Playlist
Show Playlist
Hide Playlist
Structure of Membranes – Biological Membranes
-
10 Basic BiologicalMembranes.pdf
-
Biochemistry Free and Easy.pdf
-
Reference List Biochemistry.pdf
-
Download Lecture Overview
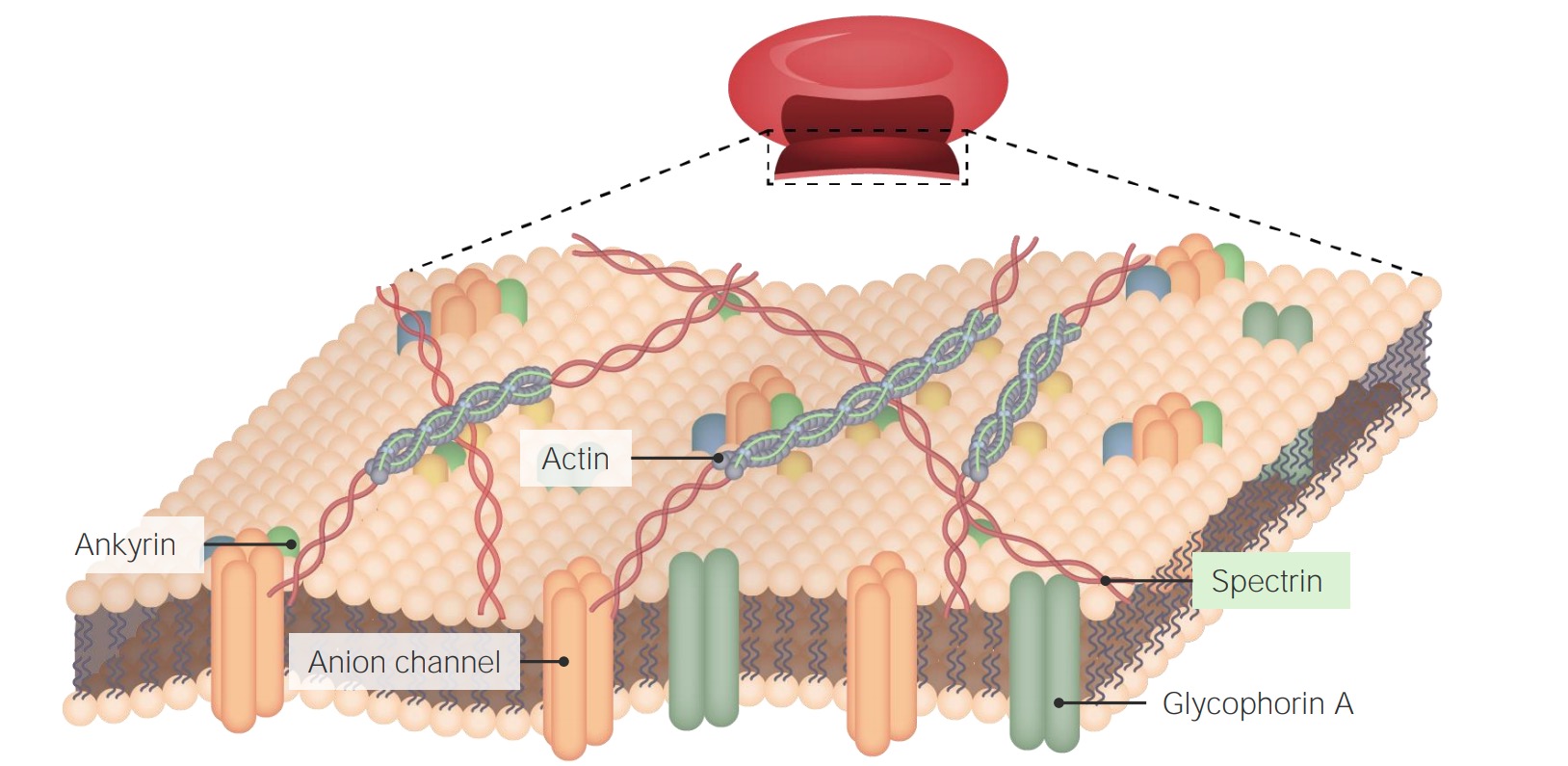
00:01 Die Lipiddoppelschicht einer Zellmembran ist sowohl die definierende Grenze als auch die Barriere zwischen der Zelle und dem Rest der sie umgebenden Welt. In dieser Vorlesung werden Membranen das Thema sein, und ich werde über die Struktur von Membranen sprechen und darüber, wie sie mit ihrer Funktion zusammenhängen. 00:15 Die Fluidität von Membranen und die Bedeutung der Fluidität im Zusammenhang warum sie für die Zellfunktionen wichtig sind. 00:28 Membranen sind ein fester Bestandteil eines jeden lebenden Systems. In Prokaryoten sind Membranen relativ einfach, weil die prokaryontische Zelle keine internen Organellen hat, wie in dieser Abbildung zu sehen ist. Die prokaryontische Zelle hat eine Lipiddoppelschicht und eine kapselförmige Zellwand, die die Zelle vor dem Rest der Welt schützt. Die eukaryontische Zelle hat normalerweise keine Zellwand, die sie schützt, zumindest in einer tierischen Zelle, und verfügt über eine ziemlich dünne Lipiddoppelschicht. Zusätzlich zu dieser Lipiddoppelschicht, die die Zellmembran bildet, gibt es aber auch interne Membranen, die die einzelnen Organellen, wie das Mitochondrium, den Zellkern usw., abdecken und schützen.
About the Lecture
The lecture Structure of Membranes – Biological Membranes by Kevin Ahern, PhD is from the course Biochemistry: Basics.
Included Quiz Questions
Which of the following cells does not have a protective cell wall around it?
- Animal cell
- Plant cell
- Algal cell
- Fungal cell
- Bacterial cell
Customer reviews
5,0 of 5 stars
| 5 Stars |
|
5 |
| 4 Stars |
|
0 |
| 3 Stars |
|
0 |
| 2 Stars |
|
0 |
| 1 Star |
|
0 |