Playlist
Show Playlist
Hide Playlist
Primary Hyperaldosteronism
-
Slides 01-02-02 Adrenal Pituitary.pdf
-
Reference List Endocrinology.pdf
-
Reference List Adrenal Gland Disorders.pdf
-
Download Lecture Overview
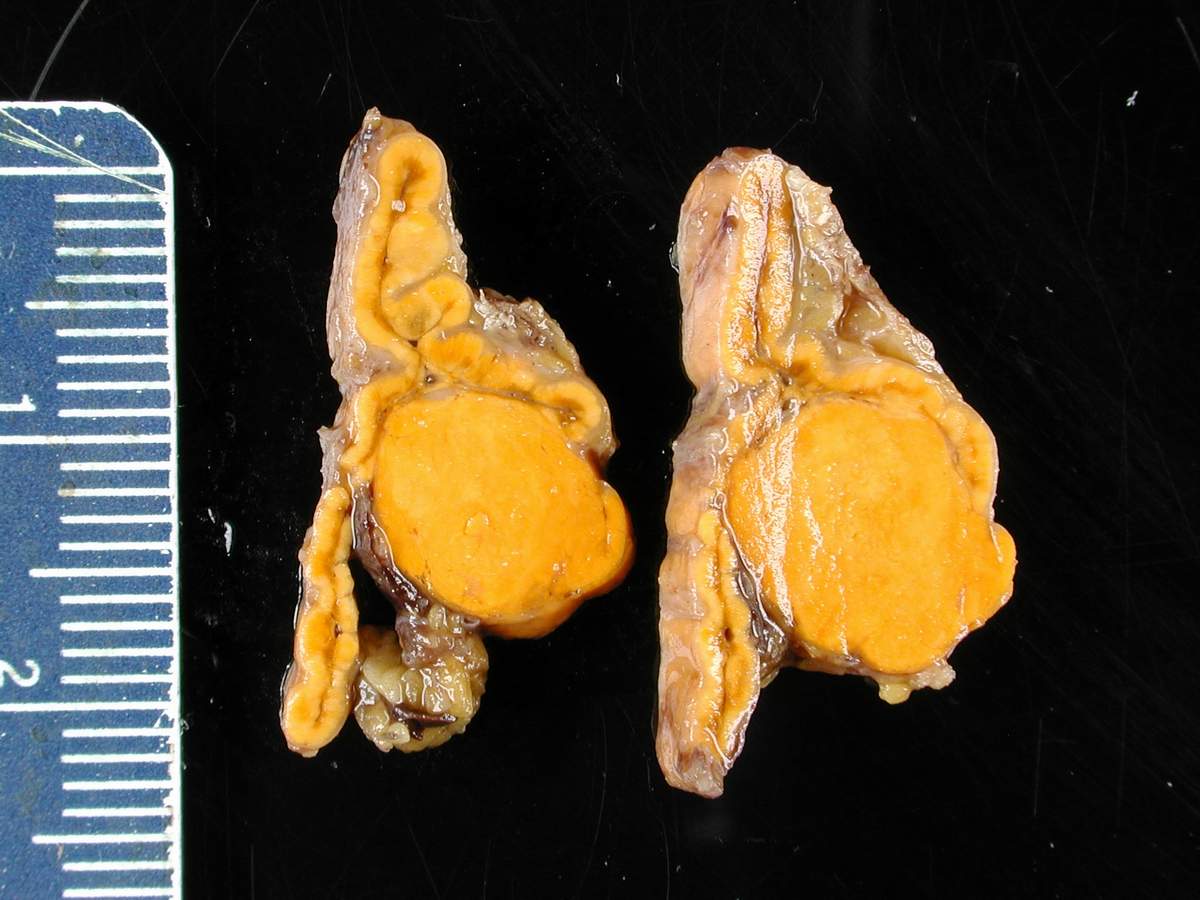
00:01 Primary hyperaldosteronism results from the autonomous secretion of excessive aldosterone. 00:06 It is relatively common occurring in approximately 10% of patients with hypertension. 00:12 Clinical features include resistant hypertension, hypokalemia, and metabolic alkalosis. 00:19 Without treatment, excessive cardiovascular morbidity and mortality can occur. 00:24 40% are aldosterone-producing adrenocortical adenomas. 00:30 60% are bilateral adrenal hyperplasia. 00:33 Unilateral adrenal hyperplasia and aldosterone-secreting adrenal carcinomas are very rare. 00:40 Familial hyperaldosteronism is uncommon. 00:43 Once the diagnosis of primary aldosteronism has been confirmed biochemically, radiographic localization with an abdominal CT is indicated. 00:53 CT is recommended over MRI in most cases due to similar efficacy but lower cost with CT. 01:00 Adrenal hyperplasia and adenomas can often be visualized and adrenocortical carcinomas can be ruled out using this modality. 01:10 The goals of treatment are to lower blood pressure. 01:13 Resolution of hypertension, however, is unlikely. 01:17 You also want to improve serum potassium. 01:21 You want to reduce plasma aldosterone even if blood pressure is controlled because elevated levels of aldosterone cause adverse cardiovascular effects. 01:33 The treatment will include laparoscopic adrenalectomy. 01:36 Non-surgical candidates can be treated with mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists. 01:42 Spironolactone is commonly used due to its proven efficacy and cost-effectiveness. 01:47 Eplerenone, a diuretic, is less likely to cause side effects such as the gynecomastia that you see in men from spironolactone and spironolactone-induced menstrual irregularities in women. 02:01 Amiloride is a potassium-sparing diuretic that blocks the aldosterone-sensitive sodium channel. 02:06 Use of amiloride in primary aldosteronism is a second-line therapy because of lower efficacy.
About the Lecture
The lecture Primary Hyperaldosteronism by Michael Lazarus, MD is from the course Adrenal Gland Disorders.
Included Quiz Questions
Which of the following is TRUE about the treatment of primary hyperaldosteronism?
- Patients who are not candidates for surgery are treated with mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists.
- Lowering aldosterone levels does not reduce cardiovascular effects.
- Improving serum potassium levels is not one of the main targets of therapy.
- Eplerenone is usually administered after adrenalectomy.
- Amiloride is the first pharmacologic agent used because of its safety profile.
Customer reviews
5,0 of 5 stars
| 5 Stars |
|
5 |
| 4 Stars |
|
0 |
| 3 Stars |
|
0 |
| 2 Stars |
|
0 |
| 1 Star |
|
0 |