Playlist
Show Playlist
Hide Playlist
Adrenal Case: 25-year-old Man with Severe Pulsatile Headache
-
Slides 01-02-02 Adrenal Pituitary.pdf
-
Reference List Endocrinology.pdf
-
Reference List Adrenal Gland Disorders.pdf
-
Download Lecture Overview
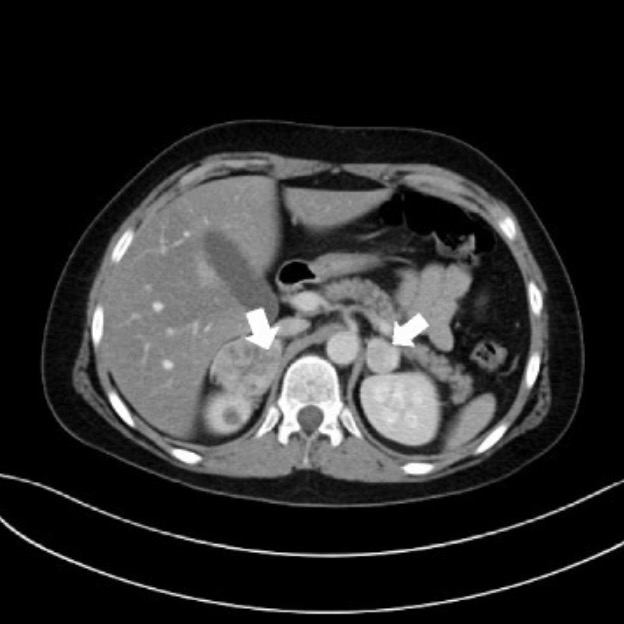
00:00 Let's go on to another case. 00:03 A25-year-old male presents to the emergency department with a severe pulsatile headache for one hour. 00:09 He says that he's having palpitations and sweating. 00:12 He adds that he has had several similar episodes in the past which resolved without seeking medical attention. 00:20 He is a nonsmoker and does not drink alcohol. 00:23 He denies the use of any illicit drugs. 00:26 He looks anxious and diaphoretic. 00:29 His temperature is 37 degrees Celsius. 00:31 His respirations are 25 breaths per minute. 00:34 Pulse rate is 107 and blood pressure is 228/160. 00:40 A CT scan of the abdomen reveals an adrenal mass. 00:44 What is the next step in the management of this patient? Based on the clinical suspicion formulated by the presentation of this patient, a pheochromocytoma or an adrenaline-secreting tumor of the adrenal gland is very high on the differential. 01:04 Usually, this manifests as the classic triad of diaphoresis, headache, and tachycardia. 01:11 CT scan findings also suggest that there is an adrenal mass which would go along with the diagnosis. 01:18 The next best step in the management of this patient would be to order a 24-hour urine metanephrine and catecholamine level to confirm the diagnosis. 01:28 Phenoxybenzamine is a non-competitive alpha blocker and is given 7-10 days prior to surgery for patients needing resection for their pheochromocytoma. 01:38 This medication blocks alpha receptors in blood vessels. 01:42 This is then followed by beta blockade using a non-selective beta blocker like propranolol which acts on the beta receptors in the heart and kidney to lower blood pressure further. 01:54 Beta blockade should be done when all the alpha-1 receptors are already blocked or else the circulating catecholamines may stimulate alpha-1 receptors precipitating a hypertensive crisis.
About the Lecture
The lecture Adrenal Case: 25-year-old Man with Severe Pulsatile Headache by Michael Lazarus, MD is from the course Adrenal Gland Disorders.
Included Quiz Questions
What is the best next step in the management of a patient with suspected pheochromocytoma?
- Evaluation of 24-hour urine metanephrine and catecholamine levels
- Surgical excision
- Administration of an alpha-blocker
- Administration of a beta-blocker
- Reevaluation in 7–10 days
Customer reviews
5,0 of 5 stars
| 5 Stars |
|
5 |
| 4 Stars |
|
0 |
| 3 Stars |
|
0 |
| 2 Stars |
|
0 |
| 1 Star |
|
0 |