Playlist
Show Playlist
Hide Playlist
Renal Replacement Therapy: Indication and Initiation
-
Slides Renal Replacement Therapy.pdf
-
Reference List Nephrology.pdf
-
Download Lecture Overview
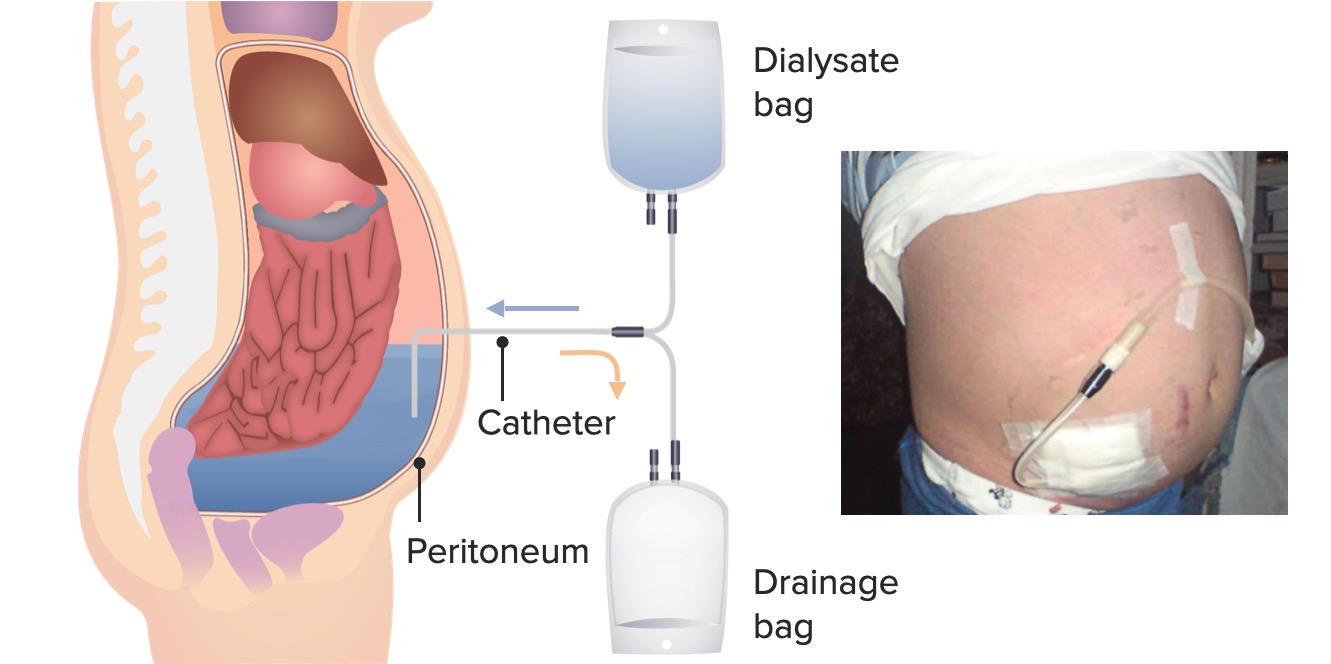
00:01 Hello, and welcome back. 00:02 Today we're going to be talking about Renal Replacement Therapy and our Nephrology Curriculum. 00:08 So, before we get started, I think it's really important to look at the prevalence of end-stage renal disease in patients in the United States. 00:16 So remember, end-stage renal disease are patients who have stage five chronic kidney disease, and are eligible for renal replacement therapy. 00:23 What I want you to notice is that on the y-axis, we have number of patients in need of renal replacement therapy by the thousands. 00:30 So that top line represents 800,000. 00:33 Whereas the x-axis represents time starting from 1980, all the way through 2016. 00:39 This is data taken from our USRDS, that's the United States Renal Data Systems looking at dialysis patients. 00:46 And what I want you to focus on is that red line. 00:49 These are all end-stage renal disease patients. 00:52 And what's interesting is that you can see in 1980 was maybe only 10s of thousands of patients who were in need of renal replacement therapy. 01:00 But look at what's happening now. 01:02 In 2016, we now have about 700,000 people that are on renal replacement therapy. 01:08 And that's either hemodialysis represented by the yellow line, peritoneal dialysis represented by the blue line, and transplant represented by the green line. 01:17 Why is this so important? In addition to causing incredible morbidity and mortality in these populations, it's also a very big cost to the healthcare system. 01:27 A dialysis patient costs about $88,000 per year. 01:31 A transplant patient cost about $27,000 per year. 01:35 So it's a significant issue when it comes to both the care of the patient, and the cost to the healthcare system. 01:42 So let's talk a little bit more about what renal replacement therapy is? It's a life supporting therapy in patients who have renal failure. 01:51 Their kidneys aren't working anymore, so we have to have something that can do the job for them. 01:56 It can be either acute or chronic. 01:59 So when a patient has acute kidney injury, and they have complications from renal failure, it would be critical to start renal replacement therapy with hemodialysis. 02:08 However, if a patient has approached chronic kidney disease, and now has transitioned to the need of renal replacement therapy because they have stage 5 chronic kidney disease, that would be chronic renal replacement therapy. 02:20 So renal replacement therapy involves: removing solute, normalization of electrolytes and acid base status, and removal of extracellular volume that means salt and water. 02:31 So what are the indications for doing renal replacement therapy in our patients? If patients develop uremic syndrome. 02:39 These are symptoms and signs that result from toxic effects of elevated levels of nitrogenous waste, and other wastes in the blood. 02:46 These are things like aliphatic amines, uremic phenols, guanidines, and middle-sized molecules like beta-2 microglobulin. 02:53 One thing I want to draw your attention to: Urea is not responsible for uremia. 02:59 We talked about it quite a bit but we only use it as a marker for solute removal. 03:04 Having a high urea level doesn't necessarily mean that a patient is uremic. 03:10 So we talked about the symptoms of uremia as being an indication for renal replacement therapy. 