Playlist
Show Playlist
Hide Playlist
Doppler Ultrasound
-
Slides Intro Imaging Ultrasound.pdf
-
Download Lecture Overview
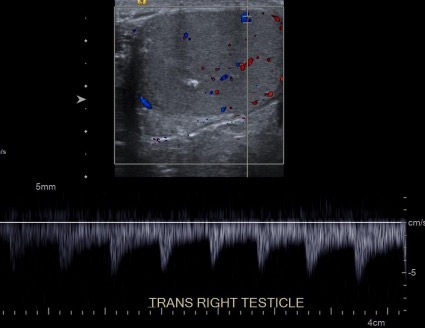
00:01 So you may have heard about the Doppler Effect. 00:03 The Doppler Effect is the change in sound frequency that's based on whether the object creating the sound is approaching or retreating from the object that's capturing the sound. 00:12 Doppler ultrasound is based on the Doppler Effect. 00:15 So it uses this concept to determine whether blood is flowing away from or towards the transducer and the direction of flow is depicted by color. 00:25 Red indicates flow towards the transducer and blue indicates flow away from the transducer and this is usually done by convention. 00:32 This is an example of Doppler ultrasound showing again the flow within the right testicle. 00:39 You can see areas of blue and you can see areas of red demonstrating flow in both directions. 00:45 Spectral Doppler demonstrates both the direction of flow and the waveform and it provides a quantitative assessment of flow. 00:55 So you can see here again of the testicle, you cans see color flow above and then you can see Doppler flow which tells you the waveform of the flow and this looks like it's an arterial waveform with a peak and then a down slope. 01:10 So ultrasound is a very safe diagnostic evaluation and it really doesn't have any know side effects. 01:18 It's not associated with ionizing radiation the way CT and radiography are, it's very small and can be portable, and it's actually very inexpensive. 01:28 It's often used in places where larger equipment is unable to be used. 01:32 It also allows for real-time evaluation using the cine images or the video. 01:37 There are many different uses of ultrasound. 01:41 It's often used to evaluate the gallbladder and the biliary system, the kidneys. 01:45 The scrotum is very well evaluated with ultrasound. 01:49 The female pelvis is a very common area of ultrasound use. 01:52 In pregnancy, ultrasound is actually one of the only things that are used because it doesn't have any radiation and it doesn't really have any side effects. 02:00 It's often used on carotid or extremity vascular ultrasound and is able to take a very good look at the superficial vessels. 02:08 So let's review. 02:12 We've now discussed radiography, CT, and ultrasound. 02:15 Radiography and CT both use ionizing radiation while ultrasound uses acoustic energy and doesn't have the risks associated with ionizing radiation. 02:24 Radiography is inexpensive and ultrasound is actually very inexpensive, even less so than radiography. CT, of the 3, is the more expensive examination. 02:35 Both radiography and ultrasound can be performed portably. 02:39 CT, however, cannot and it comes with a very large machine. 02:42 Radiography can take just a few seconds, CT takes less than minute but it is longer than a radiograph and ultrasound really can take just a few seconds as well but it's very operator dependent so whoever's performing the ultrasound can take as long as they need to evaluate the area of interest. 03:00 Radiography and ultrasound do not use any kind of contrast. 03:06 CT may or may not use contrast, depending on what area is being evaluated.
About the Lecture
The lecture Doppler Ultrasound by Hetal Verma, MD is from the course Introduction to Imaging.
Included Quiz Questions
The Doppler effect can be defined as…?
- …the change in sound frequency based on whether the object creating the sound is approaching or retreating from the object capturing the sound.
- …the change in sound direction based on whether the object capturing the sound is approaching or retreating from the object creating the sound.
- …an abnormally high brightness occurring when sound travels through a medium with an attenuation rate lower than surrounding tissue.
- …it is the attenuation of sound energy as it passes through tissue because parts of it are reflected, scattered, absorbed, refracted or diffracted.
- …the change in sound wave direction on being incident upon a tissue interface at an oblique angle.
A 24 year-old-woman at 16 weeks gestation enters the emergency room complaining of severe pain in the abdomen of sudden onset. She says that the pain started an hour after having lunch and is accompanied by nausea and one episode of vomiting. The patient’s vitals are stable with a temperature of 38° C. The physician suspects a gall bladder pathology and orders an ultrasound imaging of the abdomen as a part of diagnostic evaluation due to its safety. Which factor makes ultrasound the most optimal option for pregnant women?
- No side effects
- Expensive
- Lasts more than an hour
- Ultrasound exposes the patient and fetus to radiation
- Small in size
Which statement regarding imaging techniques is true?
- Radiography and CT both use ionizing radiation.
- CT is less expensive than an x-ray or ultrasound.
- Radiography has more radiation than CT.
- Ultrasound and x-ray machines cannot be transported.
- CT scan machine uses acoustic energy for imaging.
Customer reviews
5,0 of 5 stars
| 5 Stars |
|
1 |
| 4 Stars |
|
0 |
| 3 Stars |
|
0 |
| 2 Stars |
|
0 |
| 1 Star |
|
0 |
Very clear and easy to follow lectures. Elucidates the slides and demonstrates with the pointer.