Playlist
Show Playlist
Hide Playlist
Neuropathic Pain: Treatment
-
Slides Neuropathic Pain Syndromes.pdf
-
Download Lecture Overview
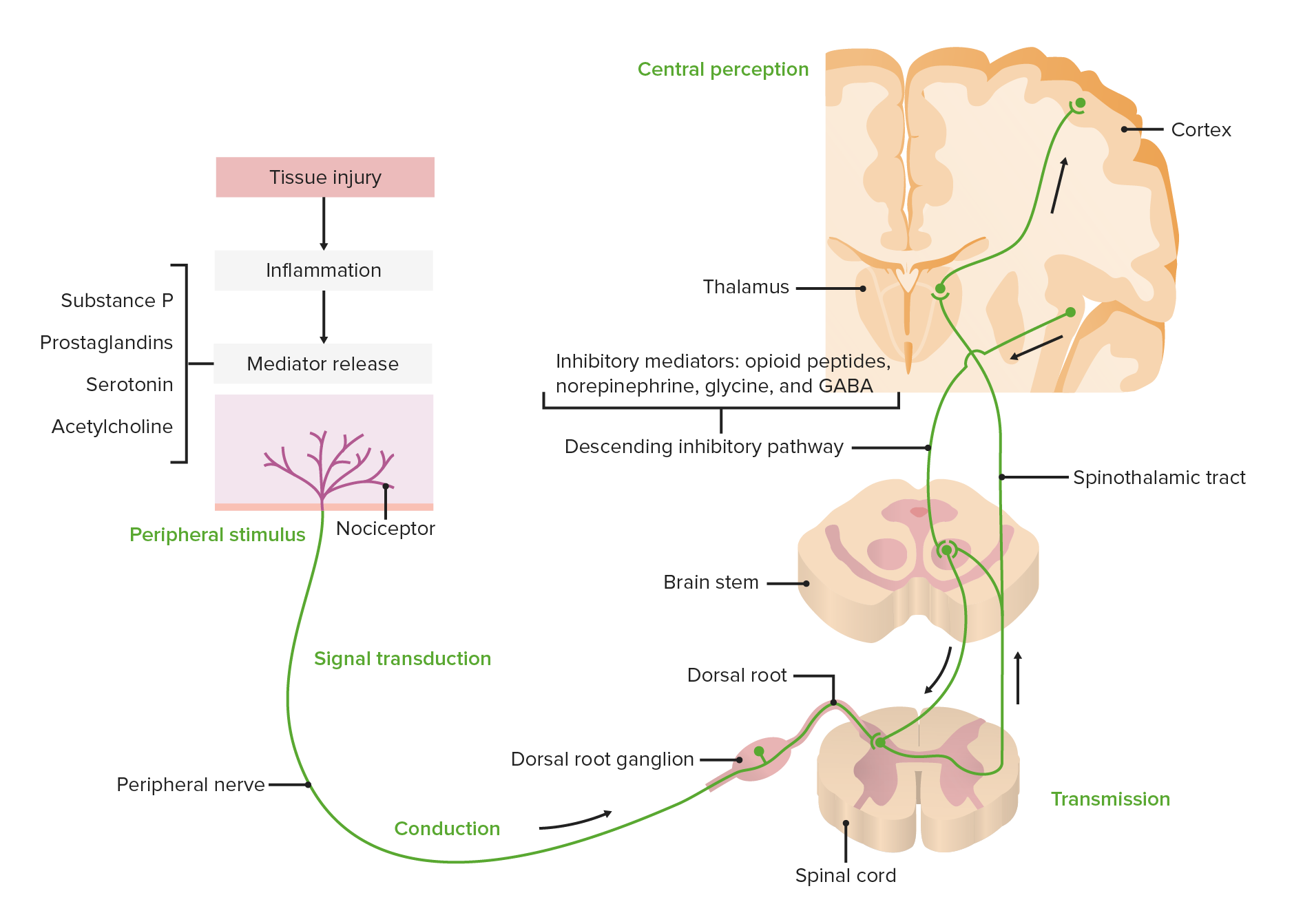
00:01 Now, let's talk about step four. What medical treatments exist for patients with neuropathic pain? Well, there are a number of types of medicines that we think about that treat neuropathic pain. 00:13 We can use one or often, a combination as we're considering rational polypharmacy in patients with severe pain disorders. 00:21 One category that I'd like for you to remember is anticonvulsants. 00:24 And we think about a number of anticonvulsants that can be used to treat neuropathic pain. 00:29 Gabapentin, pregabalin, and carbamazepine can be particularly effective, often, for peripheral localizations or peripheral causes of neuropathic pain. 00:39 Oxcarbazepine and others like Depakote, valproic acid, or topiramate can be used. 00:45 It may be effective in central neuropathic pain syndromes. 00:49 We think about antidepressants. 00:51 Duloxetine, venlafaxine, amitriptyline, nortriptyline, the two tricyclic antidepressants as well as bupropion can be used to treat patients with neuropathic pain. 01:03 Topical agents can be used. Topical lidocaine either in a patch or cream or gel, topical capsaicin. 01:10 Topical gabapentin can be compounded and used as well as topical ketamine. 01:15 With topical agents, there's reduced systemic absorption in delivery of drug right to the peripheral nerves. 01:22 Topical TCAs, including topical amitriptyline can also be used. 01:27 Sometimes, we'll combine topical agents, one neuropathic, a cream combination that I use is a combination of gabapentin, ketamine, and ketoprofen which can be effective in various peripheral pain syndromes. 01:40 And in addition, amitriptyline, ketamine, and ketoprofen. 01:44 How do we think about using and selecting these agents for patients? Well, there are a number of large groups that have come together to define, first, second, third, or fourth line agents that can be used for patients with neuropathic pain. 01:59 I don't need you to remember all the details, but see how we sequence our medications for peripheral pain syndromes compared to central pain syndromes. 02:08 So here with these criteria in terms of diabetic neuropathy, some of the first line agents are duloxetine, gabapentin, pregabalin, the TCAs and venlafaxine. 