Playlist
Show Playlist
Hide Playlist
Hormonal Regulators: Calcitonin, Estrogen and Glucocorticoids – Bone and Calcium Medications
-
Slides Hormonal Regulators Calcitonin Estrogen Glucocorticoids Bone Calcium Medications.pdf
-
Reference List Pharmacology.pdf
-
Download Lecture Overview
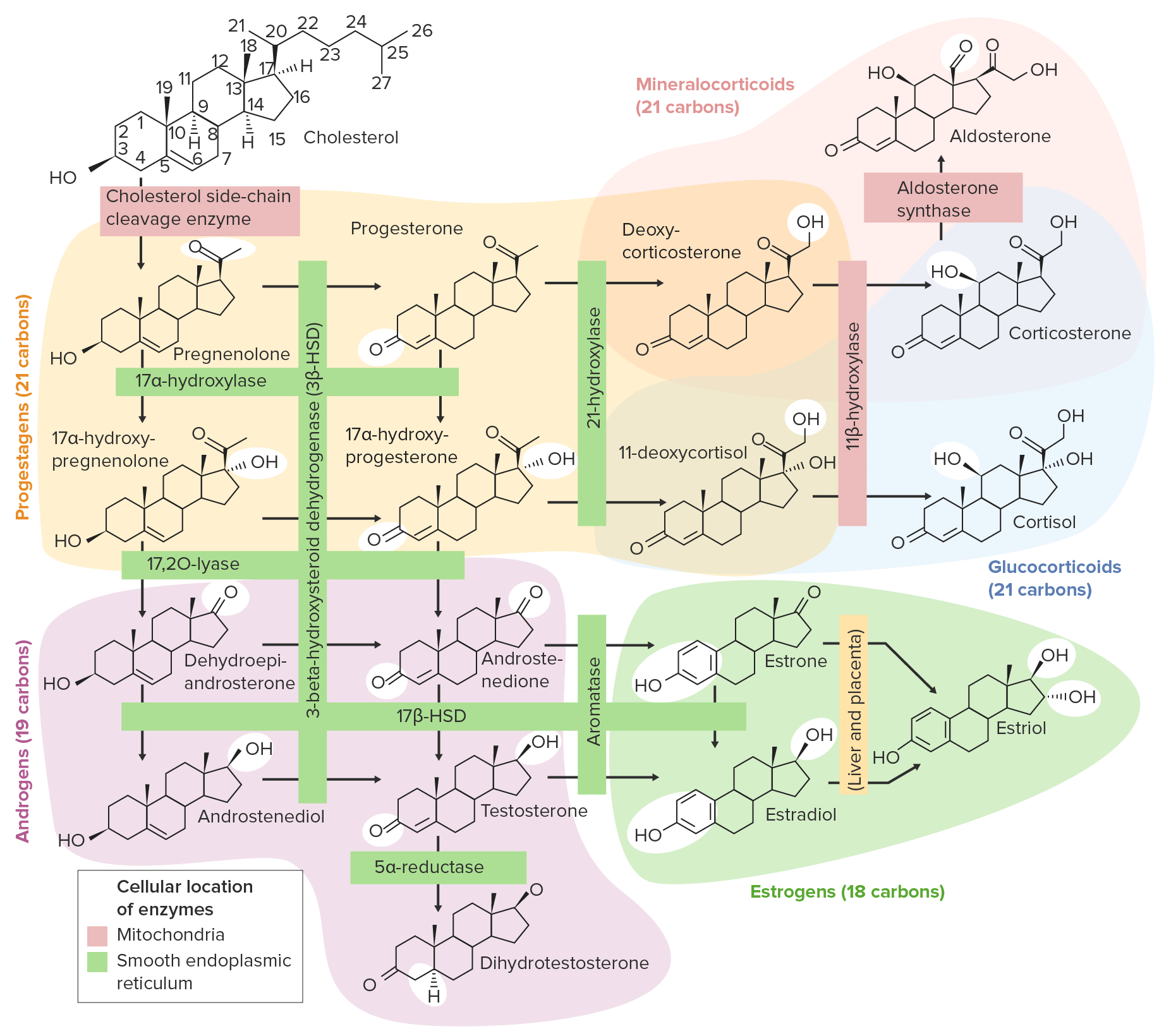
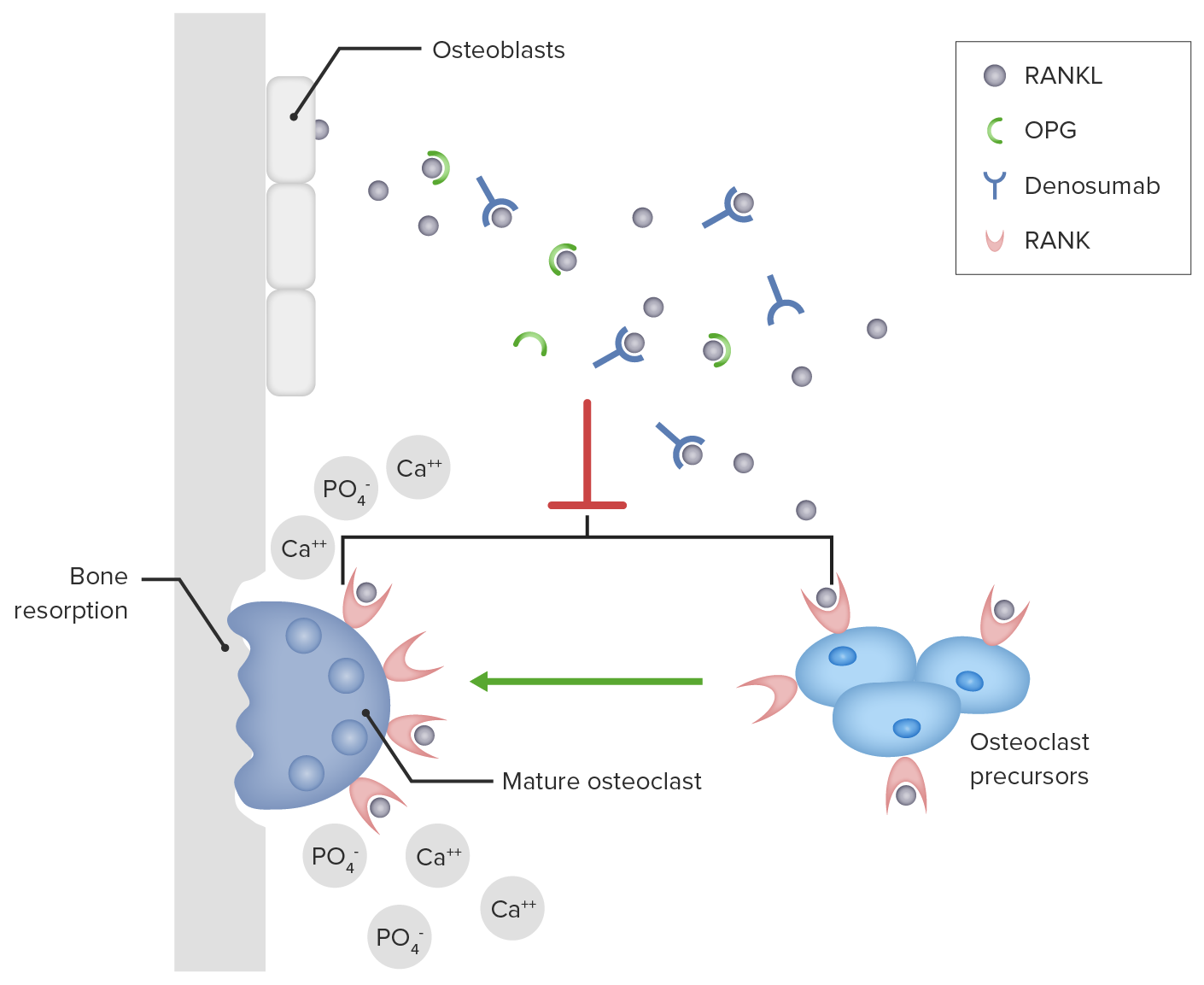
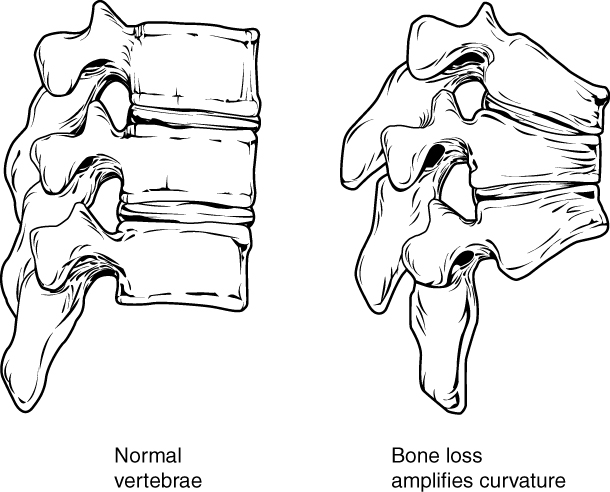
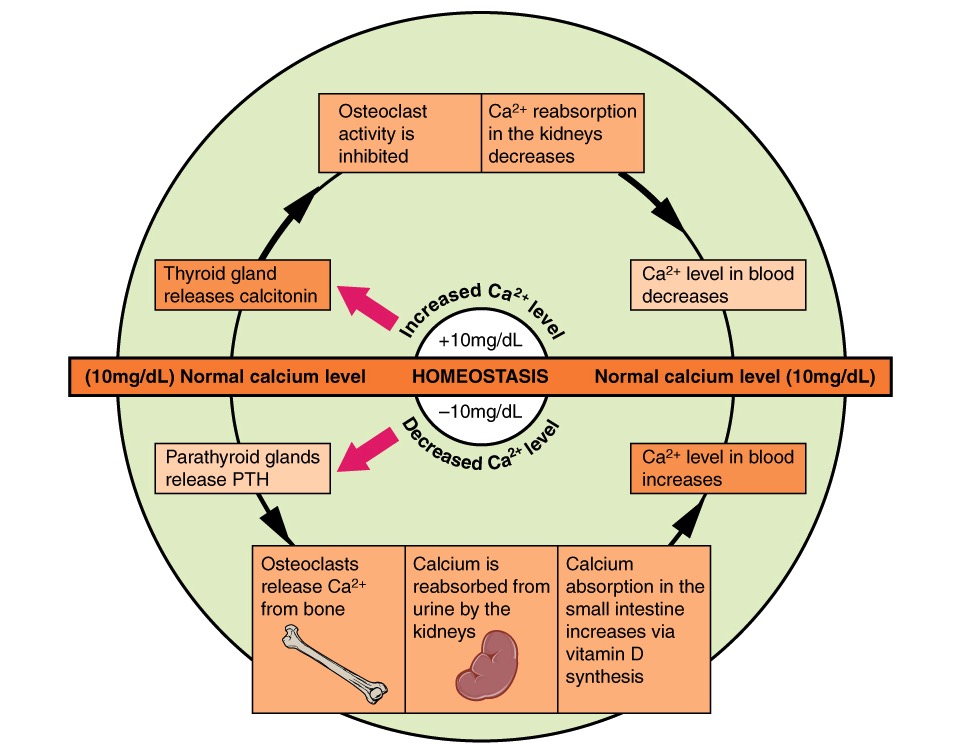
00:01 The next thing that I want to talk about is calcitonin. 00:05 What is calcitonin? Calcitonin is a peptide that is secreted by the thyroid gland. 00:11 It decreases serum calcium and serum phosphate levels. 00:16 It inhibits renal secretion or loss of calcium and phosphate. 00:22 Calcitonin is used for the treatment of hypercalcemia. 00:26 It's also used sometimes in osteoporosis because of its actions on the bone. 00:30 It is used to treat severe bone pain due to acute vertebral fractures. 00:35 Calcitonin has also been shown to reduce spinal fractures and compression wedge fractures in people with osteoporosis who cannot tolerate bisphosphonates. 00:45 You can see here in the image this person's spine has had what we call a wedge compression. 00:52 Now the spinal column is slanting forwards or hunching forwards because the vertebral column has got a wedge in it instead of a nice round cylinder. 01:03 This is a very common thing that we see in elderly patients and that's why elderly patients tend to have a bit of a stooped posture. 01:10 It's because somewhere in their spine they have a wedge compression fracture. 01:14 We can prevent this through proper treatment of osteoporosis and osteopenia. 01:19 Now we reduce spinal compression fractures with calcitonin, but it's not as effective as some other agents that I'm going to talk about later. 01:28 Long term use is also associated with a small increase in various cancers. 01:34 Calcitonin is often administered as salmon calcitonin, so it comes from the fish, the salmon. 01:42 It is a nasal spray, so it's exceedingly easy to take. 01:46 Most patients can tolerate it quite nicely. 