Playlist
Show Playlist
Hide Playlist
Insulin: Metabolic Effects and Counterregulatory Hormones
-
Slides Endocrine Pancreas Endocrine System.pdf
-
Download Lecture Overview
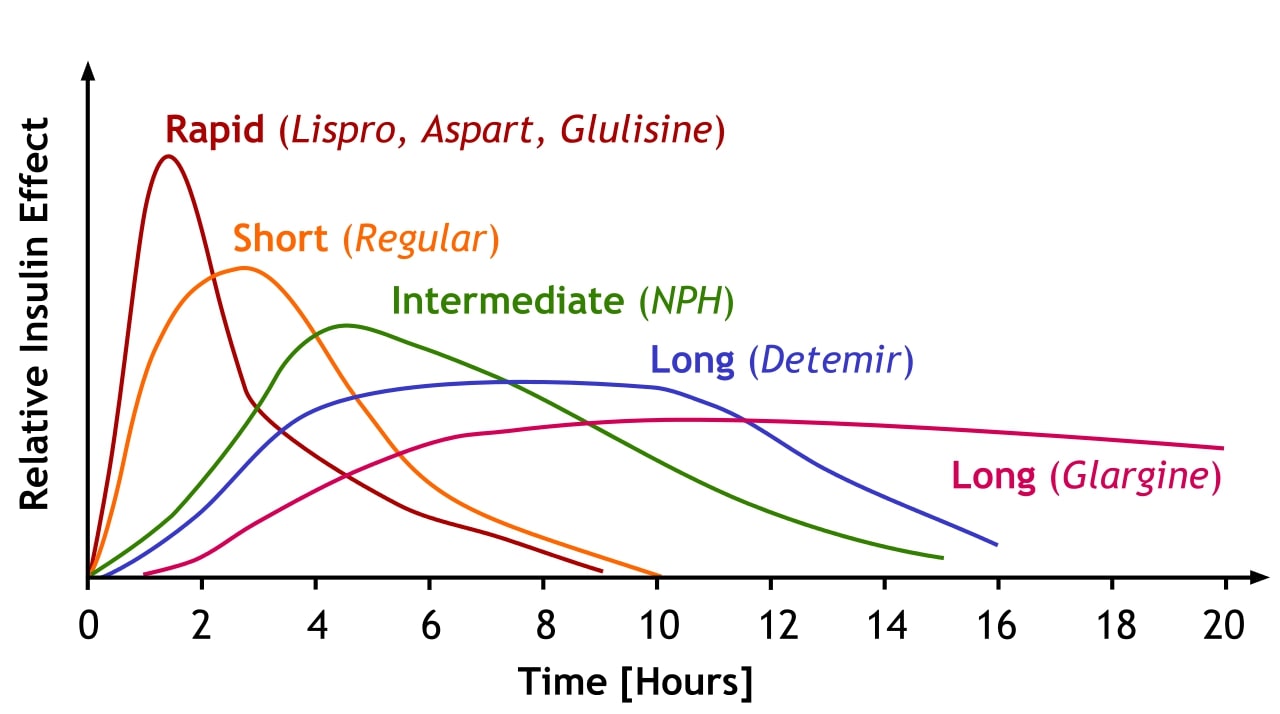
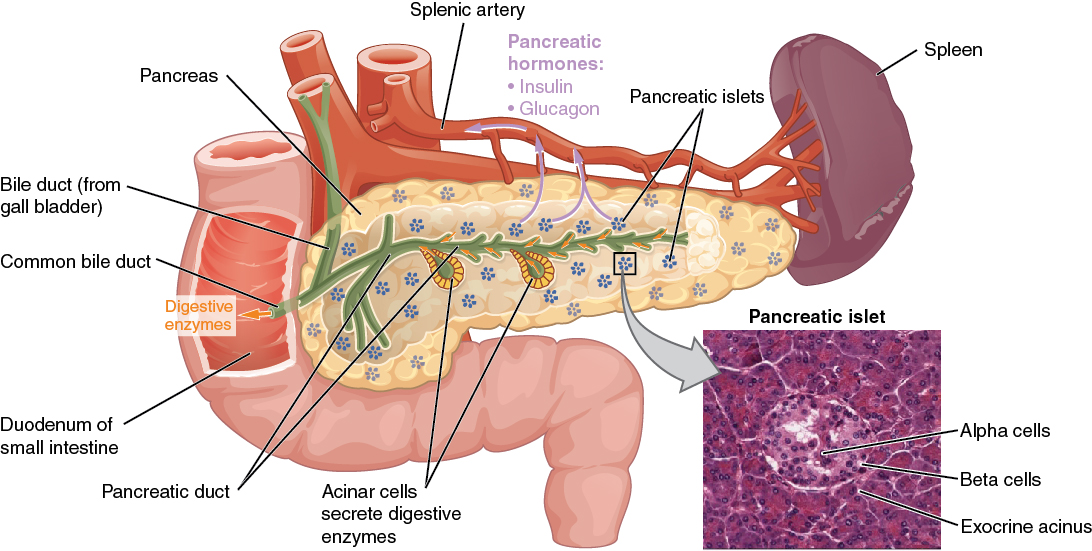
00:00 Insulin counter-regulatory hormones. 00:05 Counter-regulatory hormones now that's a mouthful isn't it. 00:09 Think about a counter-regulatory hormone as being the opposite of effect of what happens with insulin. 00:16 Though insulin does one thing if the opposite thing happens that's kind a regulatory. 00:22 So catecholamine is one of those items that can cause counter-regulatory response with insulin. 00:29 What are your catecholamines? Epinephrine, norepinephrine. 00:33 This causes glycogenolysis. 00:35 So this is the breakdown of glycogen which is the opposite of what insulin does. 00:39 Insulin causes gluconeogenesis which is making new glycogen. 00:41 Catecholamines also cause the lipolysis. 00:47 So lipolysis and increase in plasma lactate these are the opposite of what insulin would do. 00:56 If we look at our glucocorticoids -- and remember one is cortisol. 01:02 Cortisol causes effects in which you get breakdown of protein in muscle, in the liver cell, it mobilizes free fatty acids from adipose tissue. 01:14 These are all opposite effects. 01:17 They are catabolic effects while insulin does anabolic effects. 01:24 The other thing that glucocorticoids do is cause gluconeogenesis rather than glycolysis. 01:29 Growth hormones also causes glypolysis, gluconeogenesis, and it decreases glucose uptake by muscle cells or myocytes. 01:42 Those again are all things that will go in opposition to what insulin is trying to do. 01:49 So when you think about, you have to think about what is the blood glucose level, what are all those things that are stimulating it. 01:57 But then you also have to account for what are all the different hormones working against it. 02:04 Like catecholamines, glucocorticoids and growth hormone. 