Playlist
Show Playlist
Hide Playlist
Uveitis: Signs, Diagnosis, and Treatment
-
Slides Optic Pathology Uveitis.pdf
-
Reference List Pathology.pdf
-
Download Lecture Overview
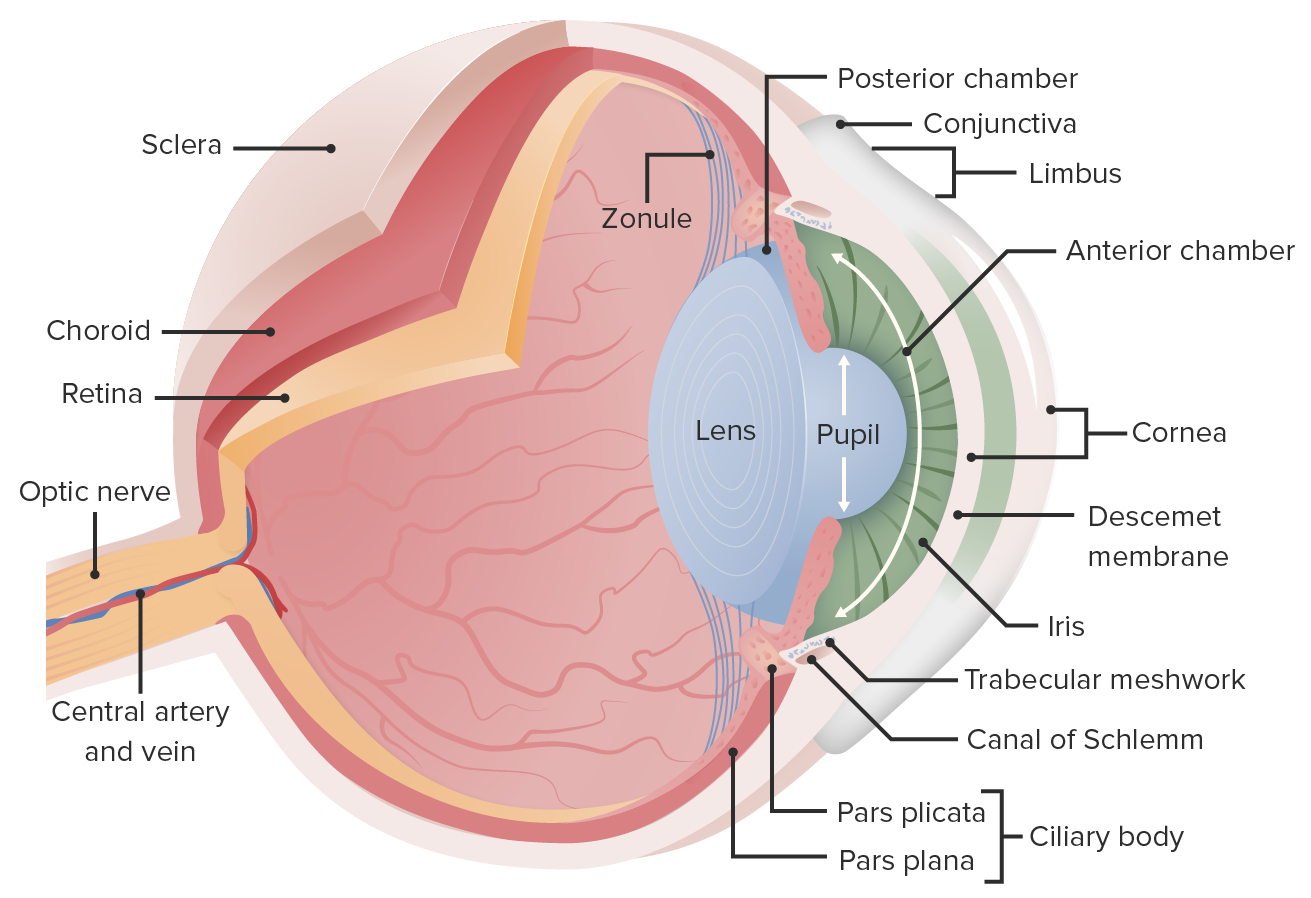
00:01 So clinical manifestations, signs and symptoms. 00:04 For anterior uveitis. 00:06 It can be unilateral or bilateral, okay? The patient, because there is some innervation, nervous innervation of the anterior portions of the eye, you can have pain, you do tend to get dilation of the pupils, so there will be photophobia. 00:23 You can see the redness there, so you're getting conjunctival inflammation with increased vascular dilation. 00:30 There is excessive tearing. 00:31 Again, we probably have inflammation that is extending secondarily up into the lacrimal gland and other areas. 00:37 So you will get excessive fluid production there that are tearing. 00:41 And as a consequence of all the edema, because of the inflammation, there will be reduced visual acuity. 00:48 The pupils can be irregular, they can be dilated, they can be constricted. 00:52 And because you have now kind of an abnormal inflammatory response involving the iris, which is going to be responsible for controlling pupil size. 01:04 In the intermediate or posterior uveitis, so things that are more involved in the posterior segment of the eye, such as the vitreous body, or now the retinitis or retina, or posterior choroid. 01:16 It's not usually associated with pain or redness, because again, we're not involving things that in the front of the eye. 01:23 You will have reduced visual acuity, however, because of the edema, that edema in the choroid will kind of distort the retina so that you will have diminished visual acuity. 01:37 We will frequently get inhomogeneities within the vitreous humor, so you will get floaters. 01:44 And there will be visual field effects because we will compromise because of edema and pressure, we will compromise neural outputs from the eyes so you will have visual field cuts. 01:55 On fundoscopic exam, it's what you see there. 01:58 It's kind of diffuse edema. 02:01 So if the vitreous looks opaque, you don't see really good vasculature at the back of the eye. 02:07 You can see the optic nerve, that area of power, but it's hard to visualize the macula. 