Playlist
Show Playlist
Hide Playlist
Hyperthyroidism – Summary
-
Slides Thyroid Disease.pdf
-
Reference List Endocrinology.pdf
-
Reference List Thyroid Disorders.pdf
-
Download Lecture Overview
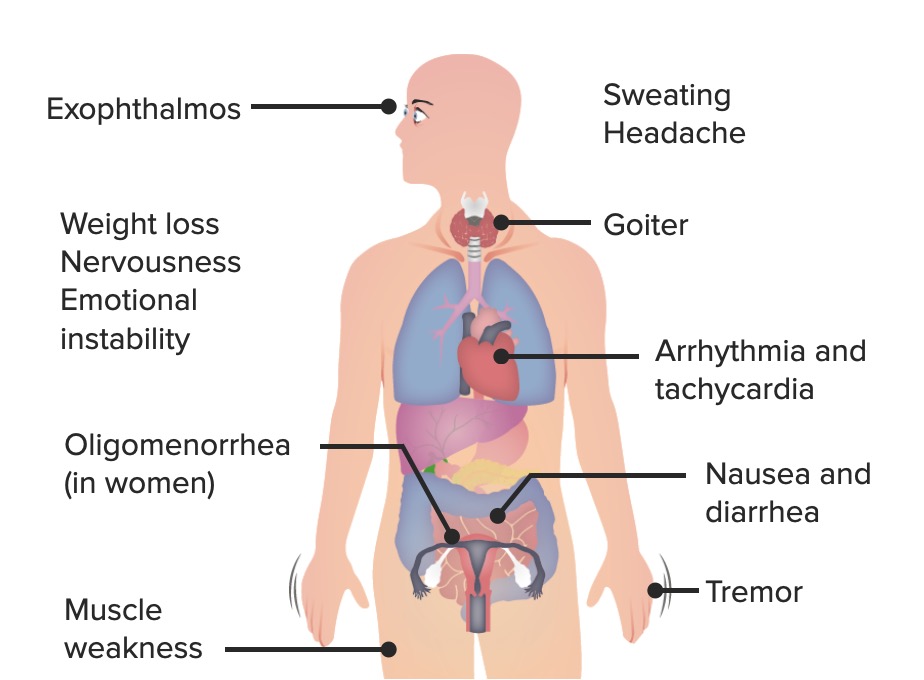
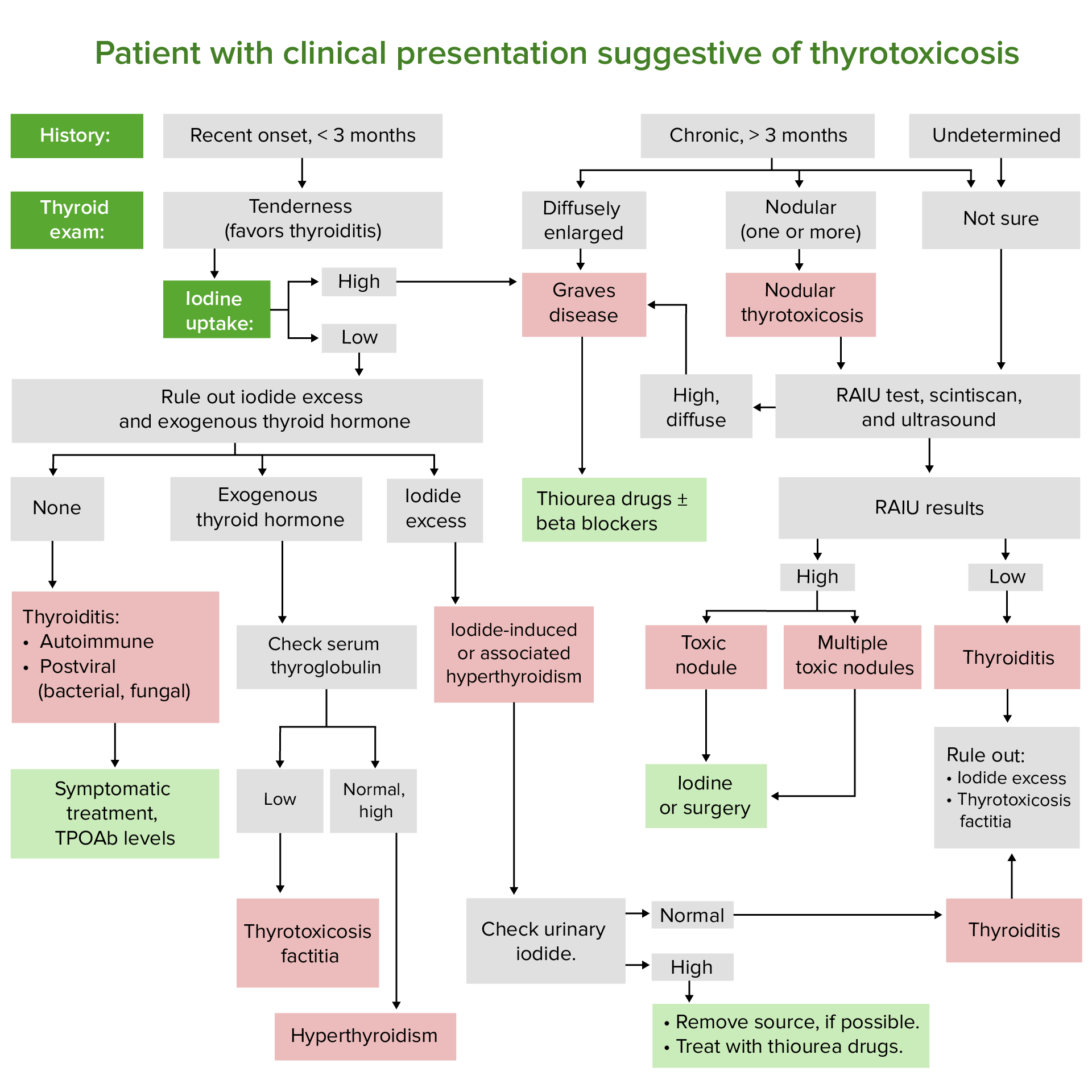
00:01 Let's revise the primary and secondary hyperthyroidism syndromes. 00:05 Graves' disease will give you the classic appearance of low TSH, high T4 and/or high T3. 00:13 Key testing that will help differentiate it is the presence of thyroid stimulating immunoglobulins and a diffuse uptake on radioactive iodine scan. 00:24 The next condition is toxic multinodular goiter. 00:27 Here the pattern of thyroid test is very similar to Graves' disease but you can differentiate it clinically but also based on the appearance of radioactive iodine uptake scanning where one see would multiple nodules with increased uptake. 00:41 In the case of a toxic adenoma, again, thyroid hormone evalualtion of the serum will be similar but radioactive iodine scanning will reveal a single area of increased uptake over the single toxic adenoma. 00:55 In subacute thyroiditis again, TSH is low, free T4 and T3 are elevated but radioactive iodine scan shows lows uptake, usually less that 10%. 01:06 And you may also have a negative TPO antibody to differentiate it from Hashimoto's thyroiditis. 01:13 And then finally, the rare condition of secondary hyperthyroidism usually caused by TSH-secreting adenoma. 01:21 Your TSH here will be normal or high in conjunction with elevated T4 and T3. 