Playlist
Show Playlist
Hide Playlist
Mpox (Monkeypox): Clinical Symptoms
-
Slides Mpox-Monkeypox-Clinical-Symptoms.pdf
-
Download Lecture Overview
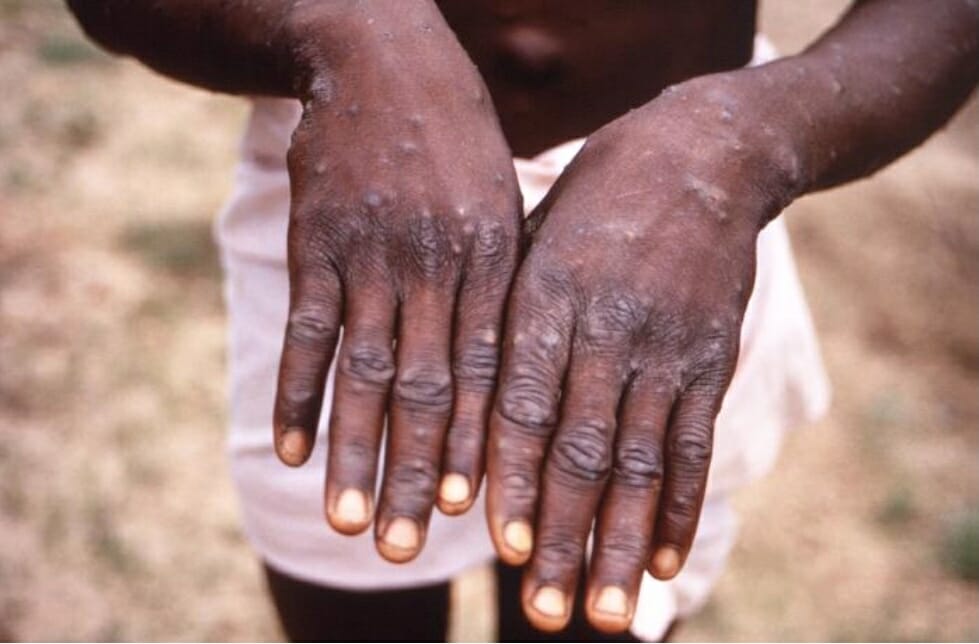
00:00 So the clinical symptoms of mpox are described in these uh figure. The most important is to know that, fever is the, the most important symptoms. 00:15 And after that you have the skin lesions and, uh, adenopathy as you can, we will show later. So, other symptoms, uh, are anorexia, chills, dysphagia, uh, uh, throat irritation and malaise. This is the lesion we, uh, we described on the period of incubation is between 4 and 21 days. And after that, we have fever, headache, chills through muscle ache and lymphadenopathy. 00:59 And after that you have the specific lesions that are maculopapular, vesicle pustules and and scalp. 01:09 So, we have, the, these description the first is macules and then the papule and vesicle and pustule, is the implication vesicle, it is papule and after that you have the scab. 01:27 Other symptom is nausea, vomiting, diarrhea and loss of appetite. And we have a lot of complication. You have the bacterial infection, bronchial pneumonia, encephalitis, sepsis ,ocular infection and dehydration. So, the lesion of, uh, of MPOX, uh, we say that these lesions are c entrifugal. This means that the lesions are most important in the in the extremity of the of the body. 02:11 You see the hands, the the head and and the feet. 02:16 On the contrary, with with the chicken pox. 02:20 In chicken pox, most lesions are on the trunk. 02:23 A few lesions on the on the extremities. 02:26 So this is a differential clinical symptoms of MPOX compared to varicella or chicken pox. 02:38 So this is a picture showing the MPOX lesion. So lymphadenopathy. Lymphadenopathy is the main symptoms of MPOX. And as I said, the skin rash are centrifugal distribution, has centrifugal distribution, first in the mouth, hands, palm of hands and soles of the feet, and the lesions are generalized over the whole body. So this is a case of MPOX with inguinal lymphadenopathy. 03:31 This is the WHO photo. 03:35 And you see here you see a rash in the mouth and rash in the palm of the hands. 03:45 And here you see the rash on the soles of feet. 03:50 And uh, clinical lymphadenopathy I saw there. This is the case. 03:58 Civil case in a in a in a child. 04:03 And there you see severe infection of an adult. 04:10 So here you see it is benign infection and subclinical infection in adult. So this is the ocular complication of MPOX bacterial conjunctivitis. 04:26 And this is mucocutaneous complication of the mpox with edema and so on. And here is a complication of MPOX, keratitis in the left eye, staphyloma in the eye, and classification of eye lesions and edema that the severe case and also the transmission of fear of infection from a pregnant woman to to the fetus. 05:02 Most of the time we have abortion and it is the transmission of the disease to the fetus. And you have a spontaneous abortion. And for the differentiation, clinical differentiation, you will think to secondary syphilis. 05:30 This is the case of secondary syphilis. 05:33 This is the case of MPOX, the formulation of MPOX. And the scars after, uh MPOX the scar of deep don't show this. The residual scars are deep. 05:55 Here. The residual scars of chicken pox are superficial.
About the Lecture
The lecture Mpox (Monkeypox): Clinical Symptoms by Jean-Jacques Muyembe-Tamfum, MD, PhD is from the course Mpox (Monkeypox): Insights and Challenges.
Included Quiz Questions
What are the three main clinical symptoms of mpox?
- Fever, skin lesions, and lymphadenopathy
- Fever, headache, and stomach pain
- Skin lesions, cough, and conjunctivitis
- Lymphadenopathy, diarrhea, and chills
- Nausea, vomiting, and dehydration
How does the distribution of skin lesions in mpox differ from that of chickenpox?
- Mpox has a centrifugal distribution (face, extremities, palms, soles), while chickenpox primarily affects the trunk
- Mpox only affects the face and trunk, while chickenpox appears on extremities
- Both diseases have identical distribution patterns but different lesion morphology
- Mpox lesions appear only on mucous membranes, while chickenpox appears on the skin
- Mpox has a random distribution while chickenpox follows dermatomes
What is the correct progression of skin lesions in a typical mpox infection?
- Macules → papules → vesicles → pustules → scabs
- Papules → macules → pustules → vesicles → scabs
- Vesicles → macules → papules → scabs → pustules
- Pustules → vesicles → papules → macules → scabs
- Scabs → macules → vesicles → papules → pustules
Customer reviews
5,0 of 5 stars
| 5 Stars |
|
5 |
| 4 Stars |
|
0 |
| 3 Stars |
|
0 |
| 2 Stars |
|
0 |
| 1 Star |
|
0 |