La aspiración de un cuerpo extraño puede provocar asfixia y muerte al AL Amyloidosis obstruir el flujo de aire en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la laringe o la tráquea. Los LOS Neisseria cuerpos extraños también pueden alojarse más profundamente en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria bronquios; esto puede no afectar la respiración, pero puede causar infección o erosión de las paredes bronquiales. Los LOS Neisseria cuerpos extraños son aspirados con más frecuencia por los LOS Neisseria niños, que pueden presentarse con tos TOS Thoracic outlet syndrome (TOS) is a broad term used for a spectrum of syndromes related to the general region of the thoracic outlet, which involves the compression or irritation of elements of the brachial plexus, subclavian artery, or subclavian vein. Thoracic Outlet Syndrome o sibilancias. Como los LOS Neisseria cuerpos extraños rara vez son visibles en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la radiografía, se deben emplear otras modalidades de imagenología, como la tomografía computarizada o la broncoscopia flexible, cuando los LOS Neisseria síntomas y la sospecha clínica lo soliciten. La frecuencia relativa con la que se aspiran varios objetos varía según la demografía del paciente. La pronta eliminación del cuerpo extraño es el tratamiento definitivo.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Los LOS Neisseria cuerpos extraños aspirados varían según la edad.
La mayoría de los LOS Neisseria casos involucran materiales que no son visibles en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum las radiografías (e.g., alimentos, madera y plástico). En EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum estos casos, las características del aspecto pulmonar pueden sugerir un cuerpo extraño. La tomografía computarizada (TC) o la broncoscopia pueden confirmar la sospecha.
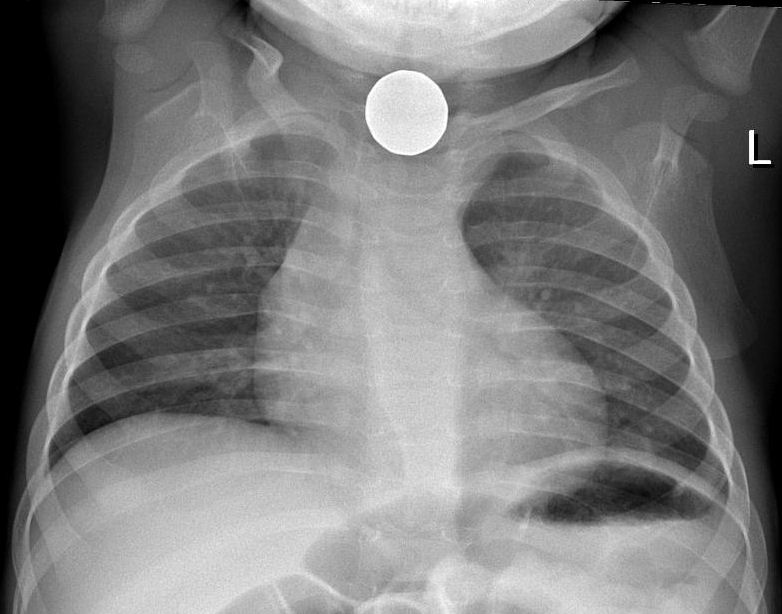
Radiografía de moneda en radiografía de tórax
Imagen: “Foreign body aspiration X-ray” por Samir. Licencia: CC BY 3.0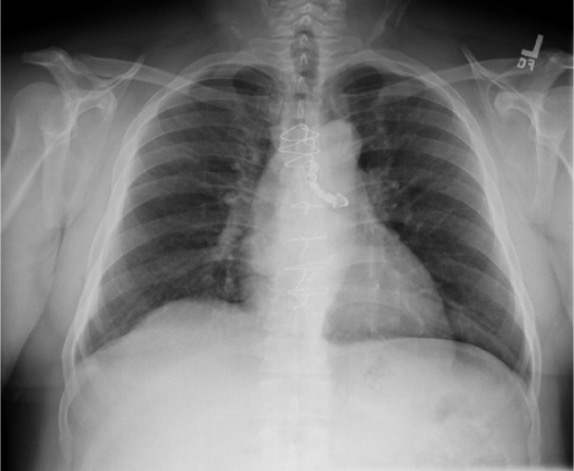
La radiografía de tórax muestra una prótesis dental alojada en el bronquio principal izquierdo.
Imagen: “Chest radiograph shows a dental prosthesis lodged in the left mainstem bronchus” por Department of Internal Medicine, Meharry Medical College, Nashville, TN 37208, USA. Licencia: CC BY 3.0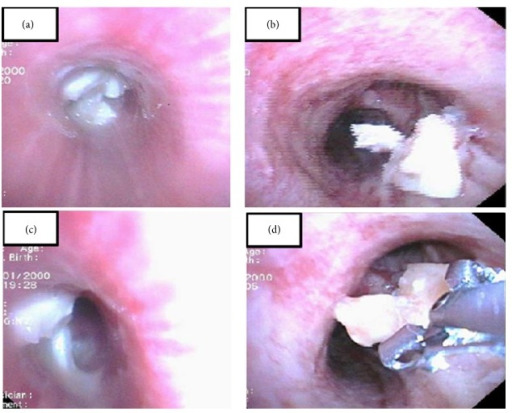
La broncoscopia puede utilizarse para el diagnóstico y la extracción de cuerpos extraños:
(a, c): Se observa un cuerpo extraño en el bronquio principal izquierdo.
