Playlist
Show Playlist
Hide Playlist
Introduction and Definitions of Pharmacodynamics – Pharmacodynamics
-
Slides Introduction Definitions Pharmacodynamics.pdf
-
Reference List Pharmacology.pdf
-
Download Lecture Overview
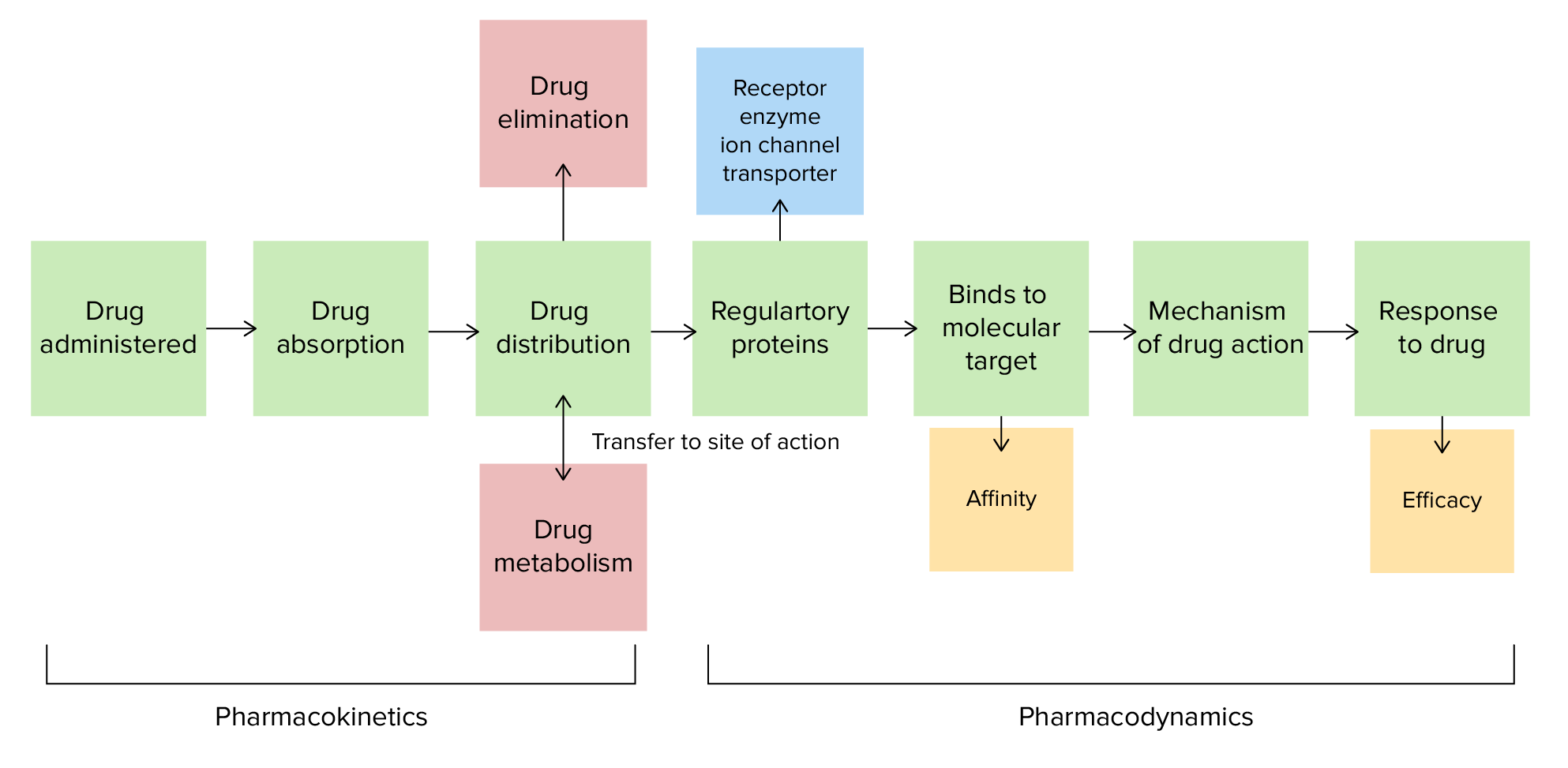
00:01 Welcome to pharmacology by Lecturio. Today's topic is pharmacodynamics. 00:06 We are going to evaluate and see how drugs move through the body in pharmacodynamics. 00:12 Let's go over a couple of definitions. Excretion is the physical removal of drug from the body. 00:19 So for example, we're excreting drug into the urine, or into the bile, or exhaling inhalational drugs. 00:27 Elimination is a biochemical process without actual removal. So, eliminating a drug means that the drug may still be in the body, but you've rendered it somehow different through a biochemical process. 00:40 A receptor is a specific protein on or in the cell that binds to the drug to effect the change. 00:48 And effectors are molecules that effect a change as a result of the receptor and drug binding together. 00:55 So, a receptor binds to the drug, and effector molecule goes and does the job of the drug. 01:02 Affinity refers to the strength of the bond between a drug and receptor. 01:08 And selectivity refers to the proportion of or a preference of a receptor has for a particular drug. 01:15 It's usually compared to another similar kind of receptor, for example, we may have selectivity for the alpha 1 receptor versus the alpha 2 receptor, and the selectivity ratio may be 1000:1. 01:28 Specificity refers to the amount of preference a receptor has for a particular drug. 01:35 So, it's usually thought of as a comparator to another drug. So for example, one drug might be more specific to a receptor than a second drug. 01:47 Agonism refers to the ability to activate the mechanisms to cause an effect. 01:53 And antagonism is the ability to inhibit the mechanism to cause a biologic effect. 01:59 Efficacy refers to the maximum effect of a drug at its highest tolerated dose. 02:05 Well, potency is a measurement of the amount of drug needed to cause an effect. 02:10 So, a drug may have a high efficacy but a low potency.
About the Lecture
The lecture Introduction and Definitions of Pharmacodynamics – Pharmacodynamics by Pravin Shukle, MD is from the course Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics.
Included Quiz Questions
Which term describes the ability of a drug to activate a biological effect?
- Agonism
- Affinity
- Efficacy
- Potency
- Incidence
What best describes the selectivity of a drug?
- The proportion of preference a receptor has for a drug
- The strength of the bond between a drug and a receptor
- The ability to activate the mechanisms to cause a biological effect
- The effect of multiple drugs
Which statement most accurately describes a drug with high efficacy and high potency?
- It requires only a small dose to exert a significant effect.
- It requires a large dose to exert a significant effect.
- The maximum dose does not cause a significant effect.
- Even a large dose will not cause a significant effect.
- No dose change will lead to a change in the clinical effect.
Customer reviews
4,4 of 5 stars
| 5 Stars |
|
3 |
| 4 Stars |
|
1 |
| 3 Stars |
|
1 |
| 2 Stars |
|
0 |
| 1 Star |
|
0 |
As a lecturer myself in another field you make something that is difficult easy to understand for learning transfer = A+ delivery thank you
5 STARS TO DR SHUKLE Because 1. He speaks clear American English. 2. Lectures are very visual, concise and substantial. 3. He behaves and dresses very professionally. 5. You learn a lot in little time with quizzes between lectures. 6. It's so much fun and easy.
3 customer reviews without text
3 user review without text