01:27 Here, radioactive iodine scanning is unhelpful and an MRI of the brain is usually required to evaluate for a pituitary mass. 01:37 Let's talk about subclinical hyperthyroidism. 01:40 Here, TSH is low with normal T4 and T3. 01:44 Patients are mostly asymptomatic or in some cases mildly thyrotoxic. 01:50 Repeat assessment of thyroid function 6-12 weeks after diagnosis is required. 01:55 Values tend to normalize in thirty percent of patients without any action. 02:01 Treatment only takes place when the thyroid stimulating hormone level is less than 0.1 milliunit per liter.
About the Lecture
The lecture Hyperthyroidism – Summary by Michael Lazarus, MD is from the course Thyroid Disorders. It contains the following chapters:
- Hyperthyroid Disorders – Summary
- Subclinical Hyperthyroidism
Included Quiz Questions
Which of the following laboratory and diagnostic tests best corresponds with the diagnosis?
- TSH low | T3/T4 elevated | RAIU diffusely positive: Graves' disease
- TSH low | T3/T4 elevated | RAIU low uptake of < 10%: toxic multinodular goiter
- TSH low | T3/T4 elevated | RAIU single area with increased uptake: subacute thyroiditis
- TSH low | T3/T4 elevated | MRI shows pituitary mass: toxic adenoma
- TSH low | T3/T4 elevated | RAIU normal: Graves' disease
At what point should treatment be initiated for subclinical hyperthyroidism?
- TSH < 0.1 mU/L
- TSH lower than normal range, with elevated T3 and T4
- TSH > 5.0 mU/L
- RAIU with < 10% uptake
- TSH lower than normal range, with elevated T3 and normal T4
Customer reviews
5,0 of 5 stars
| 5 Stars |
|
5 |
| 4 Stars |
|
0 |
| 3 Stars |
|
0 |
| 2 Stars |
|
0 |
| 1 Star |
|
0 |