Playlist
Show Playlist
Hide Playlist
Tuberous Sclerosis: Diagnosing Criteria
-
Strowd CNS Tumors Inherited Tumor Syndromes.pdf
-
Download Lecture Overview
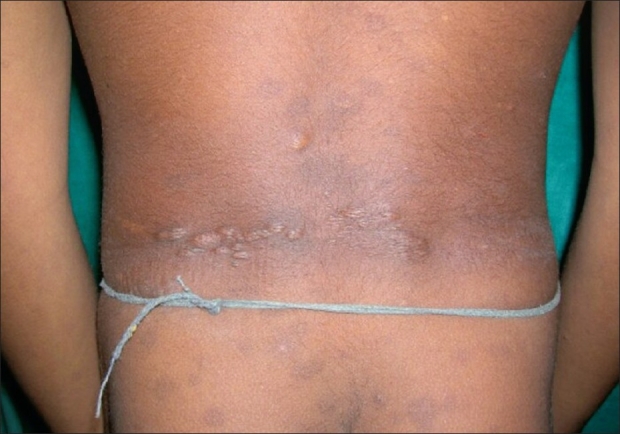
00:01 So how do we diagnose TSC? Well, again, this is a genetic condition, where we actually do more clinical assessment than gene testing in these patients. 00:10 And we're looking for a number of findings that's characteristic of this condition, and there are many. 00:16 So let's walk through them in this table. 00:18 The most common thing that we see are hypopigmented, hypomelanotic macules, Ash-leaf macules. 00:24 And you have to have three or more that are five millimeters in diameter. 00:29 The second finding we look for are angiofibromas, or something called a fibrous cephalic plaque. 00:35 Three or more angiofibromas, or one fibrous cephalic plaque is sufficient to meet one major diagnostic criteria for TSC. 00:43 Ungual fibromas. 00:45 We talked about and looked at it in pictures, two or more are required to meet a major criteria for TSC. 00:52 The Shagreen patch is a major criteria. 00:55 Retinal hamartomas, those angiofibromas, those gross the tumors that occur in the retina. 01:00 And we need two or more to establish a major criterion. 01:04 Cortical tubers, which we'll look at on imaging. 01:06 Subependymal nodules, which we'll also look at on neuro imaging. 01:11 Cardiac tumors like that cardiac rhabdomyoma that we saw in the patient in our case. 01:16 This interesting syndrome called pulmonary lymphangioleiomyoma, or LAM, which is a pulmonary finding that can be seen in adult patients with TSC. 01:26 And if present is consistent to fulfill a major criterion for TSC, And angiomyolipomas or AMLs, which are primarily seen in the kidneys, but can be seen in the liver. 01:37 That's a ton of things. And to make a diagnosis of TSC patients need at least two major criteria, or one major criteria and a few minor criteria that we'll talk about on the next slide. 01:51 What are those minor criterion? Well, these are things that are less common that can be seen out there in the normal world, but if present, and in the right clinical context of other findings suggests a diagnosis of tuberous sclerosis. 02:04 That includes confetti lesions, dental enamel pits, intraoral fibromas, retinal achromatic patch, multiple renal cysts, and nonretinal hamartomas. 02:14 Things you don't need to know or memorize but when you're seeing a patient, or thinking of an vignette about tuberous sclerosis, you would want to research.
About the Lecture
The lecture Tuberous Sclerosis: Diagnosing Criteria by Roy Strowd, MD is from the course CNS Tumors.
Included Quiz Questions
Which of the following is a major feature of tuberous sclerosis that is included in the diagnostic criteria?
- Subependymal nodules
- Pilocytic astrocytoma
- Cerebellar astrocytoma
- Optic glioma
- Hemangioblastoma
Customer reviews
5,0 of 5 stars
| 5 Stars |
|
5 |
| 4 Stars |
|
0 |
| 3 Stars |
|
0 |
| 2 Stars |
|
0 |
| 1 Star |
|
0 |