01:49 And it's a psychological benefit too, because patients don't feel that it adds to their medication burden if they're giving us a nasal spray. 01:58 They don't think of it as a pill or as a medication, so it's a nice drug that way. 02:04 Now in terms of where and when we would use salmon calcitonin and why we would use it, these are the indications. 02:12 Now I want to caution you that they're not all the same in all countries, but generally speaking I'm going to be using the US experience. 02:21 We use it in Paget's disease of the bone. 02:23 But be careful on your exam because it is not used in Paget's disease of the nipple, which has absolutely no correlation with bone disease at all. 02:31 It's just that the same doctor discovered the two different diseases. 02:35 It's used in bone metastases. 02:37 We use it in postmenopausal osteoporosis in women who cannot tolerate other treatments. 02:42 It is used to treat severe bone pain due to acute vertebral fractures. 02:46 We use it in severe hypercalcemia, which makes sense the way it works. 02:51 The next category is estrogen. 02:54 Now we know that estrogen has important interactions with bone mineral homeostasis. 02:59 We use estrogens and selective estrogen receptor modulators like roloxaphene in the treatment of several diseases. 03:08 We may delay bone loss in patients who are postmenopausal. 03:13 We also inhibit parathyroid stimulated bone resorption. 03:17 So you can see here there's a micrograph of a person's bony structure. 03:21 And the trabeculations in a normal patient are nice and thick, so the bones are very strong. 03:26 You can see on the other image, the trabeculations are narrower. 03:31 The person has some wedge compression fractures of the spine, and they have increased risk of fracture of the large bones. 03:38 Glucocorticoids is another issue. 03:40 So we don't use glucocorticoids to treat bone fractures, but put it in here because it has a very important effect on bone mineral homeostasis. 