Playlist
Show Playlist
Hide Playlist
Anterior Compartment – Anatomy of the Leg
-
Slides 06 Lower Limb Anatomy.pdf
-
Download Lecture Overview
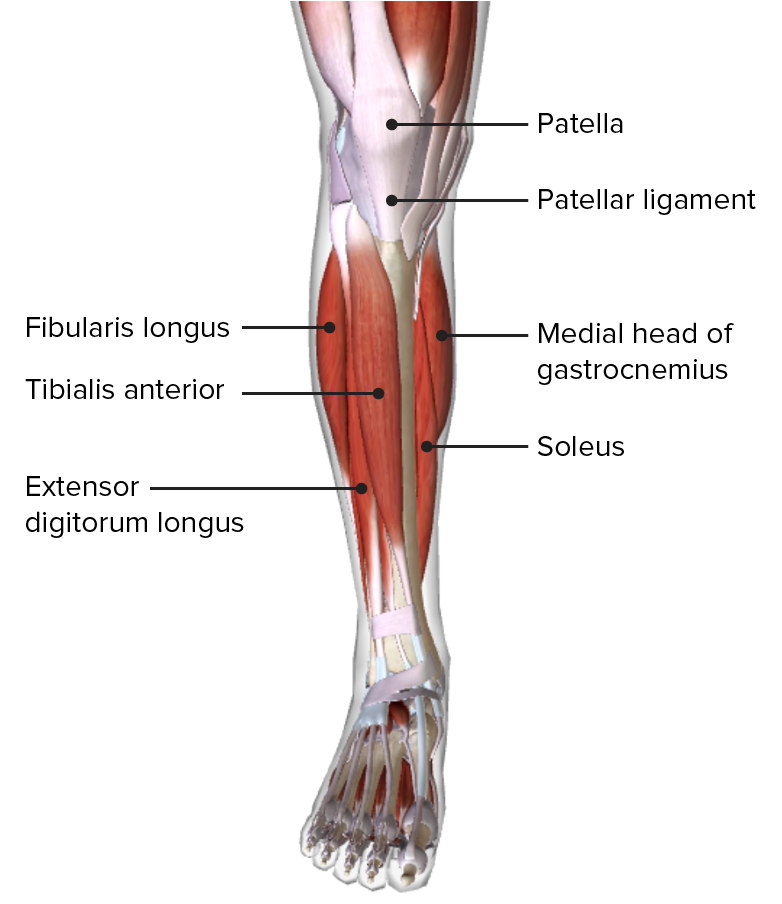
00:00 Let’s look at the anterior compartment first. We can see here, there are a number of muscles. 00:06 There are three which we’re going to cover and this lie on the anterior compartment. 00:11 They actually really lie lateral to the tibia. So we can see the tibia here. This is a right leg. We can see the lateral aspect here by the fifth digit, and we see the medial aspect here. We can see we’ve got tibialis anterior that’s passing down onto the foot. And we’ve got extensor digitorum longus, and then deep to these two more superficial muscles, we have extensor hallucis longus. Let’s have a look at the details of these muscles. 00:43 So tibialis anterior, this is coming from the lateral condyle, the lateral surface of the proximal tibia and the interosseous membrane, and it’s passing through the medial cuneiform and base of the first metatarsal. So we can see here it’s coming from the lateral condyle of the tibia, and it’s passing down and attaching to the base of the first metatarsal and the medial cuneiform. If we look at extensor digitorum longus, this is also coming from the lateral condyle of the tibia. It’s coming from the anterior surface of the fibula and interosseous membrane. This muscle is passing to the middle and distal phalanges of digits 2 to 5. So we can see it’s passing all the way down extensor digitorum longus, and it’s splitting into these tendons which are passing to the distal phalanges and the middle phalanges of digits 2 to 5. We then finally look at extensor hallucis longus, and hallucis means the great toe or the first digit. This muscle is coming from the anterior surface of the mid-fibula, and also the interosseous membrane. But as we can see, it’s actually coming from deep. It’s coming from deep to tibialis anterior and extensor digitorum longus. 02:09 And this muscle passes specifically to the distal phalanx of the great toe digit 1. All of these muscles are supplied by the deep fibular nerve. And we also have another muscle which is in the anterior compartment. But we can’t see it on this diagram and we’ll come back to it in a later slide. But this is fibularis tertius. The fibular muscles are normally located within the lateral compartment, except the fibularis tertius. And not everybody has this muscle. It’s located in a few individuals, fibularis tertius. We’ll come back to it. 02:49 It does come from the anterior surface of lower fibula and the interosseous membrane, and it passes on to the base of the fifth metatarsal. And this is, again, supplied by the deep fibular nerve. So, all of the muscles within the anterior compartment of the leg are supplied by the deep fibular nerve. Their primary function is to extend the digits and dorsiflex the ankle. The tibialis anterior muscle is involved in dorsiflexion of the ankle. It also has an important role in inverting the foot. The extensor digitorum longus is important in extending digits 2 through 5, and also dorsiflexing the ankle. 03:33 Extensor hallucis longus, this is important in extending the great toe, and also assisting in dorsiflexion of the ankle. Fibularis tertius actually is involved in dorsiflexing of the ankle and it supports eversion. And this is a common movement of the fibular muscles. 