Playlist
Show Playlist
Hide Playlist
Amino Acid Metabolism: Introduction
-
Slides AminoAcidMetabolism Biochemistry.pdf
-
Reference List Biochemistry.pdf
-
Download Lecture Overview
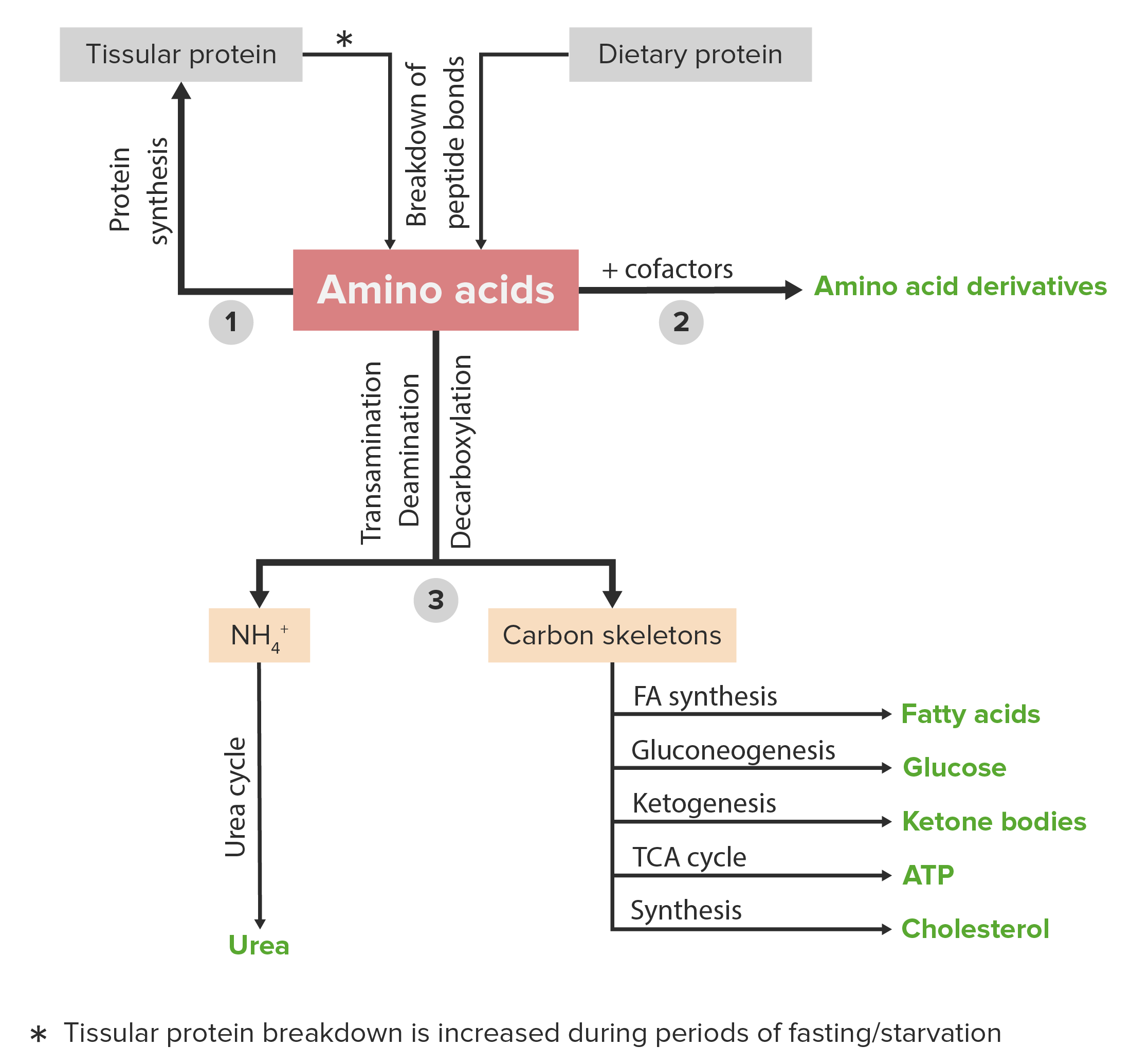
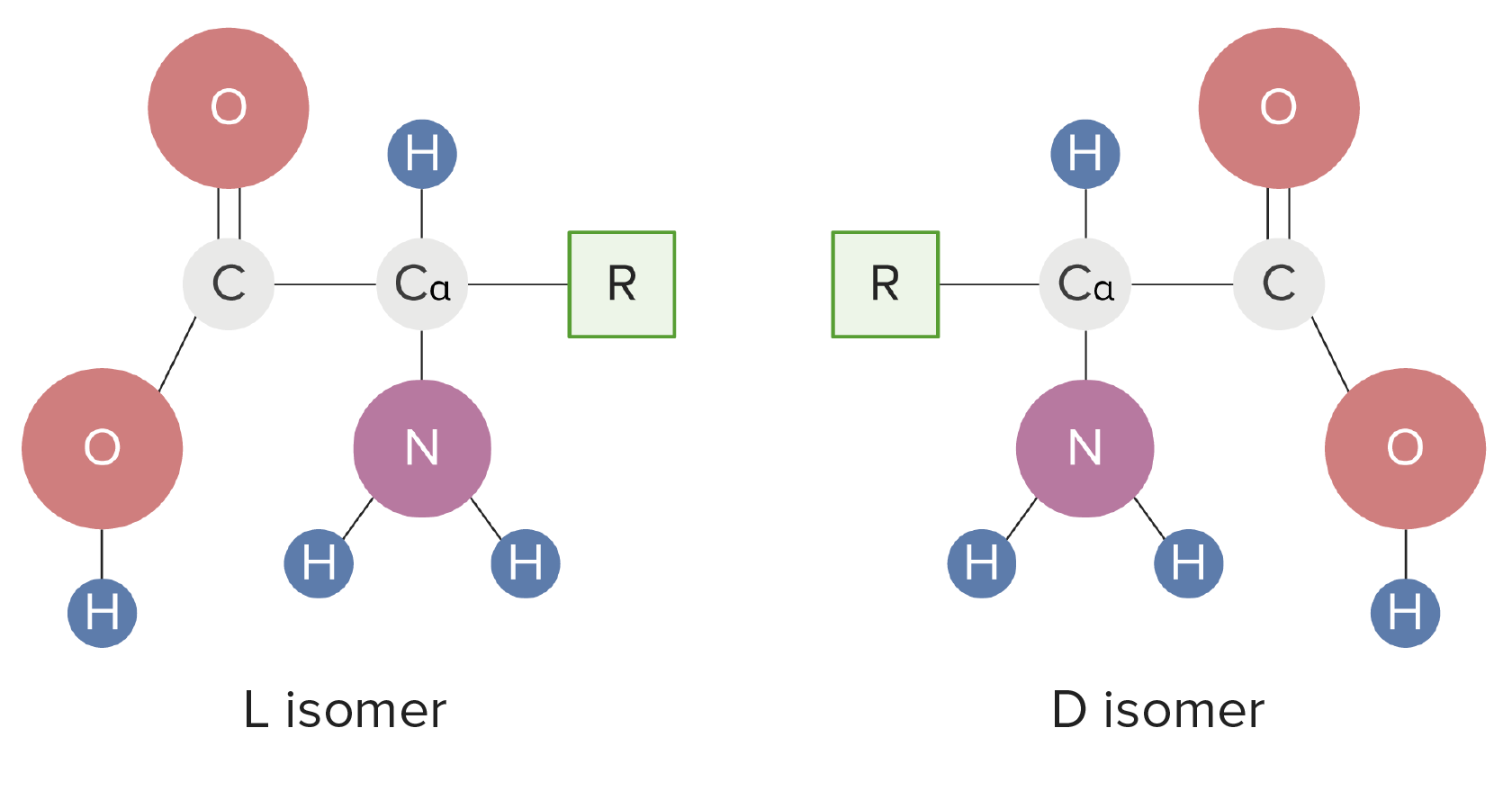
00:01 In this set of lectures, I will describe the most diverse set of metabolic processes that occur that of amino acid metabolism. 00:09 Now to review for just a second, we remember that amino acids are essential for making proteins and that there are 20 common amino acids that are found in all proteins plus an occasional rare one that I will also describe here. 00:22 The structure of amino acids can all be schematically drawn as we see in the figure on the right. 00:27 There's a central alpha carbon that's found and every amino acid has all of these structures that we see here. 00:33 Above it is the hydrogen. 00:34 To the right, an alpha carboxyl group. 00:37 Beneath it, an alpha amine. 00:38 And to the left, an R group, the part of the amino acid that gives every amino acids its characteristics: structure, function and chemistry. 00:47 There's no single pathway for amino acid metabolism, which distinguishes it from some of the other metabolic processes that happen in cells. 00:54 The synthesis pathways for amino acids are actually grouped according to common anabolic precursors that they all have. 01:00 There's a family known as the alpha-ketoglutarate family, a serine family, aspartate acid family, aromatic amino acid family, a pyruvate family, and finally the most complicated pathway, the histidine pathway. 01:14 Now in addition to talking about amino acid metabolism, I will discuss post-translational modification. 01:19 So these are chemical changes that are made to amino acids after they've been built into a protein. 