Playlist
Show Playlist
Hide Playlist
Cell-mediated Immunity: Introduction
-
Slides Cell-Mediated Immunity.pdf
-
Reference List Immune System.pdf
-
Download Lecture Overview
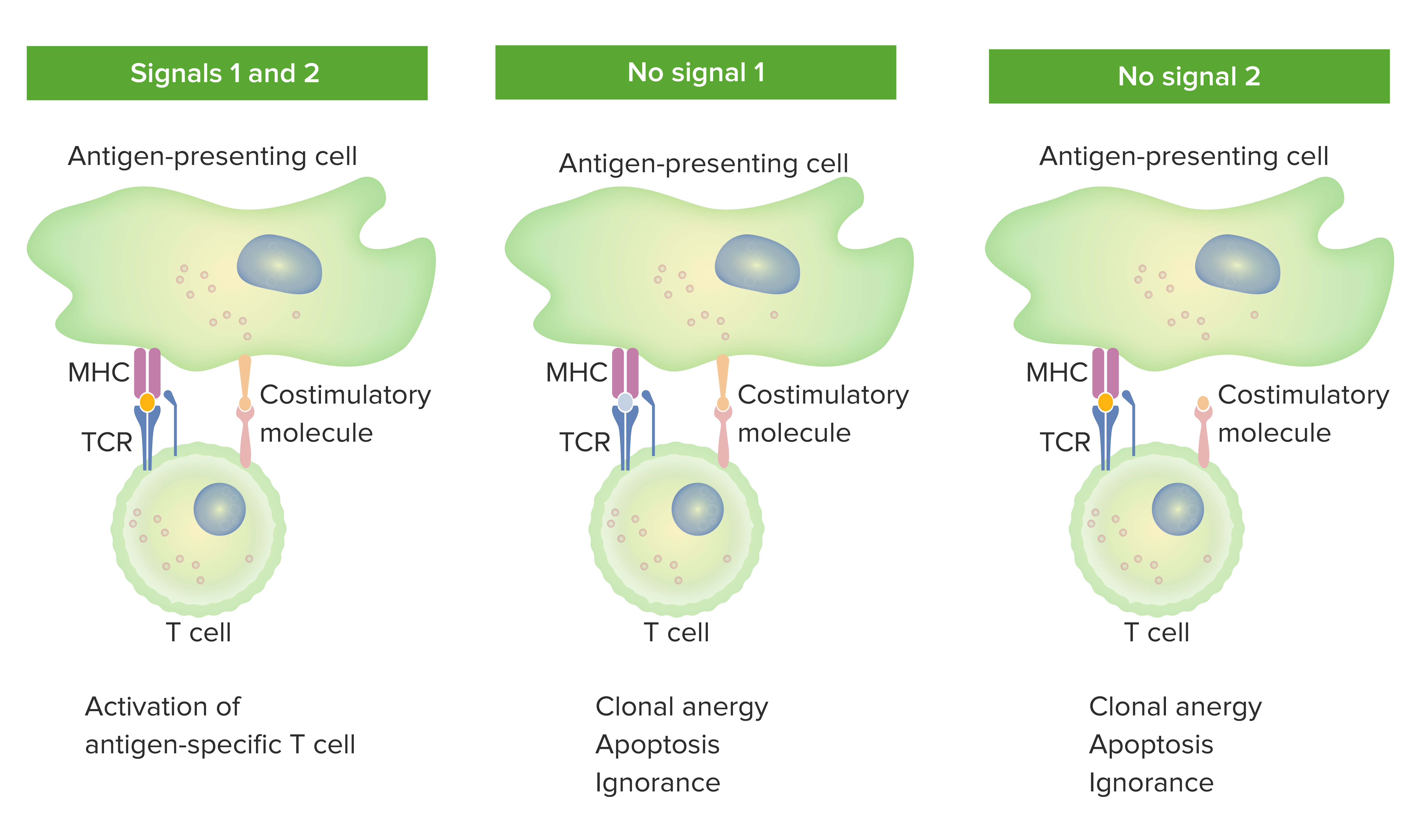
00:01 We’re going to explore cell-mediated immunity. 00:05 Cell-mediated immunity is immunity that is provided by cytotoxic T-cells and by T-helper cell-mediated activation of macrophages. 00:15 It’s required to defeat intracellular pathogens which are hidden from the effects of antibody and complement. 00:24 So if you have an organism outside of a cell, such as a bacterium or even a virus before it enters a cell, antibody and complement are great at dealing with that particular infection. 00:35 However, once organisms enter into cells as all viruses do for some of their life cycle, and also some parasites and some bacteria also spend at least some time inside cells; antibody and complement just can’t get at them. 00:51 And that’s where we need cell-mediated immunity. 00:56 So at the core of cell-mediated immunity is the helper T-cell. 01:02 And these act predominantly by producing soluble molecules called cytokines. 01:07 And these cytokines can help activate cytotoxic T-cells or cytotoxic T-lymphocytes (CTL) as we often call them. 01:17 And they can also help activate macrophages. 01:27 Let’s compare the two types of T-cell that have different T-cell receptors; in other words, the alpha-beta (αβ) T-cell and the gamma-delta (γδ) T-cell. 01:39 So here you can see the αβ T-cell with the T-cell receptor on its cell surface composed of a T-cell receptor α-chain and a T-cell receptor β-chain. 01:51 And then on the right hand side, you can see a γδ T-cell with its T-cell receptor composed of a γ-chain and a δ-chain. 02:00 Diversity for both of these types of receptors is called-- is created by recombination of T-cell receptor genes. 02:08 The T-cell receptor genes for the α-chain and the β-chain in the case of the αβ T-cell receptor, and the γ-chain and δ-chain in the case of the γδ T-cells. 02:18 And both of these recombination processes occur within the thymus; αβ T-cells recognize peptides presented by MHC molecules. In contrast, γδ T-cells can either recognize antigens directly, entirely on their own just like antibodies do, or they can recognize lipoprotein and glycolipids that are presented by the MHC-like molecule CD1.
About the Lecture
The lecture Cell-mediated Immunity: Introduction by Peter Delves, PhD is from the course Humoral Immunity and Cell-mediated Immunity.
Included Quiz Questions
Which of the following components of the immune system is most efficient at eliminating intracellular pathogens?
- Cytotoxic T cells
- Complement
- Antibodies
- Plasma cells
- B cells
Which of the following cells mediates the cellular immunity through secretion of cytokines and activation of other cells?
- Helper T cells
- Cytotoxic T cells
- B cells
- Plasma cells
- Macrophages
Customer reviews
5,0 of 5 stars
| 5 Stars |
|
5 |
| 4 Stars |
|
0 |
| 3 Stars |
|
0 |
| 2 Stars |
|
0 |
| 1 Star |
|
0 |