about the ketone bodies. 03:22 And in each of these processes, the important molecule, acetyl-CoA, plays a central role and we can see the importance of this molecule in the overall metabolism in the cell.
About the Lecture
The lecture Ketone Body Metabolism by Kevin Ahern, PhD is from the course Carbohydrate Metabolism.
Included Quiz Questions
Which of the following molecules acts as a branch point between the synthesis of ketone bodies and cholesterol in animal bodies?
- β-hydroxy-β-methylglutaryl-CoA
- Acetoacetyl-CoA
- Acetoacetate
- D-β-hydroxybutyrate
- Mevalonate
Which of the following enzymes is not a part of ketone body metabolism?
- FBPase
- Thiolase
- HMG-CoA synthetase
- HMG-CoA lyase
- β-hydroxybutyrate dehydrogenase
Which of the following statements is TRUE about thiolase?
- It catalyzes the formation of acetoacetyl-CoA from two acetyl-CoA molecules.
- It catalyzes the removal of CoA-SH2.
- It requires cAMP.
- It is important in fatty acid synthesis.
Customer reviews
5,0 of 5 stars
| 5 Stars |
|
2 |
| 4 Stars |
|
0 |
| 3 Stars |
|
0 |
| 2 Stars |
|
0 |
| 1 Star |
|
0 |
So good explications with a nice and simple way . I really appreciate your effort .
This guy just knows his stuff, on point even with the speed of his speech he has mastered his slides. I almost got scared with the previous lecture in genetics but he managed to bring me back home. Very knowledgeable keep up the good work and add more clinical correlations.