03:54 But this time, this muscle just happens to be in the anterior compartment. Remember that these muscles in the anterior compartment primarily involved in dorsiflexion of the ankle and extending the digits are supplied by the deep fibular nerves, so these anterior compartment muscles. If we look at them in more of an anatomical view, we can see here we’ve got the anterior kind of edge of the tibia. We can see its medial surface running down here. And then lateral to it, we have these three muscles. We have tibialis anterior, then we have lateral to it, extensor digitorum longus, and we can see passing between extensor hallucis longus. If we look at this, we can see that these are innervated via the deep fibular nerve and they’re supplied by the anterior tibial artery. We can also see that we have a small muscle that’s running down in this direction here. We can just see the tendon of it, and this is, in this view, our fibularis tertius tendon; that muscle I mentioned a few slides ago. Its muscle belly coming from the lower parts of the fibula and the interosseous membrane is coming from the anterior compartment. So just like in the upper limb, we also have some thickenings of the deep fascia that creates superior and inferior extensor retinacula. On the screen, we can see the image of the anterior compartment of the leg again. And we can see this inferiorly positioned Y-shaped band, and this is extending from the calcaneus, we can see here, all the way across to the medial malleolus. 05:38 So we can see a portion of dropping down here as well. And this is your inferior extensor retinacula. 05:45 This is important in creating a strong loop around fibularis tertius and extensor digitorum longus holding those tendons in place. We also have a more superiorly positioned thickening, and that’s not visible on this diagram, but it would be approximately in this position. 06:02 And it’s quite separate, but again, a thickening of the deep fascia. And that is your superior, a broad band extending across from the tibia to the fibula and this prevents bowstringing of all of the tendons from the anterior compartment.
About the Lecture
The lecture Anterior Compartment – Anatomy of the Leg by James Pickering, PhD is from the course Lower Limb Anatomy [Archive].
Included Quiz Questions
In relation to the tibia, where is the anterior compartment of the leg located?
- Lateral
- Medial
- Deep
- Superficial
- Anterior
Which muscle participates in the extension of digits 2–5?
- Extensor digitorum longus
- Extensor hallucis longus
- Fibularis longus
- Tibialis anterior
- Fibularis tertius
Which muscle inserts on the distal phalanx of the hallux?
- Extensor hallucis longus
- Extensor digitorum longus
- Fibularis longus
- Tibialis anterior
- Fibularis tertius
Which muscle is present in the anterior leg compartment of all individuals?
- Extensor digitorum longus
- Fibularis longus
- Fibularis brevis
- Semitendinosus
- Semimembranosus
Which nerve primarily innervates the anterior compartment of the leg?
- Deep fibular nerve
- Superficial fibular nerve
- Tibial nerve
- Radial nerve
- Superior gluteal nerve
Which nerve supplies the anterior compartment of the leg?
- Deep fibular nerve
- Tibial nerve
- Common fibular nerve
- Superficial fibular nerve
Customer reviews
5,0 of 5 stars
| 5 Stars |
|
5 |
| 4 Stars |
|
0 |
| 3 Stars |
|
0 |
| 2 Stars |
|
0 |
| 1 Star |
|
0 |