Playlist
Show Playlist
Hide Playlist
Retinoblastoma: Signs, Symptoms and Diagnosis
-
Slides OP Neoplasms of the Eye Retinoblastoma.pdf
-
Reference List Pathology.pdf
-
Download Lecture Overview
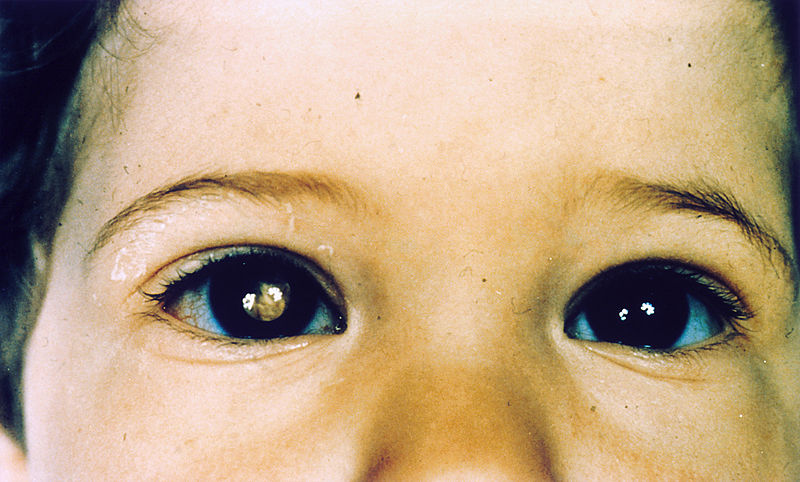
00:01 How do we pick it up? Classically, actually, parents are taking pictures of little Susie or little Sammy. 00:10 And they notice that when they do the flash photography, one eye looks red, that's the normal red reflex, you're looking at the retina, it's very vascularized. 00:19 And the other pupil doesn't look red, it looks white. 00:22 And they look at the picture to go, "That's weird." They take the child in to the doctor, and there is leukocoria. 00:30 There is whiteness of the pupil, because we're seeing a tumor lurking behind, and it's obscuring the retina. 00:37 So you don't get that red reflex. 00:39 So leukocoria, that's what's indicated here, in the green square through the pupil is one of the major ways that we pick this up because it's usually not very painful. 00:50 It's usually doesn't have much other symptoms. 00:51 And usually, it's affecting a little kid before they're two years old, and they can't tell you, "Gee, I'm seeing something in my eye." They may have because of the growth of the tumor strabismus. 01:02 So they may have deviation of the axis of the eye. 01:05 They may have decreased vision but again, it's hard to see in a child before they're able to tell you what they can and cannot see. 01:13 There may or may not be ocular inflammation as the tumor grows, it may obstruct normal fluid drainage, or may incite as tumor necrosis, focal inflammation. 01:23 You can have vitreous hemorrhage. 01:25 The tumor may have focal necrosis and bleed into the vitreous. 01:29 And because of tumor expansion, you may develop anisocoria. 01:33 So, if you compress some of the cranial nerves, oculomotor nerve III, you may have a dissymmetry in the size of the pupil, so anisocoria. 01:44 What does it look like? So if we actually look what is that leukocoria, we see this vascularized tumor, blob of white tan tissue that sitting there obscuring a lot of the back of the retina. 02:00 Pathologically summit. It's just a really beautiful thing. 02:03 I have to say that the histology of these tumors is quite lovely. 02:08 Of course, lovely to a pathologist is very different than lovely to the rest of the world. 02:12 But in any event, retinoblastoma has very characteristic organization, the cells of this tumor are nerve neural crest derived. 02:21 They are neurons that have differentiated. 02:24 And they frequently will join in form little rosettes. 02:30 So what is shown is an example of a Homer-Wright rosette. 02:34 I don't know who Homer was, I don't know who Wright was, but they got to name this accumulation of the cells that is part of the diagnosis of retinoblastoma. 02:42 So we see these small blue round nuclei, frequently around a central zero zone of neuropil, the pink in the middle is neuropil. 02:51 You can also get a different kind of rosette, which tends to have a more central area of clearing and these are the Flexner-Wintersteiner rosette. 03:01 Again, small round blue cells, all organized into little rings. 03:07 And these are part of the classic diagnosis for retinoblastoma. 03:12 So when you become an ophthalmologic pathologist, you will love these two and add pictures on your wall. 03:17 With that we'll close on tumors of the eye.
About the Lecture
The lecture Retinoblastoma: Signs, Symptoms and Diagnosis by Richard Mitchell, MD, PhD is from the course Trauma and Neoplasms of the Eye.
Included Quiz Questions
What are two common signs of retinoblastoma?
- Leukocoria and anisocoria
- Leukocoria and myopia
- Anisocoria and hyperopia
- Anisocoria and diplopia
- Leukocoria and hyperopia
From where do the cells of retinoblastoma arise?
- Neural crest cells
- Epidermal cells
- Myoblast cells
- Endodermal cells
- Endothelial cells
What is the characteristic histological finding in retinoblastoma?
- Homer Wright rosette
- True ependymal rosette
- Undifferentiated retinal cells
- Perivascular pseudorosette
- Anaplastic cells without rosette formation
Customer reviews
5,0 of 5 stars
| 5 Stars |
|
5 |
| 4 Stars |
|
0 |
| 3 Stars |
|
0 |
| 2 Stars |
|
0 |
| 1 Star |
|
0 |