02:09 If you can maintain blood glucose within this level, of about 60 to 100 milligrams, you can have an optimal delivery of glucose to the brain. 02:22 This is helpful in times of trying to stave off hypoglycemia. 02:26 And maybe we've all experience this one time or another, when you've been really light headed because you haven't eaten enough glucose. 02:34 Hyperglycemia is major health issue. 02:36 Specially if it' chronic hyperglycemia. 02:38 You can have small times in which you're blood glucose is above normal. 02:48 That's okay. 02:49 You're kidneys will take care of it by filtering out that excess glucose and you'll urinate it out. 02:55 But if you have high blood glucose levels for long periods of time, such as those that have diabetes. 03:03 This can be very problematic to a number of basal membranes such as blood vessels as well as even to nerves. 03:12 Damaging blood vessels and nerves can cause very big problems with the circulation and your ability to sense the external environment. 03:23 In fact renal function is another thing that is compromised to a great degree if a person has hyperglycemia for long periods of time.
About the Lecture
The lecture Insulin: Metabolic Effects and Counterregulatory Hormones by Thad Wilson, PhD is from the course Endocrine Physiology.
Included Quiz Questions
Growth hormone facilitates which of the below metabolic processes?
- Lipolysis
- Glycolysis
- Glycogenolysis
- Glucose uptake
Which of the following is an insulin counter-regulatory hormone?
- Epinephrine
- Serotonin
- Acetylcholine
- Dopamine
- L-DOPA
What is the normal fasting glucose level range?
- 60-100 mg/dl
- 20-25 mg/dl
- 25-50 mg/dl
- 100-120 mg/dl
- 120-160 mg/dl
Customer reviews
5,0 of 5 stars
| 5 Stars |
|
5 |
| 4 Stars |
|
0 |
| 3 Stars |
|
0 |
| 2 Stars |
|
0 |
| 1 Star |
|
0 |