Playlist
Show Playlist
Hide Playlist
Principle of Independent Assortment – Classic Mendelian Genetics
-
Slides 01 MendelianGenetics Genetics V2.pdf
-
Reference List Molecular and Cell Biology.pdf
-
Download Lecture Overview
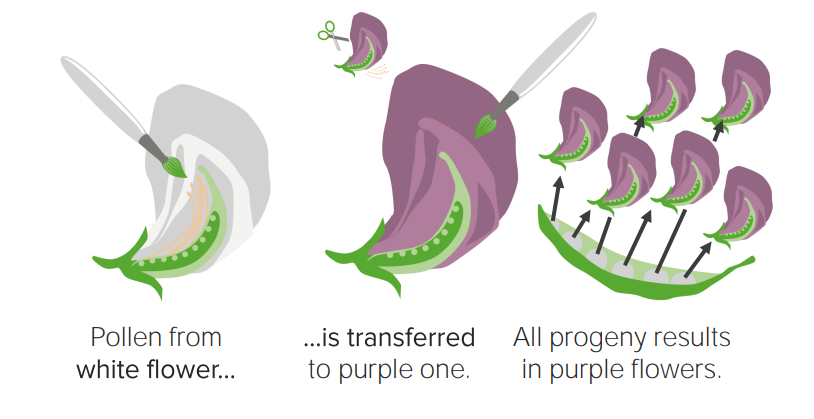
00:00 Also, rund und faltig, gelb und grün, lila und weiß, alle bewegen sich getrennt voneinander. 00:07 Nun, das liegt daran, dass sie in der Tat auf separaten Chromosomen liegen und wir so ein sehr schönes Muster haben, das sich ergibt. 00:15 Aber das Wichtige ist, dass er in der Lage war, das Prinzip der unabhängigen Auswahl zu entwickeln. 00:23 Aus dem Modell der Hybrid-Kreuzungen haben wir also die Segregation geschlussfolgert. 00:27 Das Prinzip der unabhängigen Auswahl besagt: "Ja, Segregation findet statt, aber jedes Merkmal tut dies unabhängig vom anderen Merkmal." Der Grundsatz der unabhängigen Auswahl besagt also, dass, in unserer Sprache der Meiose und der Chromosomen, während der Meiose I, die Ausrichtung der Chromosomen in der Metaphase zufällig ist, so dass sich diese Chromosomen unabhängig von anderen Faktoren voneinander abspalten können. 01:00 Wenn wir also einen Blick auf die Meiose werfen, können wir sehen, dass es sich um eine zufällige Anordnung von Chromosomenpaaren in der Metaphase der Meiose I handelt, die das Mendel'sche Prinzip der unabhängigen Auswahl unterstützen. 01:16 Auch hier gilt, dass sich jedes Paar unabhängig vom nächsten Paar trennt, weil sie sich zufällig in der Metaphase ausrichten, wo wir alle blauen auf einer Seite haben können, alle roten auf der anderen Seite oder eine Umstellung der gleichen Anordnung, wo wir einfach zwei voneinander getrennt haben. 01:40 Zum Abschluss der ersten Vorlesung, die uns in die Genetik und die Erforschungen von Mendel einführte, sollten Sie jetzt in der Lage sein zu beschreiben, was wir von Mendel wissen sowie die Ergebnisse von Mono- und Dihybrid-Kreuzungen auswerten können. 01:54 Wir sollten in der Lage sein, diese Kreuzungen mit der Bewegung der Chromosomen während der Meiose in Verbindung zu bringen und zwischen dem Prinzip der Segregation und dem Prinzip der unabhängigen Auswahl zu differenzieren können. 02:08 Vielen Dank, dass Sie zugehört haben. 02:10 Ich freue mich darauf, Sie bei der nächsten Vorlesung wiederzusehen.
About the Lecture
The lecture Principle of Independent Assortment – Classic Mendelian Genetics by Georgina Cornwall, PhD is from the course Understanding Genetics.
Included Quiz Questions
Mendel's dihybrid crosses suggested which of the following? Select all that apply.
- Factors segregate from each other independently of other factors.
- The Principle of Independent Assortment
- Meiosis involves chromosomes separating from each other to form gametes.
- The Principle of Crossing Over
- The Principle of Segregation
Which of the following statement stands TRUE for the Principle of Independent Assortment?
- Genes located on different chromosomes are transmitted independently of each other from one generation to another.
- Genes present on the same chromosomes are transmitted independently of each other from one generation to another.
- Genes present on the same side of a chromosome arm are transmitted independently of each other from one generation to another.
- Genes present near the centromere of the chromosome are transmitted independently of each other from one generation to another.
- Genes located on different chromosomes are transmitted together from one generation to another.
Customer reviews
5,0 of 5 stars
| 5 Stars |
|
5 |
| 4 Stars |
|
0 |
| 3 Stars |
|
0 |
| 2 Stars |
|
0 |
| 1 Star |
|
0 |