Playlist
Show Playlist
Hide Playlist
Cell-mediated Immunity: Chemokines, Tumor Necrosis Factors, and Transforming Growth Factors
-
Slides Cell-Mediated Immunity.pdf
-
Reference List Immune System.pdf
-
Download Lecture Overview
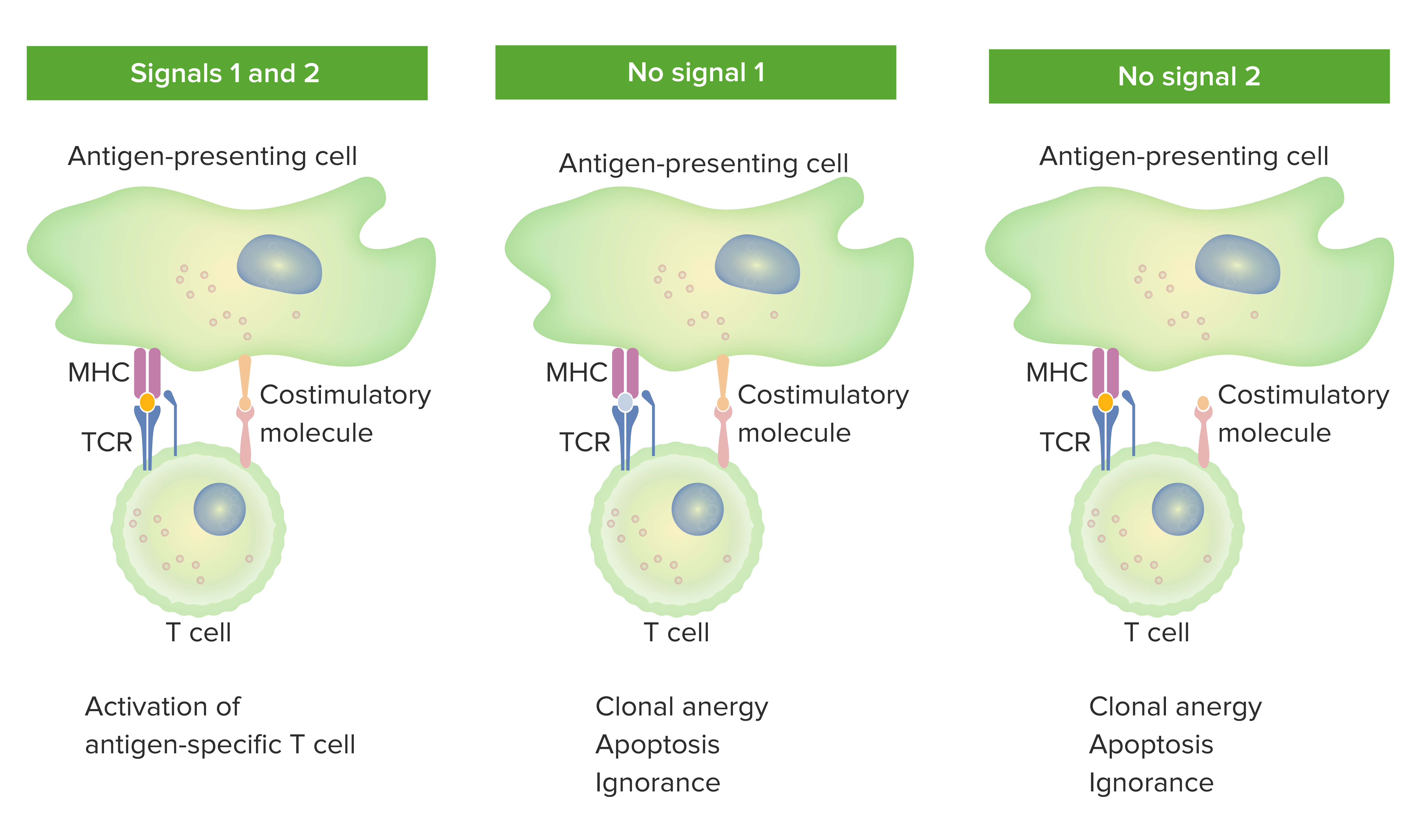
00:01 The chemokines are chemotactic cytokines, but they have multiple other effects as well. 00:07 And they are secreted by many different types of cell. 00:10 There are four families that are grouped according to the arrangement of cysteines in their structure. 00:17 The C family chemokines, an example would be lymphotactin. 00:22 CC family, an example would be RANTES, CXC - interleukin-8. 00:29 And you can see here an example of the fact that things don’t often fit neatly into the little boxes we’d like, because interleukin-8 is both an interleukin, obviously that’s its name, but it’s also a chemokine. 00:41 And then finally the CX3C chemokines, and fractalkine would be an example of that particular family. 00:49 So each family has a number of members and I’m just highlighting one example for each one. 00:57 The tumor necrosis factors, there are two main types - TNF alpha (α) and TNF beta (β) (lymphotoxin). 01:05 This is actually another good example, there are mul-- I’m afraid there are multiple examples in immunology of things that actually, their name isn’t great okay? So you would imagine from the name that these factors are really good at inducing necrotic cell death of tumor cells. 01:25 Well, they can do that, you know. 01:29 But if they were so magnificent at doing that, you’d expect that we’d be using TNF to treat lots and lots of tumors, and that’s simply not the case. 01:38 It’s named because that was the first activity when it was first discovered, it was found that it could cause necrotic cell death of tumors. 01:45 It’s actually better at causing apoptotic cell death of tumors than causing necrosis. 01:49 And in fact, it’s not particularly good at doing either of those things. 01:52 It’s an inflammatory cytokine, that’s what its main function is, to promote inflammation. 01:58 And the two main TNFs, TNFα and TNFβ are produced by multiple cell types including macrophages, monocytes, T-cells, B-cells and natural killer cells. 02:10 And there are many different things that these TNFs do, they can activate macrophages, they’re good an inducing endothelial cell adhesion molecules in acute inflammation, and they’re good at stimulating the production of other cytokines. 02:25 Transforming growth factors; the main one that is of importance in immunology is transforming growth factor β, which is mainly an inhibitory cytokine. 02:38 Secreted by regulatory T-cells and also by monocytes, it inhibits macrophage and dendritic cell activation, and can also inhibit both T and B-lymphocytes.
About the Lecture
The lecture Cell-mediated Immunity: Chemokines, Tumor Necrosis Factors, and Transforming Growth Factors by Peter Delves, PhD is from the course Humoral Immunity and Cell-mediated Immunity. It contains the following chapters:
- Chemokines
- Tumor Necrosis Factors
- Transforming Growth Factors
Included Quiz Questions
All EXCEPT which of the following cells can produce tumor necrosis factor?
- Red blood cells
- Macrophages
- T cells
- B cells
- NK cells
Customer reviews
5,0 of 5 stars
| 5 Stars |
|
5 |
| 4 Stars |
|
0 |
| 3 Stars |
|
0 |
| 2 Stars |
|
0 |
| 1 Star |
|
0 |