02:13 And what you're seeing is just basically edema throughout the eyes of result of the inflammation. 02:19 Slit lamp examination can be helpful for identifying whether you're looking at inflammation, edema, and changes in the anterior segment of the eye or whether things are more posterior segment. 02:29 And then we can do some maneuvers. 02:32 These are interesting, where you can push the eyeball from the side with various instruments, and then look through the lens and see if you can see identify areas of either hemorrhage or discrete inflammation in other areas of the choroid that we don't normally visualize with the direct fundoscopic exam looking at the back of the eye. 02:53 Treatment. 02:53 So number 1, the list of things that we're going to do is we're going to try to diminish inflammation. 02:59 And we need to do that pretty aggressively. 03:01 So we're going to give Glucocorticoids to turn the heat down on the inflammatory response. 03:09 We're going to give muscarinic receptor antagonists, so blockers. 03:12 So we will in fact get dilation of the pupil to get better flow through the eye overall. 03:20 And to relax some of the musculature, so cyclic logics are administered. 03:25 And if necessary, if we then identify either a bacterial cause or a viral cause, we may give the appropriate therapies to treat those antibiotics or antivirals. 03:37 And with that, we've talked about this rather broad topic of uveal inflammation and talked about some of the specifics related to that. 03:46 Hope you enjoyed it.
About the Lecture
The lecture Uveitis: Signs, Diagnosis, and Treatment by Richard Mitchell, MD, PhD is from the course Diseases of the Anterior Chamber and Uvea.
Included Quiz Questions
What are the characteristic symptoms of anterior uveitis?
- Pain and redness
- Reduced visual acuity and inability to close the eye
- Excessive blinking and scratching
- Purulent discharge and tearing
- Myopia and diplopia
How does the vitreous appear on the fundoscopic exam with uveitis?
- Opaque
- Translucent
- Clear
- White
- Pink
Which drugs are used in the treatment of uveitis?
- Glucocorticoids and cycloplegics
- NSAIDs and antipyretics
- Mineralocorticoids and NSAIDs
- Antibacterials and antifungals
- Saline irrigation and artificial tears
Customer reviews
5,0 of 5 stars
| 5 Stars |
|
5 |
| 4 Stars |
|
0 |
| 3 Stars |
|
0 |
| 2 Stars |
|
0 |
| 1 Star |
|
0 |