Playlist
Show Playlist
Hide Playlist
Syncope
-
Slides 11 VertigoDizziness Neuropathology II.pdf
-
Reference List Pathology.pdf
-
Download Lecture Overview
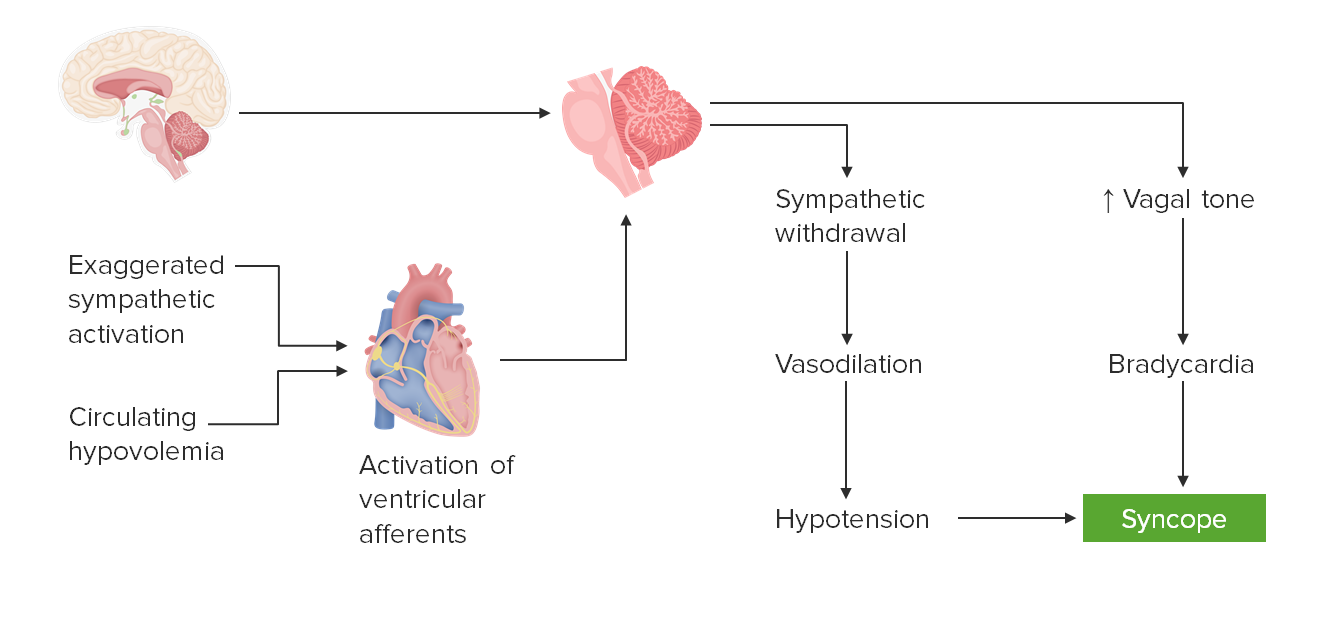
00:01 Syncope. 00:03 By definition, syncope is transient loss of consciousness and postural tone resulting from global cerebral hypoperfusion. 00:12 Global, cerebral, hypoperfusion. 00:17 Pre-syncope: Frequent sensation of lightheadedness and visual disturbance preceding syncope. 00:24 So instead of having that global hypoperfusion in which the patient may have almost like a faint-like episode, here we have frequent sensations of this. 00:35 We have headache, cognitive slowing, and buckling of the knees. 00:39 Syncope is most commonly a manifestation, most commonly a manifestation, of cardiovascular insufficiency and not necessarily neurologic, which in its own right, can be extremely dangerous. 00:54 The clinical pearls for syncope are the following: Syncope, as we just discussed, is not primarily a neurologic issue. 01:02 It is mostly a cardiovascular insufficiency. 01:05 For example, aortic stenosis. 01:08 Loss of consciousness, LOC, with syncope typically resolves immediately upon attaining a recumbent position, but may reoccur or be prolonged if patient is maintained upright. 01:23 Be careful with that. 01:24 Know the positional changes. 01:26 Convulsive syncope, what does this mean? Patients with syncope can have a few brief clonic jerks at the time they lose consciousness and this does not indicate however epilepsy or an increased risk of seizures. 01:40 Remember that with epilepsy or seizures, you can have the neurologic issues that we’ve talked about in greater detail, including our focal partial and then our generalized. 01:51 But that will be problem in the brain itself. 01:54 Here, if it’s cardiovascular, such as syncope, which is mostly what it is caused by, then during the periods of syncope, the patient seems as though that he or she might be having seizures, we call this convulsive syncope.
About the Lecture
The lecture Syncope by Carlo Raj, MD is from the course Vertigo and Dizziness.
Included Quiz Questions
What is the most common cause of syncope?
- Temporary insufficiency of blood flow to the brain
- Cerebral ischemia
- Anemia
- Migraine
- Psychiatric disturbance
What is TRUE regarding clinical manifestations of syncope?
- Patients usually regain consciousness upon attaining a recumbent position.
- Convulsive syncope is the most indicative of epilepsy.
- Syncope is primarily of a neurologic etiology.
- Loss of consciousness caused by metabolic disorders is categorized as syncope.
- It results from global cerebral hyperperfusion.
Customer reviews
5,0 of 5 stars
| 5 Stars |
|
1 |
| 4 Stars |
|
0 |
| 3 Stars |
|
0 |
| 2 Stars |
|
0 |
| 1 Star |
|
0 |
The explanation is up to the point and very precise,love each one of the video this doctor had conducted. :)