Playlist
Show Playlist
Hide Playlist
Genital Warts (Condyloma Acuminatum): Pathology, Signs & Symptoms
-
Slides GenitalWarts InfectiousDiseases.pdf
-
Reference List Infectious Diseases.pdf
-
Download Lecture Overview
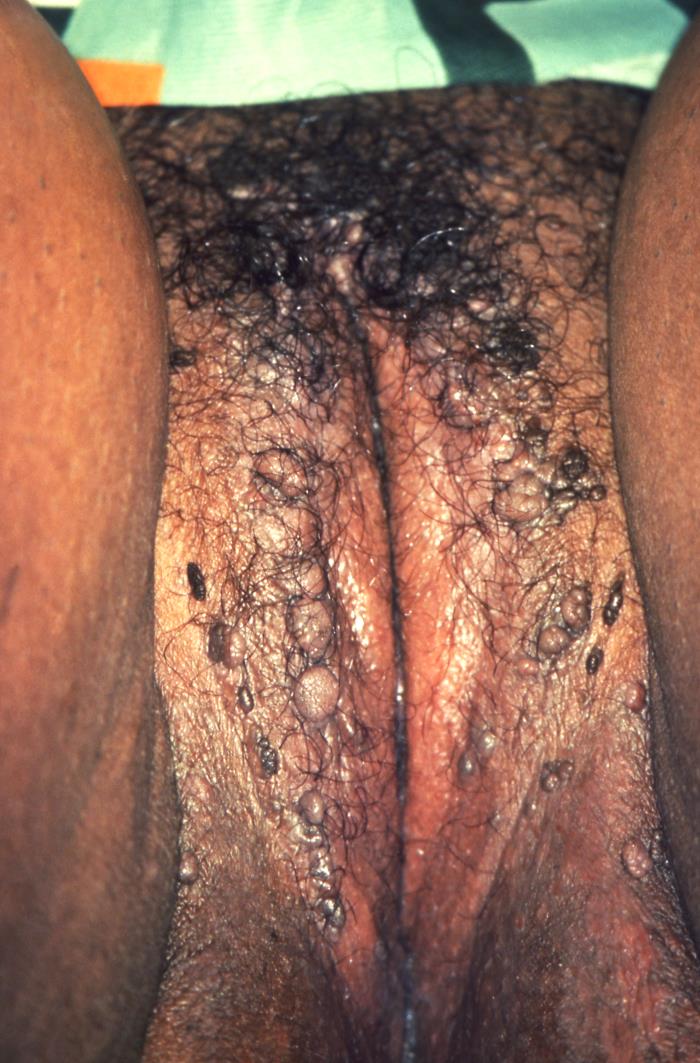
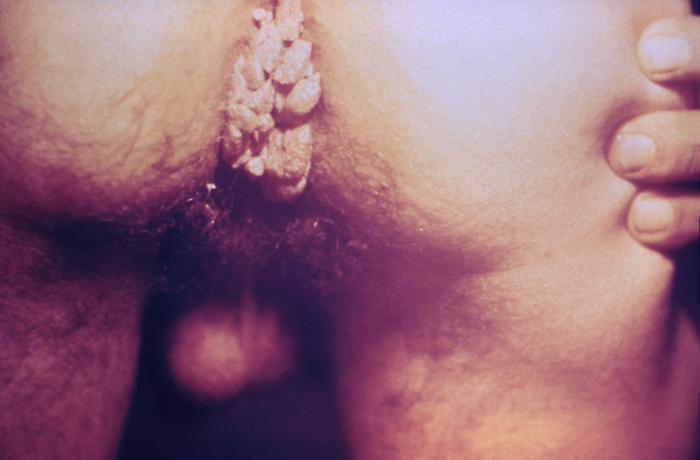
00:02 Genital warts develop in about two-thirds of sexual contacts of persons who have genital warts, so it's really highly contagious. 00:11 And what happens is the virus enters through the skin, after some break in the skin, and gets into the basal layers of the epidermis. 00:24 And there, the viral capsid modifies its conformation and enters the cell. 00:31 And so, I think you can see that problems develop in an upward direction from the basal layer. 00:39 So basal layer infected initially, and then the virus is moved to the surface with the normal proliferation of squamous epithelium. 00:50 So the virus will replicate, and then finally release the live and infectious virions from the outermost portion of the skin, which is why it is so contagious. 01:04 So all epidermal layers proliferate leading to something called acanthosis, which is simply hyperplasia of the squamous cell epithelium. 01:17 Also, parakeratosis, which is keratinization of the surface cells with retention of nuclei in the stratum corneum. 01:28 Those nuclei are not supposed to be there. 01:31 Hyperkeratosis, which produces this thickened appearance. 01:37 And then some cells transform into koilocytes, and what’s showing here is these vacuolated cells, which are called koilocytes. 01:49 That’s the hallmark pathologically of a HPV infection. 01:54 So clinically, these warts are flesh-colored to gray. 02:00 They’re hyperkeratotic and exophytic. 02:04 Exophytic means that they are proliferating out to the surface. 02:10 They’re normally sessile on the skin, which means they’re flat and attached, or they can be attached by a short, broad peduncle or stalk. 02:20 In uncircumcised men, they involve, as this picture shows, the preputial cavity 85 to 95 percent of the time. 02:31 In the circumcised men, the penile shaft is involved. 02:35 And among men who have sex with men, we get these warts in the anal mucosa. 02:42 Women get this in the posterior introitus, the labia, or clitoris. 02:48 Now, most of these warts are asymptomatic. 02:51 But occasionally, the patient will complain of itching, burning, pain, or even tenderness, but that’s not frequent.
About the Lecture
The lecture Genital Warts (Condyloma Acuminatum): Pathology, Signs & Symptoms by John Fisher, MD is from the course Genital and Sexually Transmitted Infections.
Included Quiz Questions
Which of the following is the main epithelial layer where human papillomavirus replicates?
- Basal layer
- Granular layer
- Keratin layer
- Stratum corneum
- Stratum lucidum
Which of the following best describes parakeratosis?
- The retention of nuclei in the stratum corneum
- The retention of nuclei in the stratum lucidum
- The loss of nuclei in the keratin layer
- The loss of nuclei in the basal layer
- The loss of nuclei in the granular layer
Which of the following histologic findings is a hallmark of cytopathic changes of human papilloma virus infection?
- Koilocytes
- Thickening of the stratum corneum
- Nucleated keratocytes
- Acanthosis nigricans
- Hyperkeratosis
Customer reviews
5,0 of 5 stars
| 5 Stars |
|
1 |
| 4 Stars |
|
0 |
| 3 Stars |
|
0 |
| 2 Stars |
|
0 |
| 1 Star |
|
0 |
I watched most of the STD lectures. They are well explained and I really appreciate that. THANK YOU