03:14 What are those? That includes: nausea, vomiting, anorexia, meaning that our patients just aren't hungry, dysguesia, that means patients have an abnormal taste, and they might describe their food tasting metallic in quality or like cardboard. 03:30 Pruitus, meaning that our patients are very itchy. 03:33 And having alterations in sleep. 03:35 They might have insomnia at night, but have daytime hypersomnolence. 03:39 And a sensation of being cold. 03:41 That's one of the earliest manifestations people feel, but they might be cold when everybody else is hot. 03:46 And then finally cognitive changes where they just can't think correctly. 03:50 Some of the signs of uremia this is what we can see on physical exam is that patients might have a sallow discoloration of the skin. 03:57 They might have an ammonia odor to the breath it's very distinct. 04:00 And you will be able to recognize that. 04:03 They could have a pericardial friction rub from a pericardial effusion. 04:07 So it's important to do a good cardiopulmonary examine on those patients. 04:11 They might have myoclonus or seizures. 04:13 So they have muscle irritability, and sometimes that actually manifests with hiccups as well. 04:18 They might have foot or wrist drop from uremic motor neuropathy. 04:22 And finally, they can have prolongation of bleeding time or from uremic platelet dysfunction. 04:27 So it's interesting because there is a relationship between the development of uremic syndrome, and glomerular filtration rate. 04:35 So the uremic syndrome will predictably develop when that GFR falls below 10 mL/minute. 04:42 Most patients will require renal replacement therapy once that GFR falls between 6 and 15 mL/minute. 04:47 And I do want to say, that there is no data to suggest that starting renal replacement therapy early in patients will portend a better outcome. 04:57 And in fact, with some of the data that we do have available there's a signal towards harm if you start patients too early. 05:03 So we really wait until a patient absolutely needs dialysis before starting it. 05:08 And our younger healthier patients that might be a GFR of about 6 mL/min. 05:14 So when it comes to talking about different types of renal replacement therapy, there's a few choices that we have for our patients. 05:21 This includes hemodialysis, peritoneal dialysis, and transplant.
About the Lecture
The lecture Renal Replacement Therapy: Indication and Initiation by Amy Sussman, MD is from the course Renal Replacement Therapy.
Included Quiz Questions
Which of the following is true regarding uremic syndrome?
- It is caused by excess nitrogenous waste products in the blood.
- It is caused by excess bilirubin in the blood.
- It is expected in patients with a GFR of < 40 mL/min.
- Most patients will require renal replacement therapy when GFR = 25–35 mL/min.
Which of the following is a complication of uremic syndrome?
- Motor neuropathy
- Jaundice
- Bleeding due to coagulation factor VII dysfunction
- Mineral and bone disorders
- Normocytic and normochromic anemia
Which of the following statements is true regarding renal replacement therapy?
- It is indicated for the normalization of acid-base status and electrolyte levels.
- It is contraindicated in hemodynamically unstable patients.
- It is indicated only for patients with end-stage renal disease.
- The number of patients receiving renal replacement therapy has dropped over the last 30 years.
Customer reviews
5,0 of 5 stars
| 5 Stars |
|
5 |
| 4 Stars |
|
0 |
| 3 Stars |
|
0 |
| 2 Stars |
|
0 |
| 1 Star |
|
0 |