Playlist
Show Playlist
Hide Playlist
Cholinergic Toxicity, Myasthenic Crisis and Cholinergic Crisis
-
Slides Cholinergic Toxicity Myasthenic Crisis Cholinergic Crisis.pdf
-
Reference List Pharmacology.pdf
-
Download Lecture Overview
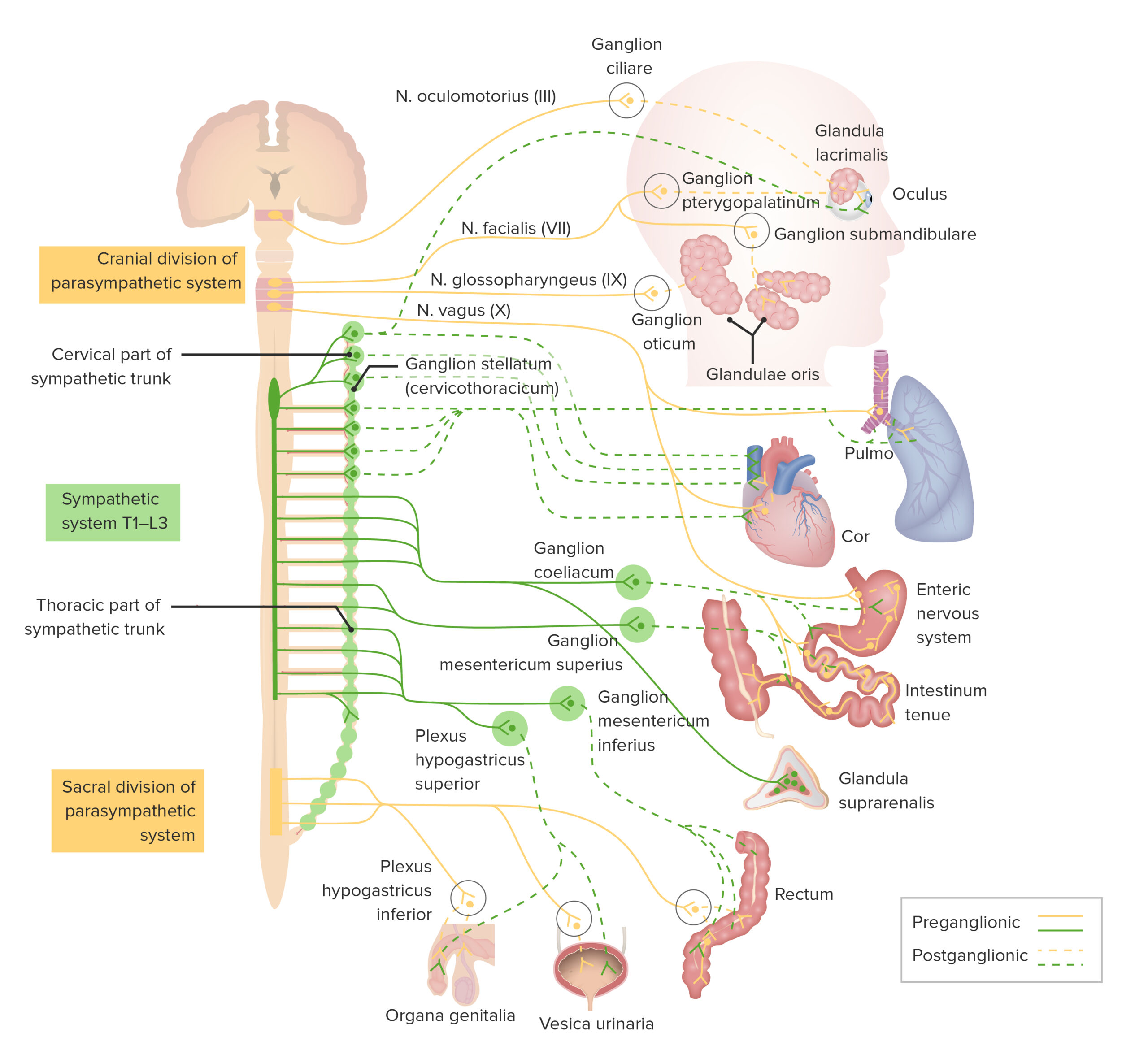
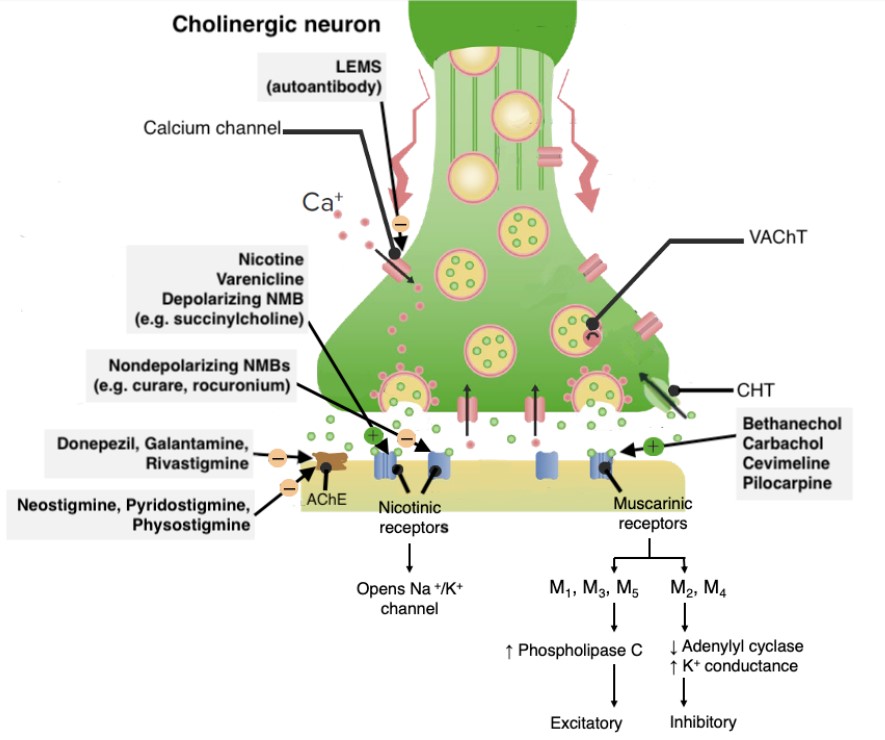
00:01 So let's talk about other issues in cholinomimetic toxicity. Let's talk about nicotine. 00:07 Think about what a person looks like or feels like when they first start smoking. 00:12 First-time smokers who are exposed to new high levels of nicotine can become quite nauseous. 00:19 Obviously you become acclimated to it and you don't feel that way later and you actually become addicted to nicotine. 00:25 Exposure to Malathion and parathion, it really only is relevant at very high doses. 00:30 Remember that these are prodrugs. So, they have to be metabolized to an active state. 00:35 Now that happens much more in insects than it does in humans. 00:39 So, when we talk about general use of Malathion and parathion that's safe for humans. 00:47 But when you get exposed to very toxic levels where you're super concentrated, then you may have toxic levels accumulate in the human. 00:55 Other aspects of cholinomimetic toxicity can be certain medicines like pyridostigmine, neostigmine, physostigmine. Here's an image of pyridostigmine. 01:06 Now, let's look at the differences between myasthenic crisis and a cholinergic crisis. 01:14 They're slightly different. The myasthenic crisis causes destruction of the acetylcholine receptor. 01:21 So there is an increase in heart rate and an increase in blood pressure. 01:26 Bowel and bladder incontinence. 01:29 There's an absent cough reflex and an absent swallow reflex. 01:33 Edrophonium gives temporary relief and the acetyl, that's because it's an acetylcholinesterase inhibitor. 