Playlist
Show Playlist
Hide Playlist
Benign Liver Masses
-
Slides BenignLiverMasses Surgery.pdf
-
Download Lecture Overview
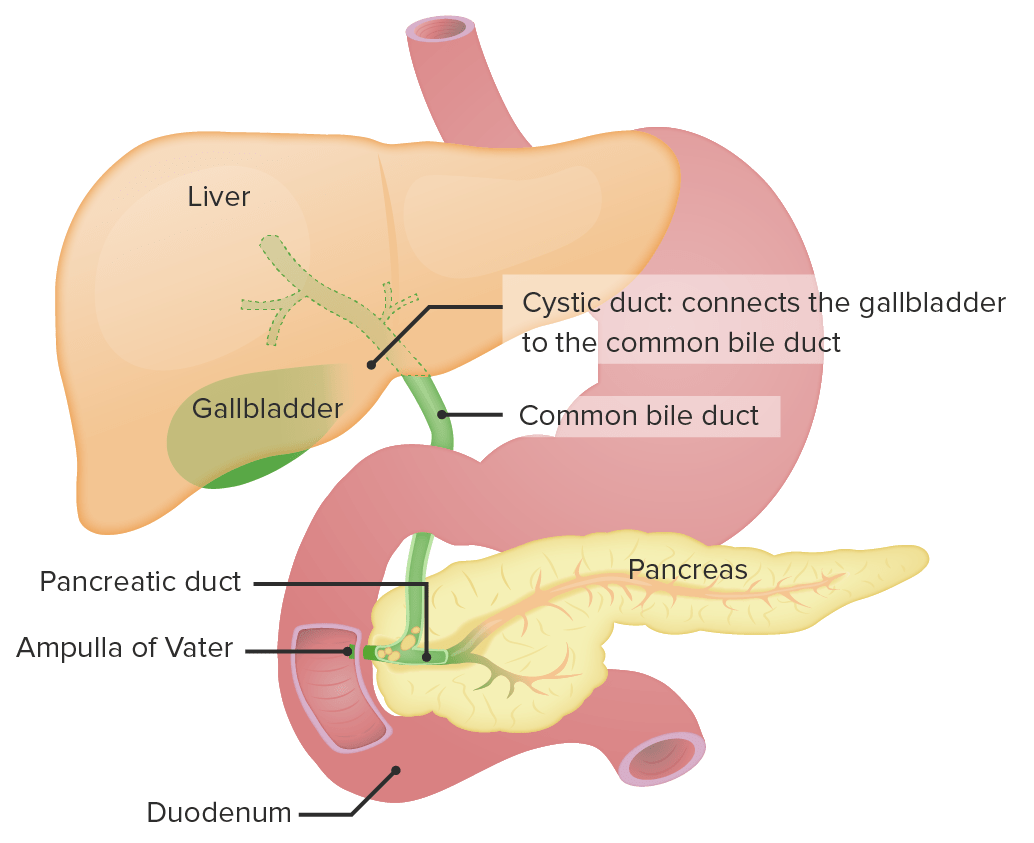
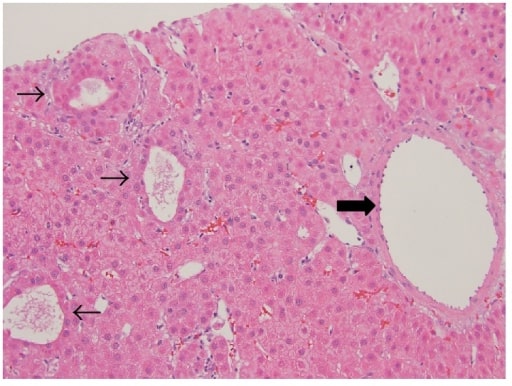
00:01 Welcome back. Thanks for joining me on this discussion of benign liver masses in this section of general surgery. Today, we’ll talk about two of the more common presentations of benign tumors, a hepatic adenoma and a hemangioma. Hepatic adenomas are commonly associated with birth control use and may have the tendency to rupture and bleed. In distinction, hemangioma is the most common tumor of the liver, benign tumor that is. Generally speaking, it’s found in young to middle age women. 00:37 As a surgeon, when I’m in the patient’s abdomen, I commonly see asymptomatic hemangiomas when I look at the liver. It’s usually of no clinical consequence and it’s a vascular malformation. 00:49 Physical findings may include right upper quadrant abdominal pain. But the vast majority of patients with both adenomas and hemangiomas are asymptomatic. You may get some routine labs. 01:05 The chemistry may be absolutely normal. In fact, the CBC is likely to be normal unless the patient is actively bleeding. This may result in a decrease in the hematocrit. Liver function tests are usually not very helpful for hemangiomas or adenomas. This is a cross sectional CT scan of the abdomen and pelvis. It demonstrates a centrally located hepatic adenoma. This looks a little bit different in the previous CT scans and is again a cross sectional CT scan of the abdomen and pelvis demonstrating hemangioma with particular or specific vascular filling or at different contrast phases. 01:48 Hemangiomas are largely observed. 01:50 You wouldn't do a biopsy as there is a increased risk of bleeding. 01:53 Rarely, there is a surgery necessary. 01:55 Of course, if it’s enlarging rapidly causing pain and bleeding similarly to the adenoma, we would offer surgery. 02:02 Medical management of hepatic adenomas include stopping oral contraceptives if feasible. 02:09 Sometimes it needs to be operated on if they’re enlarging rapidly, causing pain, or potentially bleeding. 