(b): Se observa un cuerpo extraño en el bronquio derecho.
(d): Extracción del cuerpo extraño mediante fórceps.
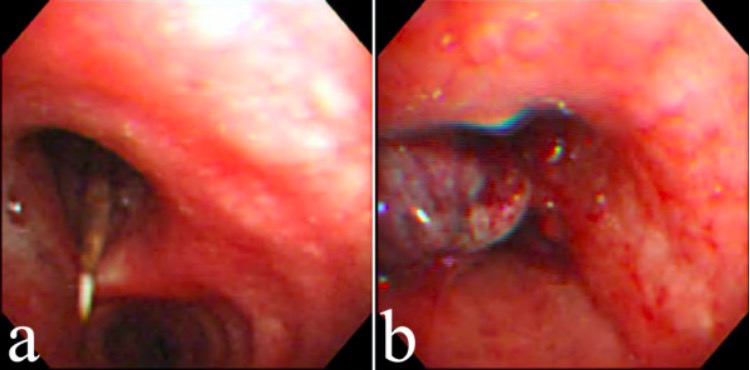
La broncoscopia de fibra óptica flexible revela un hilo dental en el bronquio principal izquierdo (a) y formación de tejido de granulación después de la extracción del objeto con pinzas de biopsia (b).
Imagen: “Flexible fiberoptic bronchoscopy” por Division of Pulmonary Medicine, Department of Internal Medicine, National Taiwan University Hospital, Taipei, Taiwan, Chung-Shan South Rd, Taipei, Taiwan. Licencia: CC BY 2.0La obstrucción de la vía aérea requiere una acción inmediata dado el alto riesgo de asfixia.
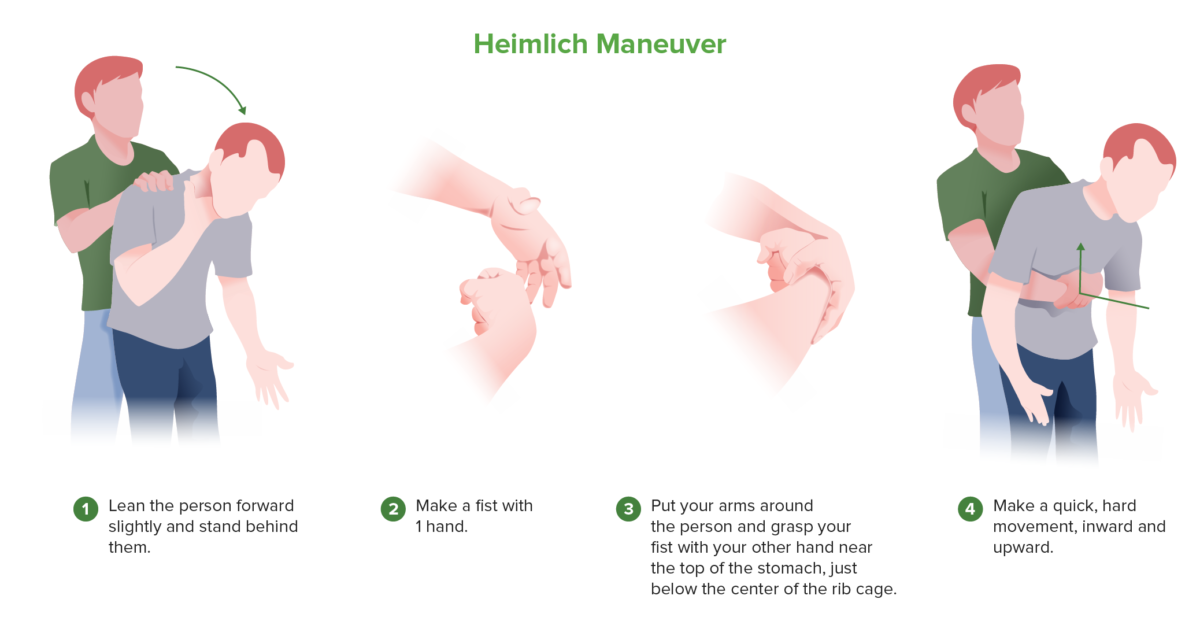
Maniobra de Heimlich
En un paciente que se asfixia o en un paciente inconsciente en el que las respiraciones de rescate no proporcionan una ventilación adecuada, se debe considerar la posibilidad de una obstrucción de las vías respiratorias con un objeto extraño. La maniobra de Heimlich funciona produciendo presión positiva en los pulmones, expulsando con fuerza cualquier cuerpo extraño en la vía aérea superior.