Playlist
Show Playlist
Hide Playlist
Aortic Dissection: Surgical Alternatives & Care Pathway
-
Emergency Medicine Aortic Dissection.pdf
-
Download Lecture Overview
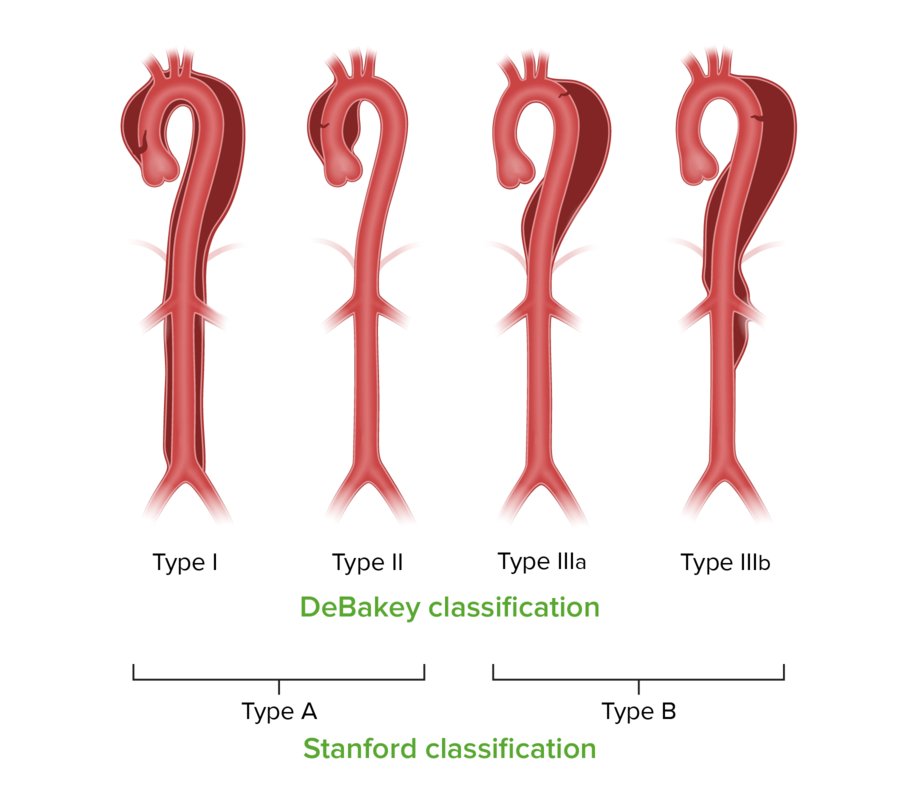
00:01 So when we consult our friends in surgery what are they gonna actually do for the patient? Well, historically, the standard has been open surgical repair with the placement of an aortic graft, so basically you resect the affected portion of the aorta and replace it with an artificial graft. 00:18 However, in recent years, we've seen endovascular alternatives come on board and now there's a common procedure called TEVAR which is Thoracic Endovascular Aortic Repair and the idea there is that you deploy a stent endovascularly with the goal of occluding the tear in the intima in order to block off the false lumen and prevent any further blood from flowing into it. 00:45 This is gonna have two effects. One, it’s gonna prevent the dissection from propagating and getting bigger and two, it’s gonna optimize flow through the true lumen because any of that blood that would have been siphoned off into the false lumen is now gonna flow where it’s supposed to go. 01:01 We're actually seeing really nice outcomes with the endovascular options, so open repairs of type A dissections carry a lot of morbidity and mortality. 01:11 Almost 15% of people will be dead at 30 days after open repair whereas that number is cut in half with endovascular repair. 01:21 Similar type B is again higher mortality associated with open repairs, lower mortality with either endovascular repair or medical management. 01:32 So again, type B patients were only gonna be with considering surgical alternatives if they have complications but it’s definitely worth considering whether the patient is a candidate for an endovascular repair because the outcomes associated with that are really better than with open surgical options. 01:50 So what if you don’t do anything with the dissection? What if you miss it? The reason this is such an important topic in emergency medicine is that really bad things happen when you miss this. 02:02 So for every hour that goes by where you don’t treat your patient’s dissection, they're gonna have an additional 1-2% mortality per hour so you miss it for 24 hours, that means they're gonna have an additional 24% chance of dying. 02:19 That’s a lot, right? So we wanna really make sure that we identify these patients, that we're not sending home missed dissections, that we're not delaying diagnosis for dissection because time matters in this disease process. 02:33 So let’s just review the pathway that we've kind of already discussed. 02:37 First and foremost, basic stabilization for everybody. OMI! Right? Oxygen, monitor, IV access; and then for patients who are hypertensive we're gonna correct their volume status. 02:48 As soon as possible we're gonna get CT angiography again, unless it serves a significant contraindication in which case we’ll have to think about other imaging modalities. 02:57 For patients who have no dissection, we're gonna go ahead and look for alternate causes for their symptoms - we still wanna exclude other serious causes of chest or abdominal pain. 03:08 For patients who have type B dissections, we're gonna stratify whether those are uncomplicated in which case they’ll be managed medically versus complicated in which case we’ll get surgery involved just as we would for any type A dissection. 03:23 And then, regardless of where the dissection is or how the definitive management is gonna be carried out, we're always gonna optimize medical management in the ED with beta blockade, blood pressure control, placement of an arterial line, careful monitoring of vital signs - all of the things that we already discussed in order to optimize our patient’s physiologic outcomes. 03:44 So take home points about dissection, one is that those classic symptoms we learned about in medical school are lots of fun to think about. 03:52 They make a lot of physiologic sense but you don’t always see them in clinical practice. 03:56 Two, you should always suspect aortic dissection with sudden severe chest, abdominal or back pain especially in a patient who's at risk because of their demographics or their identified risk factors. 04:11 Three, don’t rely on chest x-ray to rule out dissection it’s not good enough to exclude a diagnosis, so if you're thinking about dissection you need to move on to CT angiography, MRA, or TEE if you can't obtain a CT for some reason. 04:27 You wanna make sure you get surgery involved for any type A dissection and for complicated type B dissections. 04:33 And then every patient is gonna get medically managed with normalization of blood pressure, beta blockade and additional vasoactive agents if needed to achieve your physiologic goals. 04:46 Thank you very much.
About the Lecture
The lecture Aortic Dissection: Surgical Alternatives & Care Pathway by Julianna Jung, MD, FACEP is from the course Cardiovascular Emergencies and Shock.
Included Quiz Questions
What is the test of choice for patients with suspected aortic dissection?
- CT angiography
- Chest radiograph
- Trans-esophageal echocardiography
- 2D-echocardiography
- Magnetic resonance angiography
Customer reviews
5,0 of 5 stars
| 5 Stars |
|
1 |
| 4 Stars |
|
0 |
| 3 Stars |
|
0 |
| 2 Stars |
|
0 |
| 1 Star |
|
0 |
The lecture is wonderful. I feel completely confident to treat a patient with this diagnosis in the hospital now. It would be great to include the needed doses of the medications, though.