03:50 Glucocorticoids, of course, are anti-inflammatory agents, and I cover those drugs in another lecture. 03:57 But let's talk about how they affect bone mineral homeostasis. 04:01 It inhibits bone mineral maintenance. 04:05 The patients who are on chronic use end up developing osteoporosis in many, many, many cases. 04:12 And it can be used in short-term treatment of hypercalcemia, because it reduces calcium levels in the serum. 04:20 How do glucocorticoids work? Now, you can also have a look at my glucocorticoid lecture to see how these things interact with the corticosteroid binding units in the host cell DNA. 04:32 But here's a little bit of a recap. 04:34 Now, we're going to do a slightly different diagram and mechanism just because we're focusing on bone minerals. 04:42 So first of all, the CBG, that's the corticosteroid binding globulin, binds to the substrate, or in this case, let's say a drug like prednisone. 04:53 The prednisone substrate enters into the cell. 04:56 It enters as a free molecule and it binds to the receptor inside the cell. 05:02 The receptor is represented by an R. 05:05 Now, there is another protein on there called an HSP98 protein that is bound to the receptor. 05:12 When the drug binds to the receptor, the HSP is discarded. 05:18 And now you have an active receptor represented by the R with a star beside it. 05:24 So we have this steroid receptor that is an activated receptor. 05:28 That receptor steroid complex enters into the nucleus of the cell. 05:33 That's where all the DNA is. 05:35 And the DNA has a GRE or a glucocorticoid response element in it, which binds to the steroid receptor complex. 05:44 When these two get together, gene transcription is activated and you have the machinery responsible for bone resorption. 05:55 Thyroid hormones play a critical role in skeletal development and bone maintenance. 05:59 They are essential for normal growth and development. 06:02 And both excess and deficiency can lead to significant bone pathology. 