02:17 Hemangiomas are largely observed. Rarely, a surgery is necessary. Of course, if it’s enlarging rapidly causing pain and bleeding similarly to the adenoma, we would offer surgery. Let me pose a question to you. How do you differentiate between a focal nodular hyperplasia versus an adenoma? I’ll give you a second to think about this. The answer is a sulfur colloid scan. A sulfur colloid scan it involves using a Tc-99m scan, and a colloid which is tag is preferencially taken up by Kupffer cells of the liver. 03:04 Let's take a look at the differences between adenoma and Focal Nodular Hyperplasia. 03:09 For adenomas, they're generally associated with right upper quadrant abdominal pain. 03:14 And on a sulfur colloid skin, they don't have any uptake of the dye because they lack Kupffer cells. 03:22 They maybe consider precancerous and associated with oral contraceptives. 03:27 Contrastly, for focal nodular hyperplasia, these lesions are usually asymptomatic. 03:34 They do uptake the sulfur colloid, are not precancerous, and not associated with oral contraceptives. 03:43 Remember some of the important clinical pearls. 03:47 Hepatic adenomas are at risk for rupture and can cause significant bleeding. 03:52 In these patients, surgery is usually recommended. 03:55 For your test, hepatic adenomas are associated with oral contraceptives, whereas the other benign tumors are not. 04:06 Thank you very much for joining me on this discussion of benign liver tumors.
About the Lecture
The lecture Benign Liver Masses by Kevin Pei, MD is from the course General Surgery.
Included Quiz Questions
Which of the following is NOT true about hepatic adenomas?
- It shows uptake on sulfur colloid scans.
- It is a benign lesion.
- Rupture is common.
- It can be associated with oral contraceptive pills.
- Hemorrhagic adenomas are common.
Which of the following is NOT true about hepatic hemangiomas?
- It typically presents as right lower quadrant discomfort.
- Liver function tests are usually normal.
- It is the most common benign liver mass.
- It is common in young women.
- It is a vascular malformation.
Which of the following is an indication for Tc-99m sulfur colloid scans?
- Differentiating hepatic adenoma from focal nodular hyperplasia
- Differentiating hepatic adenoma from hepatic hemangioma
- Differentiating hepatic adenoma from hepatic cancer
- Differentiating hepatic hemangioma from hepatic cancer
- It is not helpful in liver pathologies.
Customer reviews
5,0 of 5 stars
| 5 Stars |
|
5 |
| 4 Stars |
|
0 |
| 3 Stars |
|
0 |
| 2 Stars |
|
0 |
| 1 Star |
|
0 |