Playlist
Show Playlist
Hide Playlist
Additional Cystic Diseases of the Kidney
-
Slides RenalCystrePathology IntegratedRenalPathology.pdf
-
Reference List Pathology.pdf
-
Download Lecture Overview
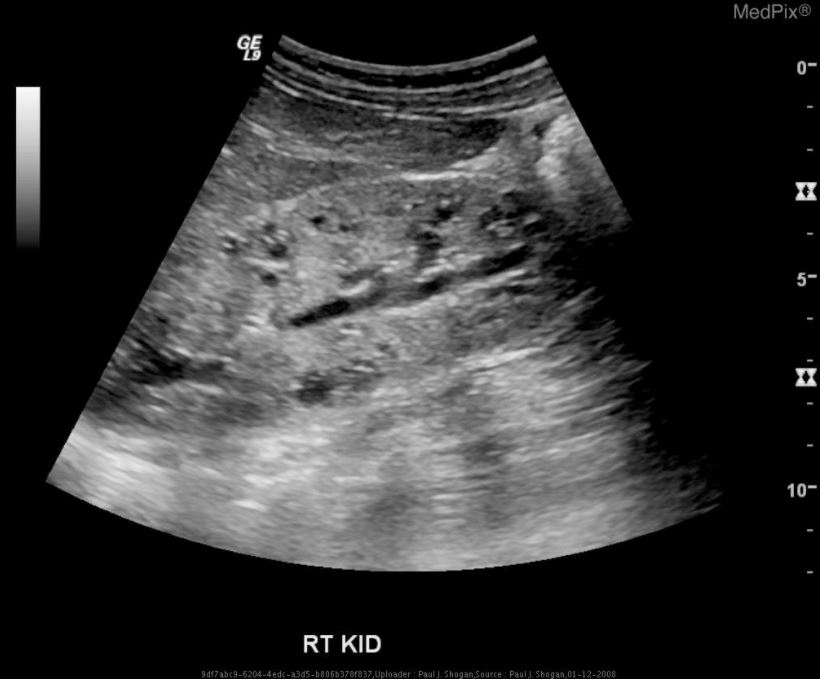
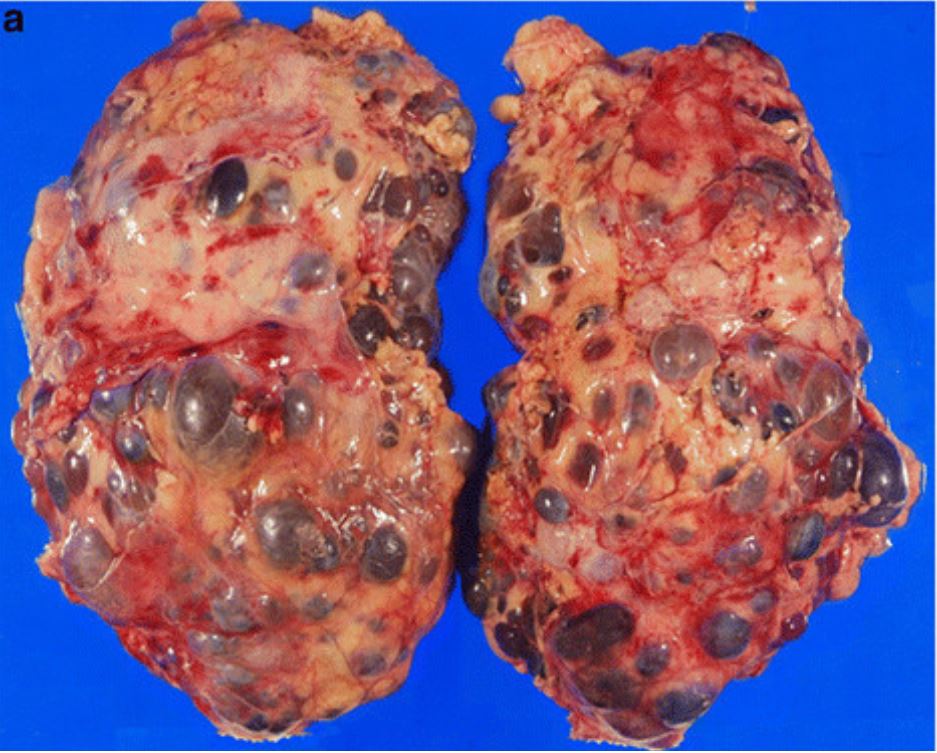
00:01 Medullary sponge kidney. 00:02 Now, after those discussions, things become a little bit easier and as far as how you can find these cysts and the clues become very straightforward. 00:11 Once again, Medullary sponge kidney, no inheritance pattern, point number one, most commonly discovered with a pyelogram, striations are present in the papillary duct. 00:23 What’s papillary duct mean to you? In the medulla. 00:28 I want you to think of the pyramid. 00:29 The pyramid is an entire structure where the nephron is located, isn’t it? I want you to go deep in the medulla. 00:35 What’s that portion where you start forming a minor, major callus, and a pelvis? That’s called your papilla. 00:41 Be really careful here with anatomy of the kidney. 00:44 Things that should be absolutely clear for you before we move on. 00:48 There are three major structures begin with P, P, pyramid, P, papilla, P, pelvis. 00:54 You must know what those are before you have any pathologic conditions. 00:59 Multiple cysts of the collecting duct are present in the medulla. 01:03 Swiss-cheese like appearance, Medullary sponge kidney. 01:07 Recurrent urinary tract infection is a big one for you to pay attention to. 01:11 Acquired polycystic kidney disease. 01:14 Who’s your patient most likely here? See, what’s highlighted? Renal dialysis. 01:19 So this is a big deal? Mm-hmm. 01:21 Dialysis clinics are like gas stations. 01:24 You open up one gas station, what’s on the other side of the street? Holy cow! Another gas station, amazing, this is no joke. 01:32 This is not even funny. 01:33 The fact that we have so many dialysis clinics throughout the United States only means every one of those clinics are filled with patients that have - good, nephropathy. 01:44 So these individuals are then predisposed to what? Acquired polycystic kidney disease. 01:51 Tubules obstructed interstitial fibrosis and oxalate crystals. 01:56 Simple retention cysts, these are the most common cysts of adults. 