02:18 With post-herpetic neuralgia, also a peripheral pain syndrome, we have a similar group, gabapentin, pregabalin, the TCAs and lidocaine patch for that localized pain that we see with post-herpetic neuralgia. 02:30 In contrast, for the central nervous system syndromes like trigeminal neuralgia, we see carbamazepine and oxcarbazepine as first line agents. 02:39 For central thalamic pain syndrome, gabapentin, pregabalin, and the TCAs are often considered first line. 02:45 Tramadol, strong and weak opioids can be considered. 02:49 Lamotrigine and even the cannabinoids can be used for these patients where response is often incomplete. 02:56 There are other groups that have described similar criteria to consider treatment of neuropathic pain. 03:03 Again, we commonly see the TCAs, duloxetine, gabapentin, and pregabalin, as well as topical agents. 03:10 For trigeminal neuralgia, carbamazepine and oxcarbazepine are typically first line. 03:14 In addition to oral and topical agents, other non-medical interventions can be used. 03:19 Occipital or other nerve blocks can be effective when pain is localized to a specific nerve. 03:25 Spinal cord stimulators may help to reduce the central nervous system relay of pain. 03:31 Transcranial magnetic stimulation is increasingly being utilized and studied for the use of neuropathic pain, as well as radiofrequent rhizotomy or treating a nerve that is resulting in localized pain as well as other interventions. 03:47 We also want to think about complementary and alternative therapies integrated in to our medical and surgical treatments. 03:53 Things like yoga, acupuncture, meditation, massage, stress relaxation techniques have been studied in a variety of neuropathic pain syndromes and can be helpful adjuncts in patients with neuropathic pain.
About the Lecture
The lecture Neuropathic Pain: Treatment by Roy Strowd, MD is from the course Neuropathic Pain Syndromes.
Included Quiz Questions
What is one of the classes of medications used to treat neuropathic pain?
- Anticonvulsants
- Opioid analgesics
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory agents
- Steroids
- Benzodiazepines
Which of the following medications are effective in treating peripheral neuropathies such as diabetic neuropathy? (Select all that apply.)
- Serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs)
- Tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs)
- Gabapentin
- Acetaminophen
- Oxcarbazepine
Customer reviews
5,0 of 5 stars
| 5 Stars |
|
5 |
| 4 Stars |
|
0 |
| 3 Stars |
|
0 |
| 2 Stars |
|
0 |
| 1 Star |
|
0 |