Playlist
Show Playlist
Hide Playlist
Amiodarone-induced Thyroiditis – Hyperthyroidism (Thyrotoxicosis)
-
Slides Hyperthyroidism incl. Graves Disease.pdf
-
Reference List Pathology.pdf
-
Download Lecture Overview
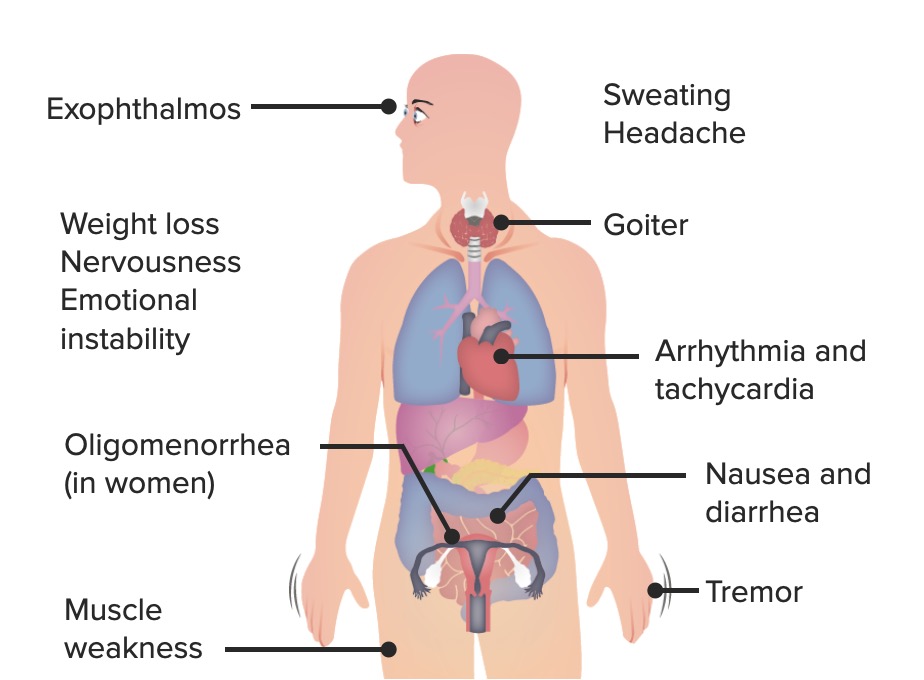
00:02 Amiodarone Induced Thyroiditis, with this it could be… patient may present either with hypo or hyperthyroidism, structure resembled that of your thyroid hormone because it contains iodine, seen in approximately 3 percent of amiodarone, 1 to 3 years of therapy, thyroid is not enlarged or tender, can cause both hypo and/or hyperthyroidism. 00:27 Hypothyroidism by blocking the peripheral conversion of T4 to T3, hyperthyroidism Low blood flow on color flow Doppler thyroid ultrasound is what you are thinking of in general with thyroiditis. 00:43 Take a look at Riedel. 00:45 With Riedel’s thyroiditis, we called this fibrous. 00:48 It is a primary fibrosing disorder, if you then take a look at the picture on the right. 00:54 On the far right, a remnant of or sparing of a little bit of your thyroid histology whereas on the left, you are seeing quite a bit of fibrosis taking place of your thyroid gland. 01:08 So, now, two different things that are taking place in a thyroid gland, earlier referred to granulomatous and that would be more or less your subacute type, maybe viral infection and with viral infection, you are thinking about painless or painful, excuse me, whereas if it is painless and a silent lymphocytic infiltration, this is primary fibrous in disorder. 01:35 Women, much more so than men, elderly, dense fibrosis, that replaces the normal thyroid parenchyma with macrophage and eosinophil infiltration. 01:45 Fibrosis, once again, take a look at the picture histologically on your left, would be areas of that fibrosis which is then replacing any type of thyroid normal tissue that may exist. 01:58 Meaning to say, the far right in that homogenous pink region represents your colloid. 02:04 The fibrosis invades the adjacent structures and that is important for you to pay attention to of the neck and extends beyond the thyroid capsule. 02:11 So, therefore, now, you are thinking about other areas adjacent such as the esophagus that might be affected, may present therefore with dysphagia. 02:21 Hard, woody gland treat surgery if compressive symptoms. 02:26 Like I told you earlier, that fibrosis can be quite dangerous especially if it starts growing and therefore, causing fibrosis of perhaps behind it; you are thinking about the trachea or perhaps even the esophagus, dysphagia and dyspnea. 02:40 Then we have multinodular goiter. 02:44 With multinodular goiter, you are thinking about a patient who is a little bit older and if you were to take a look at the neck, this is a thyroid gland in which it has numerous nodules throughout the thyroid gland causing this diffused enlargement of the neck. 03:04 The gross pathology here would be the multinodular goiter with huge cystic nodules with excessive colloids. 03:12 Hemorrhage has occurred and could occur because whenever you have a cyst and it keeps enlarging, there might be every possibility of rupture of a blood vessel or capillary. 03:21 Therefore, blood then hemorrhaging into your cyst itself, multinodular goiter. 03:26 Treatment. 03:27 So, how do you want to take care of your toxic nodule disease? First, while you have toxic multinodular and solitary toxic adenoma known as Plummer’s disease are overall less frequent than Graves’ disease, but in terms of presentation may present more so with hyperthyroidism. 03:47 Who is your patient with multinodular or toxic adenoma of the thyroid? These patients are almost always elderly, elderly. 03:57 Remission, not seen with antithyroid drugs; radioactive iodine is a treatment of choice; through surgery is a reasonable option but once again, when you get in here and therefore, you want to ablate, ablate your thyroid. 04:13 Your surgery would only be considered if your patient is now suffering from the constructive effects of that goiter enlargement, dysphagia, dyspnea or perhaps hoarseness.
About the Lecture
The lecture Amiodarone-induced Thyroiditis – Hyperthyroidism (Thyrotoxicosis) by Carlo Raj, MD is from the course Thyroid Gland Disorders.
Included Quiz Questions
How does amiodarone induce thyroiditis?
- It is structurally similar to thyroid hormone and contains iodine.
- It binds to TBG, increasing free thyroid hormone in serum.
- It upregulates TSH receptors.
- It is structurally similar to TRH, and stimulates the release of TSH.
- It rapidly converts T4 to T3.
A biopsy of a thyroid gland reveals fibrosis with macrophages and eosinophils. What is the most likely diagnosis?
- Riedel's thyroiditis
- Amiodarone-induced thyroiditis
- Subacute thyroiditis
- Acute infectious thyroiditis
- Silent thyroiditis
What is NOT associated with multinodular goiters?
- Fibrosis and eosinophilia
- Diffuse enlargement of the anterior neck
- Older patients
- Cystic nodules filled with excessive colloid
- Hemorrhage into cysts
Customer reviews
5,0 of 5 stars
| 5 Stars |
|
5 |
| 4 Stars |
|
0 |
| 3 Stars |
|
0 |
| 2 Stars |
|
0 |
| 1 Star |
|
0 |