01:41 So there's more acetylcholine in the synaptic cleft that overcomes the lower numbers of the acetylcholine receptors that have been destroyed. 01:51 That's why Edrophonium works in myasthenic crisis. 01:55 Atropine doesn't help these symptoms. Now let's talk about a cholinergic crisis. 02:02 A cholinergic crisis is when you have excess acetylcholine. 02:06 An example is sarin gas. You have a decrease in blood pressure. 02:11 You have abdominal cramps, nausea, vomiting and diarrhea. 02:16 You have blurred vision you have pallor. 02:19 You have some twitching in the face. 02:22 Edrophonium does not help in this case but actually may precipitate either a cholinergic crisis and subacute patients or worsen the cholinergic crisis through an over dosage of the acetylcholine. 02:38 And atropine here will improve symptoms and pralidoxime will counteract the nicotinic effects of muscle weakness and paralysis, by reactivating acetylcholinesterase. 02:48 So you can see the difference between myasthenic crisis and cholinergic crisis. 02:53 The difference is, and the important knowledge that edrophonium works in one and doesn't in another. 02:58 And atropine will work in another and not in one. 03:03 Okay. That's a tough topic, you did well. 03:05 Go write your exam and show them what you know.
About the Lecture
The lecture Cholinergic Toxicity, Myasthenic Crisis and Cholinergic Crisis by Pravin Shukle, MD is from the course ANS - Pharmacology.
Included Quiz Questions
Which drug provides temporary relief during a myasthenic crisis?
- Edrophonium
- Atropine
- Pralidoxime
- Phenylephrine
- Benztropine
Which of the following signs/symptoms is LEAST likely during a cholinergic crisis?
- Urinary retention
- Abdominal cramps
- Facial muscle twitching
- Blurred vision
- Diarrhea
Customer reviews
5,0 of 5 stars
| 5 Stars |
|
1 |
| 4 Stars |
|
0 |
| 3 Stars |
|
0 |
| 2 Stars |
|
0 |
| 1 Star |
|
0 |
Teaches very well, makes everything easy and simple to understand.