Playlist
Show Playlist
Hide Playlist
Furuncles and Carbuncles in Darker Skin
-
Slides Furuncles Carbuncles in Darker Skin.pdf
-
Download Lecture Overview
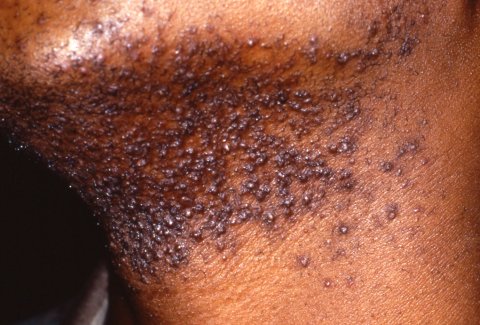
00:02 Welcome to our lecture on Furuncles and Carbuncles. 00:07 What is a furuncle ? The other lay term language for uncle is a boil. 00:11 It's deep infection of a hair follicle. 00:14 And a carbuncle, on the other hand, is clusters of furuncles that are subcutaneously connected. 00:20 So furuncle, it's one boil, and carbuncle is a combination of boils. And this tends to occur deep down in the follicle. 00:30 It's common in adolescence and early adult life, and carbuncles are relatively rare compared to fair angles. 00:38 What are some of the risk factors? Obesity, immunodeficiency, for example, patients who have HIV infection , AIDS, or are on chemotherapy for malignancy and older people. Diabetes mellitus is also a predisposing factor for carbuncles of our ankles. 00:56 Of course smoking and low hemoglobin anemia. 01:00 So what are the etiological agents of these two conditions, it's usually due to staph aureus. 01:07 And of course, methicillin resistant staph aureus is a common finding. Which areas are affected in patients with furuncles or carbuncles: the face, the neck, the axillae, and the buttocks. Now let's focus on the ankle. 01:26 How do we describe it? Clinically, it's a tender red perifollicular swelling, which can lead to a pustule that discharge necrotic tissue and pus. 01:37 And remember, in dark skin, you may not actually appreciate the erythema, or the redness, may lead to a permanent scar after healing. And then again in black patients you may even get post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation that we spoke about. 01:53 So we spoke about the furuncle. 01:56 Now let's move on and talk about furunculosis . 02:00 It's acute and recurrent appearance of multiple furuncles on multiple skin sites. So now you can differentiate between a furuncle, furunculosis and now we're moving on to the third type the carbuncle. 02:15 So how do we define a carbuncle. 02:17 It's a hard, painful red lump about 3 to 10cm in diameter. You can get suppuration, which is pus that is discharged from the multiple follicular orifices. 02:31 It may be associated with malaise, fever, lymphangitis that is inflammation of your lymphatic vessels, and lymphadenitis, which is inflammation and painful lymph nodes. 02:44 The complications include abscesses, cellulitis, post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation, which is unique to dark skin. 02:52 So how do we diagnose these conditions? The clinical history and physical examination findings are important. 03:00 As we have described, a password for microbiological examination is prudent. And this should be sent for microscopy culture and sensitivity. And now looking at the differential diagnosis. 03:14 One of the differential diagnoses is superficial staphylococcal folliculitis. 03:19 Perifollicular swelling not seen unlike in furuncle and carbuncle. The second one is a ruptured epidermoid cyst, which is a sterile, purulent, keratinous material that is seen coming out of an epidermoid cyst. 03:37 You can also confuse it with pharyngula meiosis, but usually here you see larva, but this is not commonly seen. 03:46 Management of these conditions involve incision and drainage of an abscess. Usually MRSA effective antibiotics are recommended as well. 04:00 The antibiotics that are effective against MRSA are tetracyclines and trimethoprim sulfamethoxazole.
About the Lecture
The lecture Furuncles and Carbuncles in Darker Skin by Ncoza Dlova is from the course Bacterial Skin Infections in Patients with Darker Skin.
Included Quiz Questions
What is the key characteristic that differentiates a carbuncle from a furuncle?
- Carbuncles are clusters of furuncles that are subcutaneously connected
- Carbuncles only occur on the face while furuncles affect the trunk
- Furuncles are caused by MRSA while carbuncles are caused by Streptococcus
- Furuncles are deep infections while carbuncles are superficial
- Carbuncles never lead to scarring but furuncles typically do
Which systemic symptom is commonly associated with carbuncles but not typically with simple furuncles?
- Fever and malaise
- Hair loss around the affected area
- Hypertension
- Visual disturbances
- Joint pain in adjacent limbs
Customer reviews
5,0 of 5 stars
| 5 Stars |
|
5 |
| 4 Stars |
|
0 |
| 3 Stars |
|
0 |
| 2 Stars |
|
0 |
| 1 Star |
|
0 |