01:25 When we talk about amino acids, we hear the term essential and I want to define what that is. 01:30 So essential amino acids are amino acids that an organism must have in their diet. 01:35 They can't synthesize those. 01:37 Where by contrast, the non-essential amino acids are ones that can be made by an organism. 01:43 Essential versus non-essential varies in humans, and it also varies from one organism to another and also between child and adult. 01:50 So they're not an absolute list. 01:53 One list of essential amino acids and non-essential amino acids for humans is shown here. 01:58 We say for example the ones that have aromatic rings like tryptophan and phenylalanine, we will later discover have common metabolic pathways. 02:06 The tyrosine amino acid which is also an aromatic amino acid can be made from phenylalanine. 02:11 So is tyrosine essential or not essential? Well, if phenylalanine is in the diet, it's not essential. 02:16 If it's not in the diet, it becomes essential.
About the Lecture
The lecture Amino Acid Metabolism: Introduction by Kevin Ahern, PhD is from the course Amino Acid Metabolism.
Included Quiz Questions
Which part of the amino acid gives it unique characteristics, structure, function, and chemistry?
- R group
- Alpha carbon
- Alpha amine
- Carbonyl carbon
- Hydroxyl group
Essential amino acids are amino acids that must be...?
- ...in an organism’s diet.
- ...synthesized by an organism.
- ...in the ribosome.
- ...in the endoplasmic reticulum.
- ...in the nucleus.
Customer reviews
5,0 of 5 stars
| 5 Stars |
|
2 |
| 4 Stars |
|
0 |
| 3 Stars |
|
0 |
| 2 Stars |
|
0 |
| 1 Star |
|
0 |
I LIKE THE PRESENTATION AND I LEARN . PROFF. USE A SIMPLE AND UNDERSTANDABLE LANGUAGE
it was very good lecture it will help me in my med biochem class thanku