02:04 What was the most common cyst of a child? Renal dysplasia, good. 02:10 May produce hematuria and requires needle aspiration to distinguish it from RCC, that’s important when it distinguishes from RCC. 02:21 Show you some pictures that are important for us. 02:26 Take a look at this kidney, it’s tiny, it’s a child. 02:29 This would be renal dysplasia. 02:31 Any inheritance pattern, yes, or no? No, good. 02:36 What ends up here, what ends up happening here? You have immature collecting ductules. 02:40 So rather chaotic in nature, a very common cyst found in what? Children, multicysts. 02:49 Could you have both of the kidneys involved? Sure. 02:52 Could you have only one kidney involved? Yes. 02:55 Adult but more importantly, and more technically, what do we have here? Autosomal Dominant Polycystic kidney disease. 03:05 Tell me which gene did we find in great abundance? PKD1, what chromosome? 16. 03:11 Whenever you find cysts like you do in the adult kidneys what you’re seeing the picture of, could you then find cysts in the liver as well? Sure you can. 03:19 What else are you looking for? Hypertension. 03:22 What other clues or associations apart from the kidney and the liver? Maybe Mitral valve prolapse, sigmoid diverticulosis. 03:30 What about chronic renal failure? Will take place a little bit later. 03:34 Take a look at the kidney, both kidneys are involved, and all over the kidney; cortex, medulla, there’s no specific point.
About the Lecture
The lecture Additional Cystic Diseases of the Kidney by Carlo Raj, MD is from the course Cystic Diseases (Renal Cystic Pathology).
Included Quiz Questions
Which of the following pathologies presents with cysts in the medulla without involvement of the cortex?
- Medullary sponge kidney
- Renal dysplasia
- Simple retention cysts
- Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease
- Autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease
Which of the following is a common presentation of medullary sponge kidney?
- Recurrent urinary tract infections
- Uric acid stones
- Chronic renal failure
- Hepatic fibrosis
- Bilateral palpable kidneys
Which of the following patients carry the highest risk of developing acquired cystic kidney disease?
- Dialysis patients
- Patients with cirrhosis
- Patients with recurrent urinary tract infections
- Patients with renal cell carcinoma
- Patients with berry aneurysms
Customer reviews
5,0 of 5 stars
| 5 Stars |
|
5 |
| 4 Stars |
|
0 |
| 3 Stars |
|
0 |
| 2 Stars |
|
0 |
| 1 Star |
|
0 |