Playlist
Show Playlist
Hide Playlist
RNA Interference, AlterRNAtive Splicing and RNA Editing
-
Slides 11 GeneRegulationEukaryotes Genetics.pdf
-
Reference List Molecular and Cell Biology.pdf
-
Download Lecture Overview
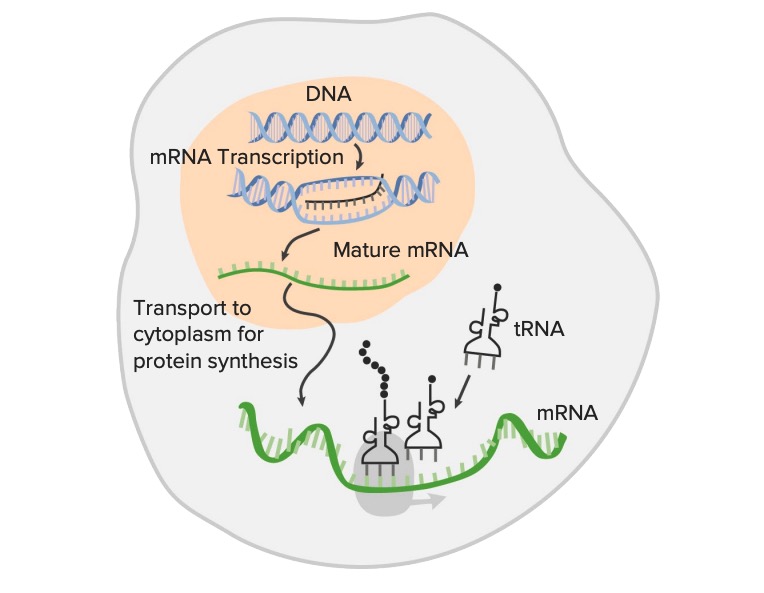
00:01 Now we have a few more mechanisms to cover in levels of possibility for regulating gene expression. RNA interference, we have already visited alternative splicing as well as RNA editing. 00:16 So what is RNA interference? RNA interference involves small interfering RNAs or siRNAs and micro RNAs (miRNAs). 00:27 So we introduced those when we looked at translation. Lots of different RNAs involved in the process of gene expression. Here is where these guys come into play. I told you I will bring them up again. They can be involved in selected degradation of messenger RNA. 00:48 They will breakdown that messenger RNA perhaps by binding with different parts of it to make them inaccessible to the ribosomes. We could have inhibition of translation because they again get in the way may be block sites for binding of TRNAs. And then we could have alteration of chromatin structure. In the section on epigenetics, I also introduced the idea of RNAs becoming associated with chromatin and impacting how enzymes can access it. All sorts of different ways that we can regulate expression even after we have RNA produced through the process of transcription. Lots of things, alternative splicing. Recall that there are different patterns that we could remove introns and exons. We can have different polypeptides from the same gene because we take a different selection of expressed sequences from the original RNA and slice them alternatively so that we get different protein results. 02:06 Gene expression is regulated there naturally. Then we have RNA editing something we have not previously discussed, but RNA editing is where there are enzymes out in the cytosol that can potentially alter the RNA transcripts so that it doesn't produce the same proteins. Again you could get multiple different peptides from one gene because there are other molecules out there that are interested in editing. We are learning more and more about these. One example that we are fairly well aware of is apolipoprotein B, which is involved in the formation of LDLs, low-density lipoproteins that carry cholesterol around. 02:53 There are two forms of this apolipoprotein B. There is one that is much longer and one that has been cut a section of the messenger RNA, it turns out has been cut out after processing. 03:08 So out in the cytosol, section gets cut off and we see that the edited form only appears in the intestinal cells, so there has to be some reason that the edited form is more useful there in packing LDLs differently than we see in the liver where we see the full form in packing LDLs. RNA editing, a big upcoming field. Again, another way we see RNA editing in conjunction with alternative splicing is in serotonin receptors. There are loads of serotonin receptors and some of them are the way they are because of RNA editing and some because of alternative splicing. But the point is having many different sorts of serotonin receptors clearly we might be able to explain some of these varieties of receptors impact how people deal with serotonin and could eventually be associated with different behaviours and effectiveness of drugs and so on and so forth. Anyway, so really really interesting fields in gene expression at the moment and lots and lots of things to learn about. There is more and more coming out every day.
About the Lecture
The lecture RNA Interference, AlterRNAtive Splicing and RNA Editing by Georgina Cornwall, PhD is from the course Gene Regulation.
Included Quiz Questions
Which of the following statements is INCORRECT regarding RNA interference?
- RNA interference involves the participation of RNA polymerase in processing mature mRNA molecules to alter their tertiary structures.
- RNA interference involves the participation of RNA molecules to inhibit gene expression or translation by neutralizing target mRNAs.
- miRNA and siRNA are the central players of RNA interference that control the activities of mRNAs by binding to them.
- RNA interference plays an essential role in protecting cells against viruses and transposons.
- During RNA interference, miRNA and siRNA inhibit translation by preventing the binding of tRNA.
Which of the following processes creates two distinct forms of apolipoprotein B (apoB100 and apoB48)?
- RNA editing
- RNA interference
- Alternative splicing
- Faulty transcription
- A mutation in the apolipoprotein B gene
Customer reviews
5,0 of 5 stars
| 5 Stars |
|
5 |
| 4 Stars |
|
0 |
| 3 Stars |
|
0 |
| 2 Stars |
|
0 |
| 1 Star |
|
0 |