Playlist
Show Playlist
Hide Playlist
Acute Inflammation Triggers
-
Slides Acute and Chronic Inflammation Cellular response.pdf
-
Reference List Pathology.pdf
-
Download Lecture Overview
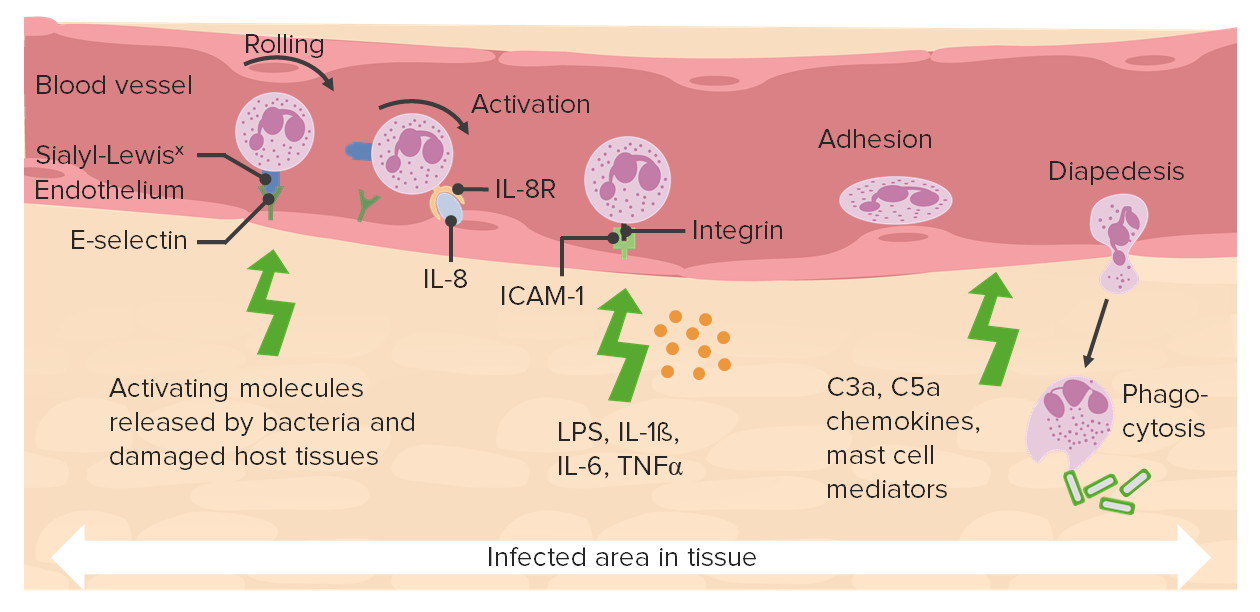
00:01 First of all, we have to ask, what's triggering this response? In a previous topic discussion, we said, "It's danger." Well, yeah, it is danger. 00:10 But what is danger? And danger represents a variety of things. 00:14 So what are the triggers? Necrotic debris not otherwise specified. 00:18 Fragments of cells, denatured proteins, things that should be intracellular that are now extracellular. 00:27 We'll have those in a second. 00:30 Infections in a particularly bacterial infections, elaborate a variety of molecules that are very attractive to neutrophils. 00:38 So that will be an important trigger. 00:41 There are things on the surface of bacteria and this on the surface of fungi, or that get broken down when the bacterial cell or fungal wall gets broken down. 00:51 That will be recruiting triggers for a acute inflammation. 00:56 Denature proteins such as will happen in a blood clot or from danger that has led to injury of the tissues will also recruit nonspecifically. 01:09 Thrombus. Clearly if we have had bleeding and the formation of a blood clot, there must have been some damage. 01:15 So we need to recruit the inflammatory cells. 01:19 Uric acid, very important. 01:21 So uric acid comes from the breakdown of DNA. 01:24 Normally, we would not have broken DNA in the extra vascular space. 01:30 And if we start seeing the capilites, the metabolic breakdown products of that DNA in the form of uric acid, that's a signal that something has happened. 01:41 One of the other triggers related to that is ATP. 01:45 Cells will not release ATP because that's an important energy source. 01:50 If we see ATP in the extra vascular space, that's also an important trigger. 01:57 Mast cells, macrophages, and fibroblasts also all release mediators. 02:02 Those are sentinel cells that live in the extra vascular space. 02:06 And when they get appropriately triggered, they will release additional molecules that will recruit acute inflammation. 02:13 And endothelial cells can be directly activated by a variety of molecules that are present on infectious agents, or happen when there has been damaged to a particular tissue.
About the Lecture
The lecture Acute Inflammation Triggers by Richard Mitchell, MD, PhD is from the course Acute and Chronic Inflammation.
Included Quiz Questions
Which of the following does NOT trigger acute inflammation?
- Apoptotic cells
- Bacteria
- Denatured proteins
- Uric acid
- Adenosine triphosphate
Customer reviews
5,0 of 5 stars
| 5 Stars |
|
5 |
| 4 Stars |
|
0 |
| 3 Stars |
|
0 |
| 2 Stars |
|
0 |
| 1 Star |
|
0 |