Playlist
Show Playlist
Hide Playlist
Sublingual Region
-
Slides Anatomy Sublingual Region.pdf
-
Reference List Anatomy.pdf
-
Download Lecture Overview
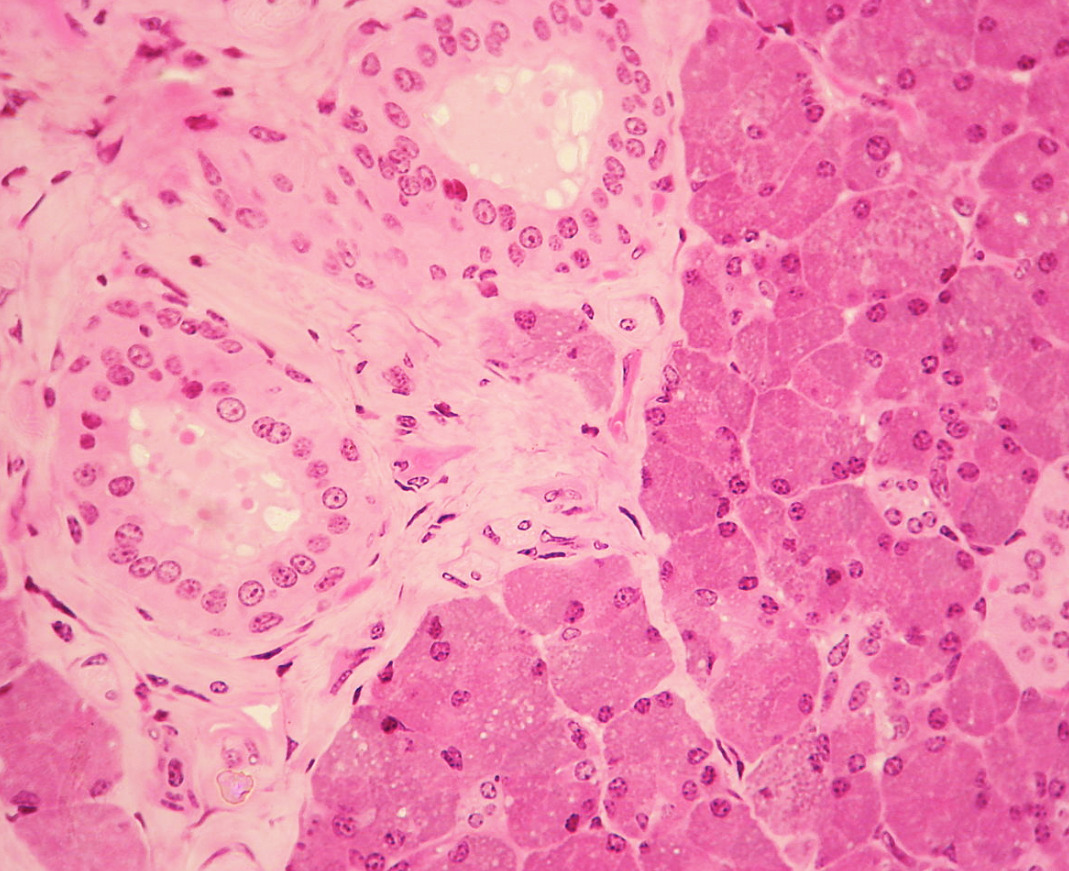
00:01 The next region we'll look at is the area under the tongue or what we call the sublingual region. 00:09 So here we see the intrinsic muscles of the tongue sitting on the superior aspect of the tongue. 00:17 We also see some of the oral mucosa or the mucosa that lines the oral cavity. 00:23 Medially, we see one of those extrinsic tongue muscles, the genioglossus. 00:29 As well as the geniohyoid, one of the suprahyoid muscles. 00:35 In the inferior lateral aspect, we see the wide flat muscle that we call the mylohyoid muscle. 00:42 And then anteriorly, we have the mandible. 00:47 Posteriorly, we have communications with the submandibular and parapharyngeal spaces. 00:56 In terms of contents of the sublingual region, we see the hyoglossus muscle, which is very closely related to one of our salivary glands, the submandibular gland. 01:12 We see the submandibular gland has this duct to carry its contents out to the oral cavity called the submandibular duct. 01:23 And this submandibular gland is sort of pinching around that other muscle we saw that has a very wide flat shape called the mylohyoid. 01:33 And then beyond that, we have our smaller sublingual gland which is directly under the tongue. 01:40 And there are sublingual ducts that enter directly into the oral cavity. 01:45 And then some of the other ones will join the submandibular duct on its way into the opening of the oral cavity. 01:52 We also have the lingual nerve, which is that branch of the mandibular nerve or cranial nerve V3 coming down to supply the tongue. 02:05 From sort of a posterior lateral view, we can see a different aspect of the submandibular gland here and we can see just how closely it is associated to that mylohyoid, sort of wrapping around the mylohyoid. 02:20 We also see the lingual nerve coming down and innervating the tongue, we see the submandibular duct making its way towards the oral cavity to deliver saliva. 02:31 And then the sublingual gland, which is again a bit smaller than the submandibular gland but located more directly underneath the tongue. 02:40 Here we see the common carotid branching into the external carotid while the internal carotid makes its way to the cranial cavity. 02:49 One of those branches of the external carotid is the lingual artery, which we can see here traveling past the hyoglossus muscle. 