06:07 Hyperthyroidism is associated with increased bone resorption and risk of osteoporosis, while hypothyroidism can result in delayed skeletal development and impaired bone mineral increase. 06:21 Growth hormone and its mediator, insulin-like growth factor, are crucial for bone formation and remodeling. 06:30 GH directly stimulates osteoblast activity and bone formation, while IGF-I acts in an endocrine and autocrine paracrine manner to regulate bone growth and maintenance. 06:43 GH deficiency is associated with decreased bone mass, and GH replacement therapy has been shown to increase bone turnover and bone mass. 06:54 Insulin also has significant effects on bone metabolism. 06:58 Insulin receptor signaling in osteoblast is essential for postnatal bone acquisition and maintenance. 07:05 Insulin deficiency, as seen in type 1 diabetes or insulin resistance, as seen in type 2 diabetes, can negatively impact bone health, leading to decreased bone formation and increased fracture risk.
About the Lecture
The lecture Hormonal Regulators: Calcitonin, Estrogen and Glucocorticoids – Bone and Calcium Medications by Pravin Shukle, MD is from the course Endocrine Pharmacology.
Included Quiz Questions
What is a function of calcitonin?
- Decreases serum calcium
- Increased hepatic secretion of calcium
- Increased renal secretion of phosphate
- Increased thyroid activity
- Increased secretion of calcium in the colon
Calcitonin is extracted from which animal?
- Salmon
- Carp
- Cow
- Sheep
- African catfish
Calcitonin may be indicated for the management of which disease?
- Paget disease of bone
- Extramammary Paget disease
- Paget disease of the breast
- Paget-Schroetter disease
- Paget abscess
What is a selective estrogen receptor modulator used for the management of osteoporosis in postmenopausal women?
- Raloxifene
- Strontium ranelate
- Teriparatide
- Alendronate
- Zoledronic acid
Which protein binds to the glucocorticoid receptor inside the cell before the drug binds?
- Hsp90
- Albumin
- Transferrin
- Ferritin
- Insulin
Customer reviews
5,0 of 5 stars
| 5 Stars |
|
5 |
| 4 Stars |
|
0 |
| 3 Stars |
|
0 |
| 2 Stars |
|
0 |
| 1 Star |
|
0 |