Playlist
Show Playlist
Hide Playlist
Genital Herpes: Management and Etiology
-
Slides GenitalHerpes InfectiousDiseases.pdf
-
Reference List Infectious Diseases.pdf
-
Download Lecture Overview
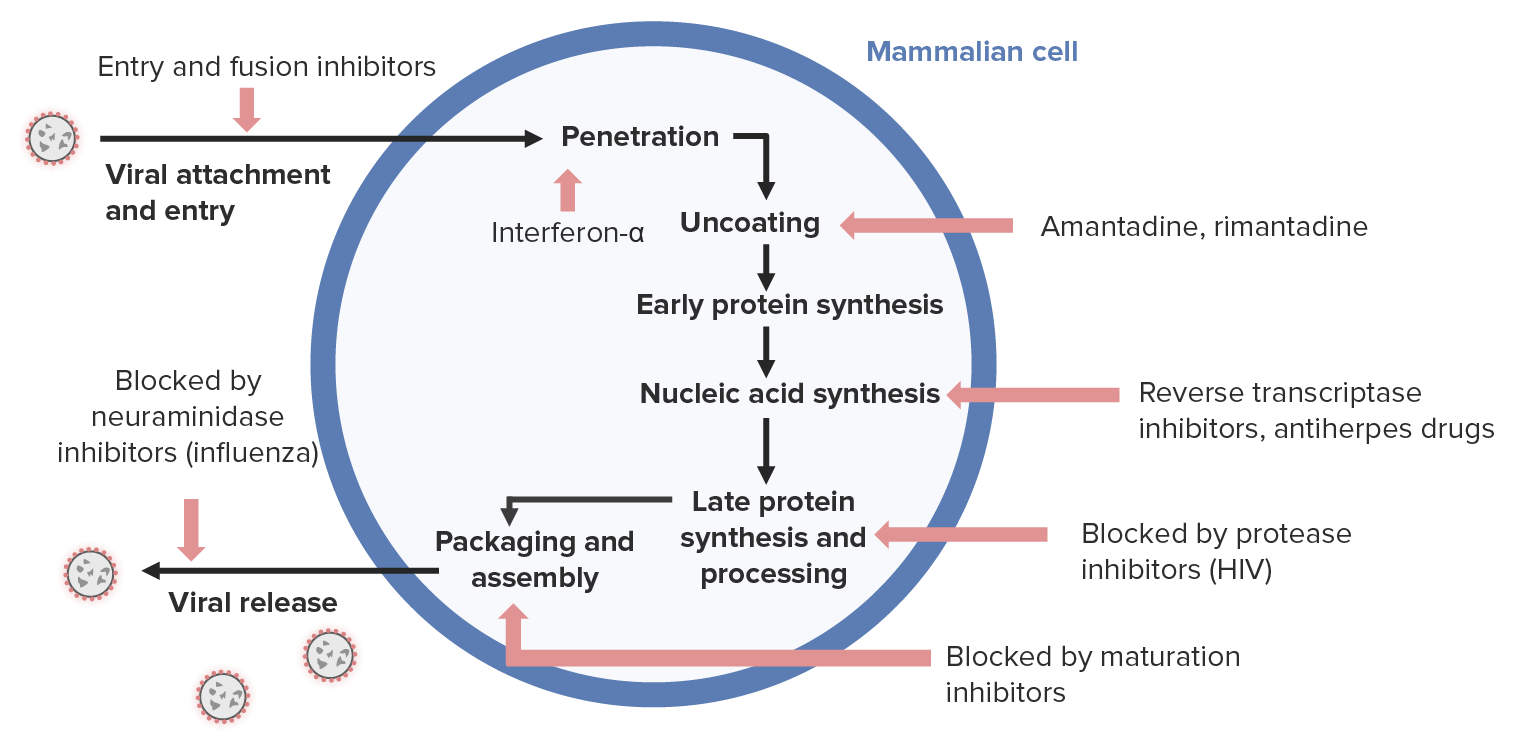
00:01 So turning now to the treatment of herpes simplex infections, let’s talk about how you treat the first clinical episode. 00:11 And the duration of that therapy is 7 to 10 days, and you can use either acyclovir, valacyclovir, or famciclovir. 00:23 These agents work by being chain terminators. 00:28 So as the herpes virus is trying to make more DNA, these are false basis so the chain of DNA is broken. 00:39 If you're talking about recurrent episodes, the duration of treatment is variable, but you use the same agents for 2 to 5 days, 3 to 5 days, or 1 to 5 days. 00:55 Now, how do you manage recurrences? First of all, you have to define what’s frequent. 01:02 And if a patient has, for example, one or two episodes a year, then it’s probably prudent to treat those individual episodes and not use any kind of suppressive therapy. 01:17 So if you have a professional person who’s job is interfered by the number of recurrences, you might consider suppressive therapy, and you do that with acyclovir orally twice a day, and the efficacy has been established for 6 years, or you could use valacyclovir. 01:44 Now, the difference between valacyclovir and acyclovir is, valacyclovir is the valine ester of acyclovir. 01:53 In other words, when you take that medication, it is better absorbed. 01:57 Once in the system, it becomes acyclovir. 02:01 So it’s got better bioavailability, and as you can imagine, it’s much more expensive. 02:09 Or you could use 1 gram of valacyclovir once a day, famciclovir – twice a day. 02:17 Now what about counseling people with genital herpes? Well, their sex partners should certainly be informed that they have had herpes. 02:31 Because of asymptomatic shedding of the virus, you could infect the person when you, yourself, were not symptomatic and you can actually give a person herpes simplex genitalis during asymptomatic periods. 02:49 Certainly and obviously, persons with genital herpes should remain abstinent when any lesions or any prodromal symptoms are still present. 03:01 And that concludes my discussion of herpes simplex genitalis.
About the Lecture
The lecture Genital Herpes: Management and Etiology by John Fisher, MD is from the course Genital and Sexually Transmitted Infections. It contains the following chapters:
- Genital Herpes – Management
- Genital Herpes – Etiology
Included Quiz Questions
Which of the following is the most appropriate antiviral therapy of a first episode of genital herpes simplex virus infection?
- A 10-day course of oral acyclovir
- A 30-day course of oral valacyclovir
- A single dose of oral valacyclovir
- A single dose of oral acyclovir
- Antiviral therapy is not recommended.
Which of the following statements regarding the transmission of the herpes simplex virus is TRUE?
- Transmission can occur when symptoms are absent.
- Viral shedding only occurs with active lesions.
- Viral shedding is highest in patients with prodromal symptoms.
- The majority of transmissions occur in patients with HIV infection.
Which of the following treatment options is most appropriate in a currently asymptomatic patient who has ≥6 recurrent severe clinical episodes of genital herpes virus infection per year?
- Acyclovir: 400 mg twice daily
- Acyclovir: 400 mg daily
- Famciclovir: 500 mg twice daily
- Famciclovir: 500 mg daily
- No antiviral treatment is recommended at this point in time.
Customer reviews
5,0 of 5 stars
| 5 Stars |
|
5 |
| 4 Stars |
|
0 |
| 3 Stars |
|
0 |
| 2 Stars |
|
0 |
| 1 Star |
|
0 |