02:58 We have the dorsal lingual branch and sublingual branch, as well as the deep lingual branch. 03:07 We also have venous drainage in this area that pretty much mirrors the arterial supply. 03:14 And we see it's coming back to the lingual vein on its way to the common facial vein and eventually into the internal jugular. 03:24 Although there's variation in this area in terms of whether it's all passing deep two or lateral two the hyoglossus muscle. 03:33 In terms of nerves, here's where we see the hypoglossal nerve or cranial nerve XII. 03:40 More superiorly is where we see the lingual nerve or cranial nerve V3. 03:47 And it's coming from a more superior aspect because it actually parallels the inferior alveolar nerve that was coming through the mandibular foramen or canal. 03:57 It also forms a little ganglion here called the submandibular ganglion. 04:04 Now the submandibular ganglion is another area where the cranial nerve VII is hitching a ride with the lingual nerve. 04:13 So here we see the lingual nerve coming down and those fibers that are being provided by cranial nerve V3 are providing general sensation to the tongue. 04:25 But via this little shortcut called the chorda tympani, some branches of cranial nerve VII will join the lingual nerve. 04:33 On its way to provide taste sensation to the anterior two thirds of the tongue. 04:38 But it's also going to provide some autonomic innervation, specifically the preganglionic fibers of parasympathetic fibers are going to go towards the submandibular ganglion. 04:52 And then from there, there are going to be branches that are going to supply the sublingual gland and the submandibular gland. 05:00 And in this way cranial nerve VII, again pretty much hitches a ride to carry out its functions in this area, namely taste sensation to the anterior two thirds of the tongue and parasympathetic innervation to the sublingual and submandibular salivary glands.
About the Lecture
The lecture Sublingual Region by Darren Salmi, MD, MS is from the course Upper Aerodigestive Tract.
Included Quiz Questions
What is NOT part of the sublingual region?
- Parotid gland
- Hyoglossus
- Submandibular gland
- Submandibular duct
- Mylohyoid
The lingual artery has how many branches?
- 3
- 2
- 4
- 5
- 6
The chorda tympani serves what functions? Select all that apply.
- Taste sensation
- Parasympathetic
- General sensation
- Sympathetic
- Movement
Customer reviews
5,0 of 5 stars
| 5 Stars |
|
5 |
| 4 Stars |
|
0 |
| 3 Stars |
|
0 |
| 2 Stars |
|
0 |
| 1 Star |
|
0 |